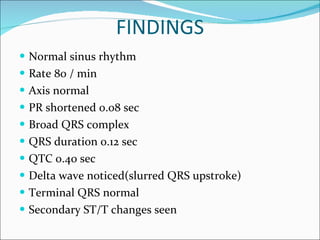
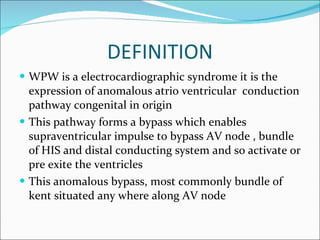
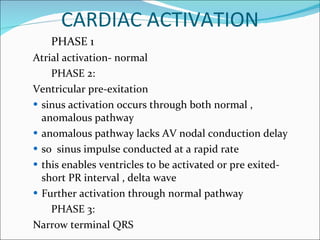
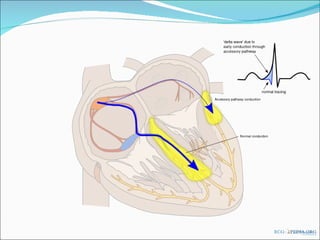
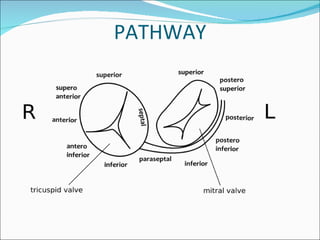
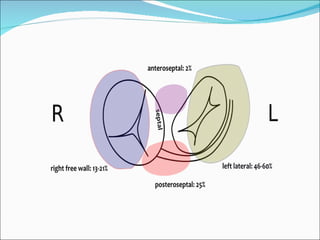
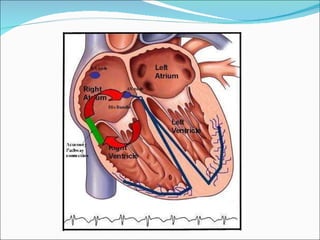
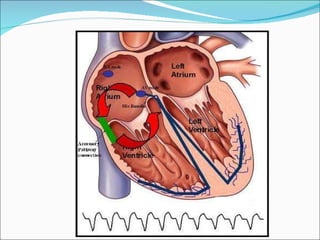
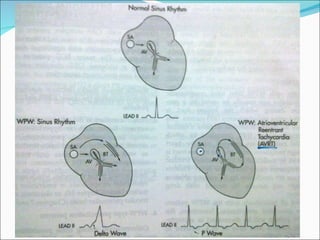
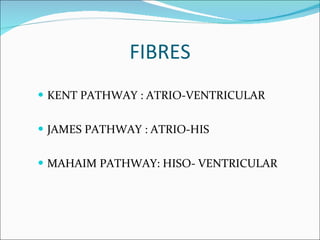
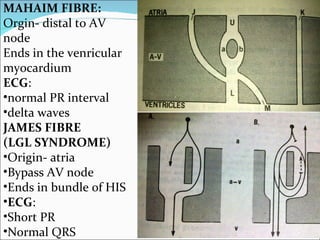
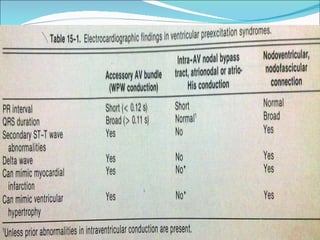
A 45-year-old female presented with difficulty breathing, palpitations, and sweating for 4 hours. An ECG showed Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome, characterized by a short PR interval, delta wave, and widened QRS complex. WPW is a congenital condition involving an accessory pathway that allows supraventricular impulses to bypass the AV node and activate the ventricles early. Treatment options include antiarrhythmic drugs or radiofrequency ablation to destroy the accessory pathway.