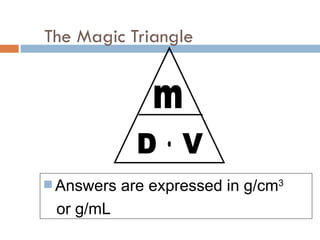
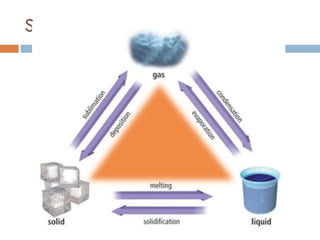
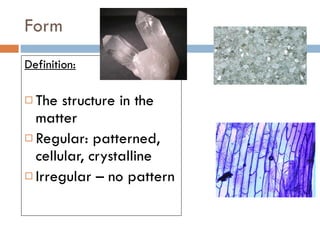
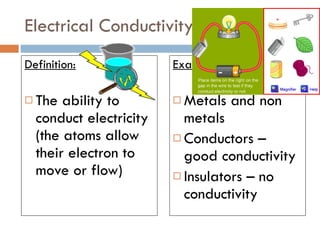
The document discusses different types of properties of matter including physical, chemical, and biological properties. It defines physical properties as those that can be observed without changing the identity of the substance such as mass, volume, density, state, color, odor, and hardness. Chemical properties describe a substance's ability to change into a new substance with different properties through chemical reactions. Biological properties distinguish living from nonliving things.