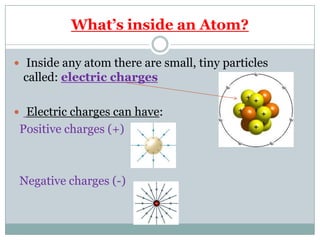
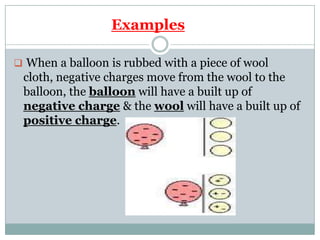
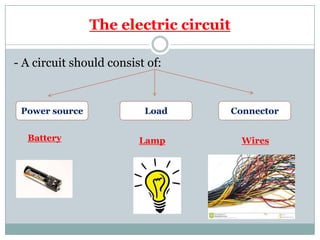
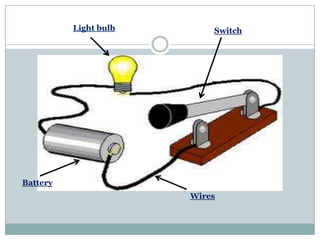
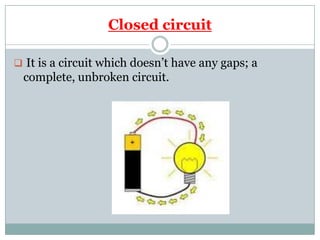
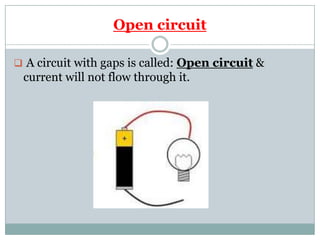
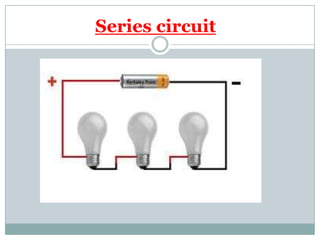
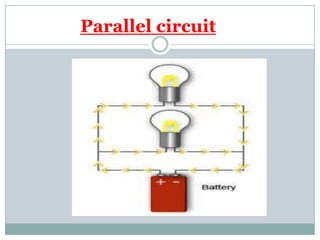
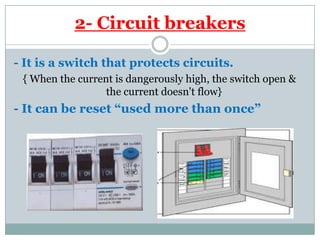
Electricity affects our lives in many ways. It is the flow of electric charges called current. Electricity allows devices like lights and appliances to function. Current flows through circuits which must be closed loops with a power source, wires, and a load. Circuits can be connected in series or parallel. Safety devices like fuses and circuit breakers help control electric current and prevent hazards by opening the circuit if current flow becomes too high. Proper use and understanding of electricity helps ensure it benefits our lives safely.