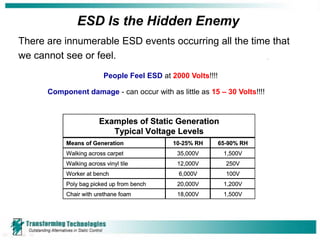
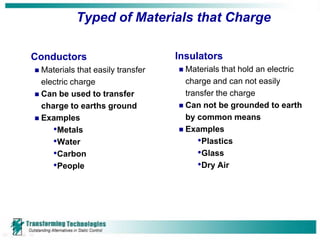
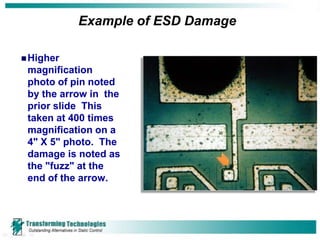
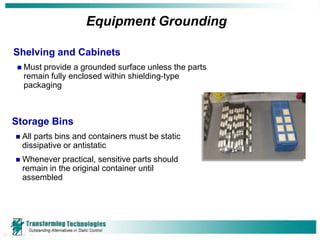
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) refers to the transfer of static electricity between two objects with different electrical potentials. ESD events are common and occur whenever two materials contact and separate, such as walking across a carpet. While people may feel an ESD event at 2000 volts, component damage can occur at voltages as low as 15-30 volts. Proper ESD control programs aim to prevent such damage and include employee training, establishing ESD protected areas, ensuring proper grounding of equipment and personnel, and using ionizers to neutralize static charges that cannot be grounded. ESD can cause both immediate failures as well as latent defects, resulting in significant costs to the electronics industry.