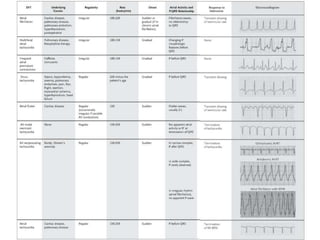
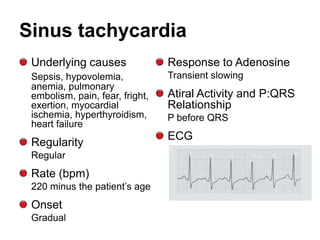
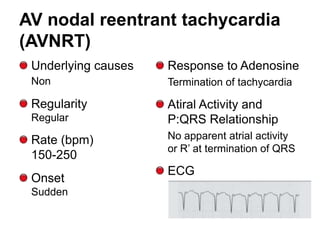
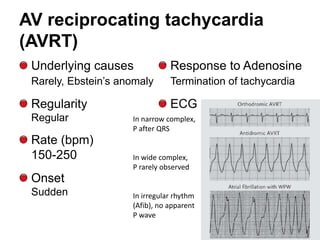
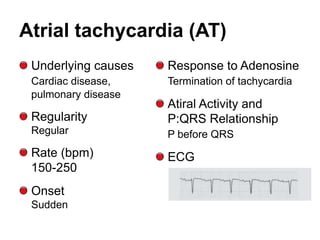
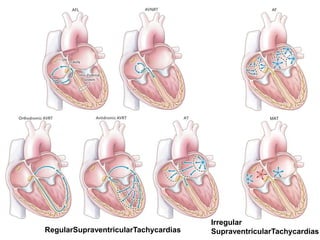
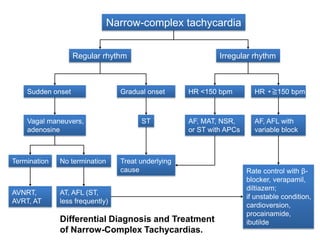
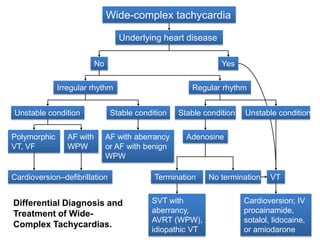
This document provides information to help differentiate types of supraventricular tachycardia, including:
1. The initial differential diagnosis should focus on regularity, rate, and onset rather than atrial activity on ECG.
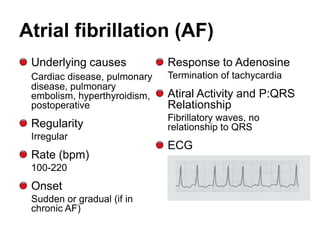
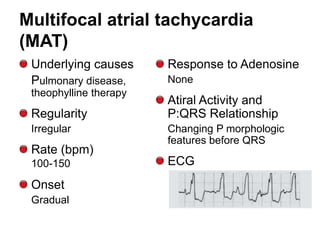
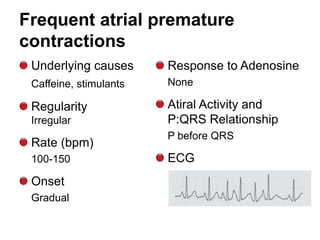
2. Regular types include sinus tachycardia, atrial flutter, AV nodal reentrant tachycardia, AV reciprocating tachycardia, and atrial tachycardia. Irregular types include atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter with irregular conduction, and multifocal atrial tachycardia.
3. Adenosine can help distinguish types by terminating rhythms dependent on AV node conduction like AV nodal reentrant