This document discusses various digital modulation techniques including:
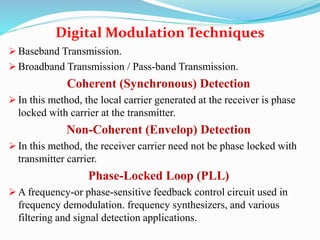
- Coherent and non-coherent detection methods for baseband and broadband signals
- Phase-locked loops used in frequency demodulation
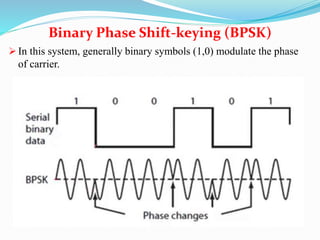
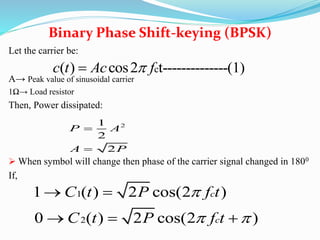
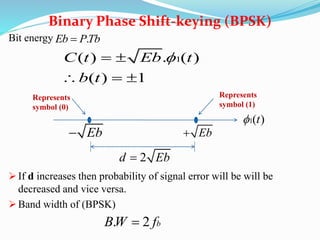
- Digital modulation techniques where binary symbols modulate the carrier phase, including BPSK where the carrier phase is shifted by 180 degrees to represent 1s and 0s
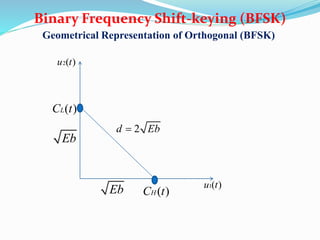
- BFSK where the carrier frequency is shifted according to the binary symbols while keeping the phase unchanged
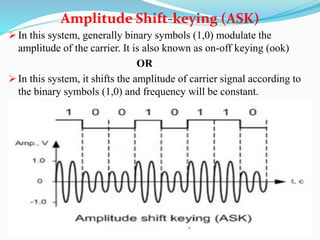
- ASK where the carrier amplitude is shifted according to the binary symbols to keep the frequency constant
- Pulse modulation techniques where pulse amplitude, width, or time is varied to transmit analog data.