Embed presentation
Downloaded 27 times

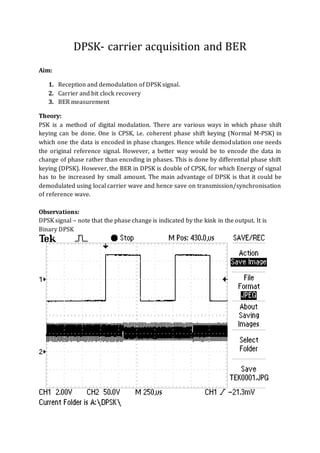
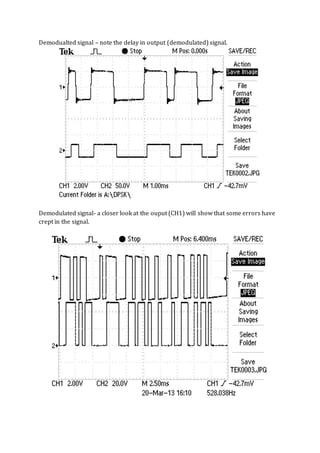


This document summarizes an experiment on differential phase shift keying (DPSK) carrier acquisition and bit error rate (BER) measurement. The aims of the experiment were to receive and demodulate a DPSK signal, recover the carrier and bit clock, and measure the BER. DPSK was observed to have a higher BER than coherent phase shift keying but does not require transmission of a reference carrier wave. Synchronization between the input and output signals could not be achieved, preventing accurate BER calculation.



