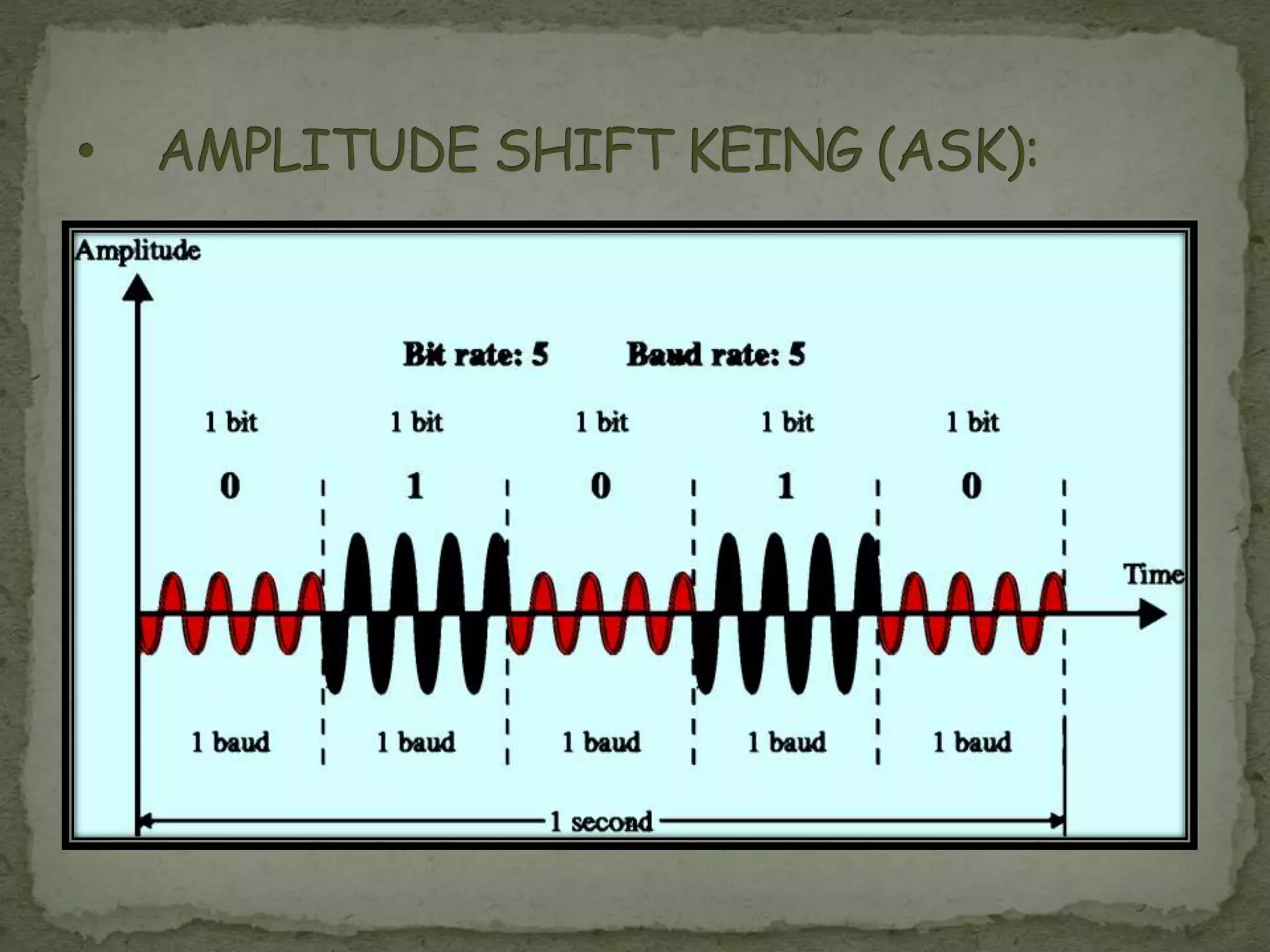
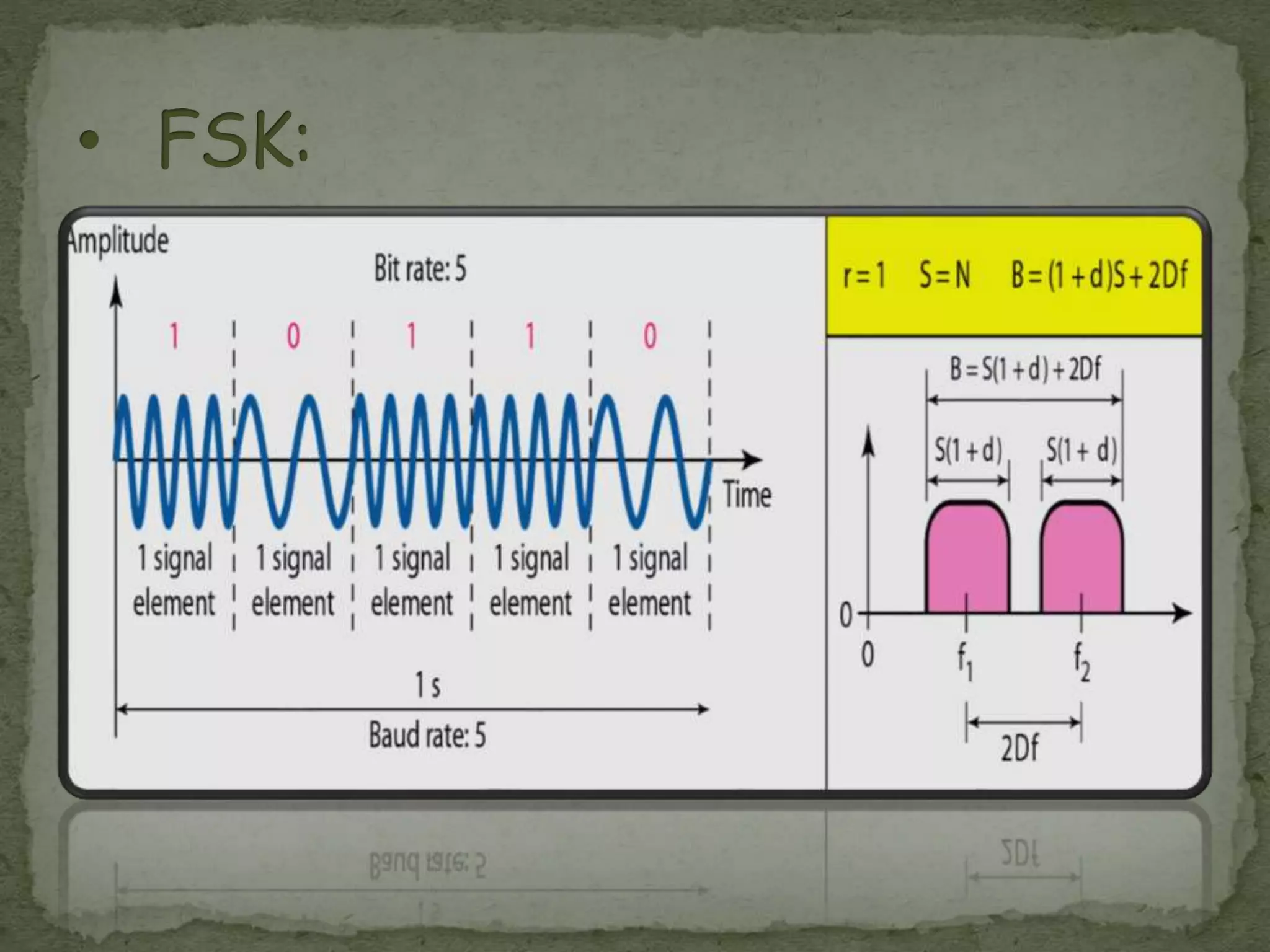
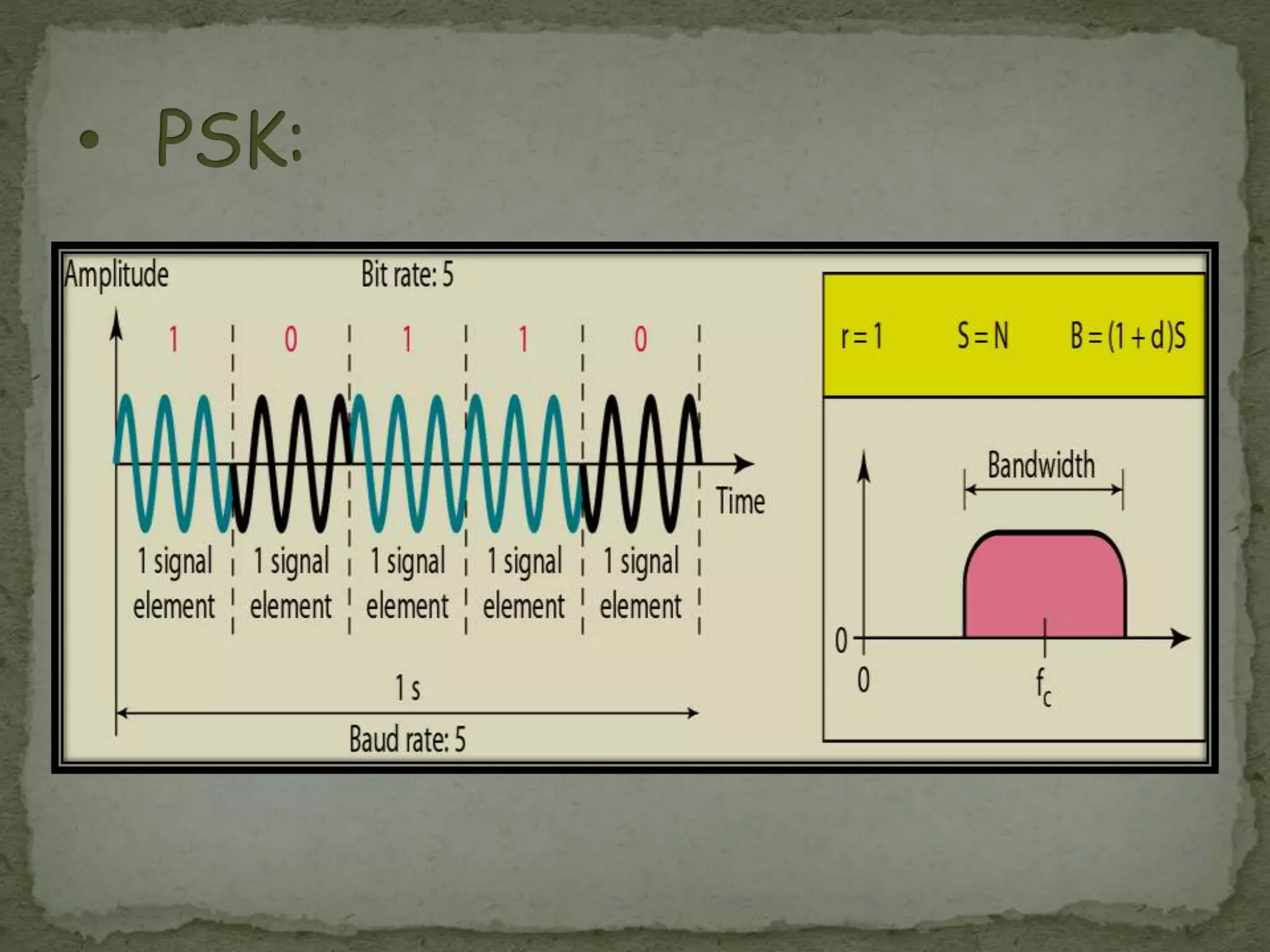
Noman Khan, a 4th semester Computer Science student at GSSCP College, presented on digital modulation techniques ASK, FSK, and PSK. ASK varies the amplitude of a carrier signal to transmit information, making it susceptible to noise interference. FSK varies the frequency, keeping amplitude and phase constant. PSK varies the phase of the carrier while keeping amplitude and frequency constant. PSK has become more common than ASK or FSK and requires less bandwidth than FSK.