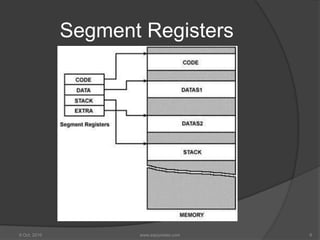
The document discusses memory segmentation in the Intel 8086 processor. It explains that the 8086's 1MB of memory is divided into segments of varying sizes, including code, data, stack, and extra segments. Each segment is addressed by a 16-bit segment register that stores the segment's base address. To generate the full 20-bit physical address, the base address is combined with a 16-bit offset value contained in registers like IP, BX, DI, SI, and SP. This allows each segment to be up to 64KB in size. Examples are provided to demonstrate how logical addresses are translated to physical memory locations using the segment registers and offsets.