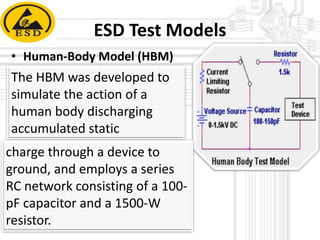
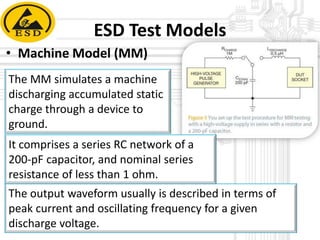
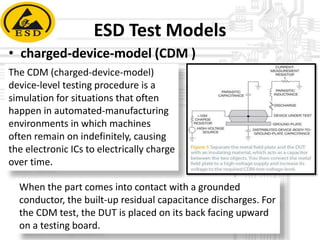
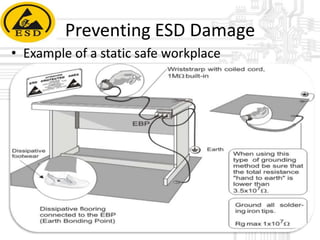
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a spark or discharge caused by a buildup of static electricity. It can damage electronics like computer components. The document discusses ESD, how it occurs, common test models used to evaluate ESD thresholds, types of damage it can cause, and ways to prevent ESD such as proper grounding, neutralization, and using anti-static protective equipment and bags in work areas. It also lists components of a static safe workplace and names team members who contributed to the document.