- The Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome is a type of heart arrhythmia caused by an extra electrical pathway between the atria and ventricles, bypassing the atrioventricular node.
- Normally electrical signals pass through the atrioventricular node, which causes a delay, but in WPW the extra pathway allows electrical signals to pass directly from the atria to the ventricles without delay.
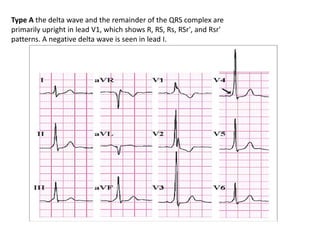
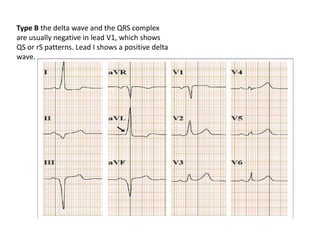
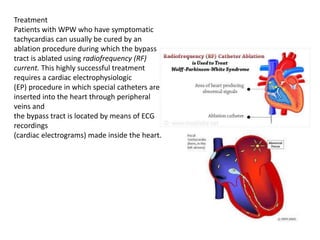
- The ECG in WPW shows a shortened PR interval, widened QRS complex with an abnormal slurred upstroke called a delta wave, and inverted T waves opposite to the QRS complex. Treatment involves catheter ablation to destroy the extra pathway.