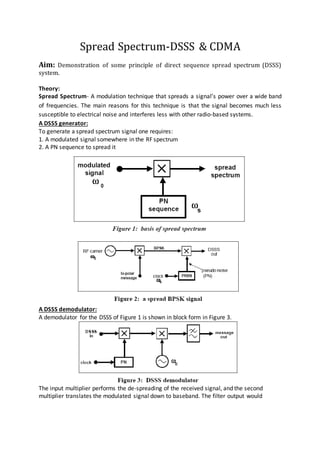
1. The document describes an experiment demonstrating principles of direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) transmission.
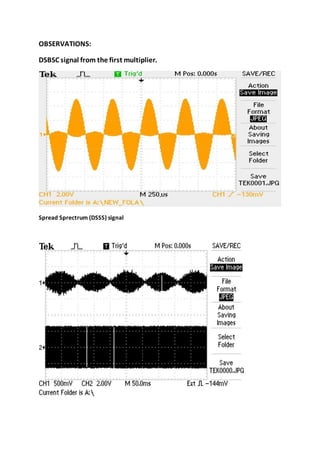
2. In DSSS, a signal's power is spread over a wide bandwidth of frequencies, making it less susceptible to noise and interference. A DSSS transmitter uses a modulated signal and a pseudorandom number (PN) sequence to spread the signal.
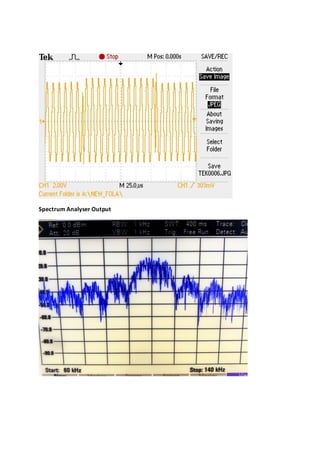
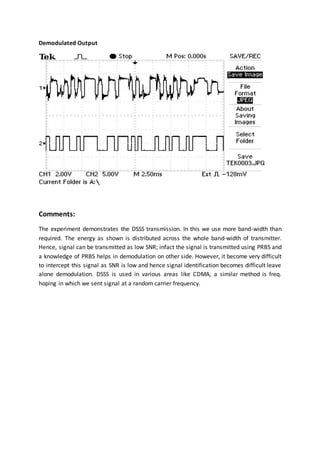
3. At the receiver, the PN sequence acts as a key to de-spread the signal. It must match the transmitter in clock, bit pattern, and alignment with the transmitted sequence. MATLAB code is provided to generate and modulate a DSSS signal for demonstration purposes.

![probably require further processing - not shown - to ‘clean up’ the waveform to binary
format.
The PN sequence at the receiver acts as a ‘key’ to the transmission. It must not only have the
same clock and bit pattern; it must be aligned properly with the sequence at the transmitter.
MATLAB code:
% Direct SequenceSpread Spectrum
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
clc
clear
% Generating the bit pattern witheach bit 6 sampleslong
b=round(rand(1,20));
pattern=[];
fork=1:20
if b(1,k)==0
sig=zeros(1,6);
else
sig=ones(1,6);
end
pattern=[pattern sig];
end
plot(pattern);
axis([-1130 -.5 1.5]);
title('bfitOriginal Bit Sequence');
% Generating the pseudo randombitpattern forspreading
spread_sig=round(rand(1,120));
figure,plot(spread_sig);
axis([-1130 -.5 1.5]);
title('bfitPseudorandomBitSequence');
% XORing the pattern withthe spread signal
hopped_sig=xor(pattern,spread_sig);
% Modulating thehopped signal
dsss_sig=[];
t=[0:100];
fc=.1
c1=cos(2*pi*fc*t);
c2=cos(2*pi*fc*t+pi);
fork=1:120
if hopped_sig(1,k)==0
dsss_sig=[dsss_sig c1];
else
dsss_sig=[dsss_sig c2];
end
end
figure,plot([1:12120],dsss_sig);
axis([-112220 -1.5 1.5]);
title('bfitDSSSSignal');](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eep316-ask-150219124947-conversion-gate01/85/EEL316-ASK-3-320.jpg)
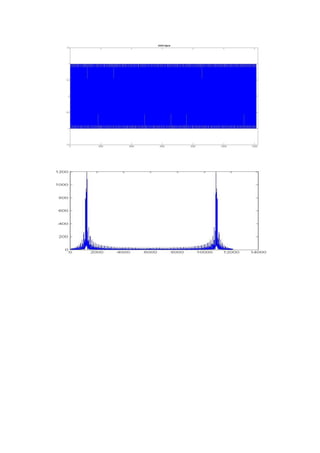
![% Plotting the FFT of DSSSsignal
figure,plot([1:12120],abs(fft(dsss_sig)))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eep316-ask-150219124947-conversion-gate01/85/EEL316-ASK-4-320.jpg)