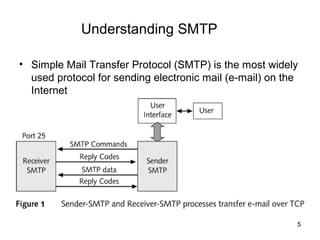
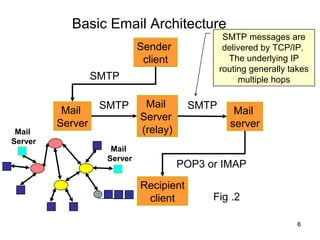
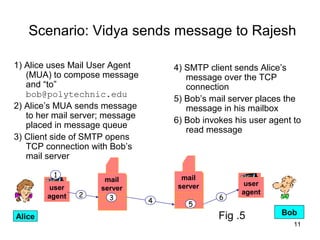
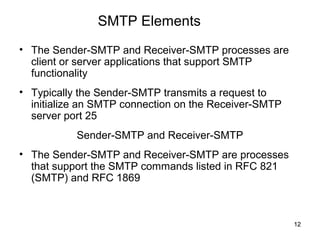
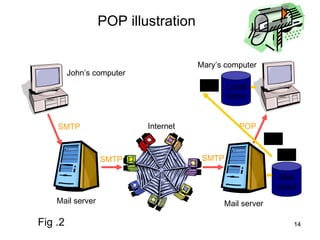
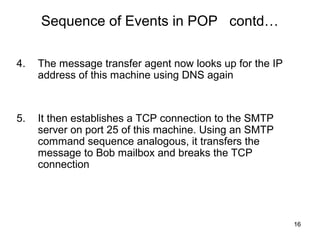
SMTP and POP are the main protocols used to transfer emails. SMTP is used to deliver emails from client to local mail server and between mail servers, while POP is used for user access to delivered emails. SMTP uses TCP connections on port 25 to transfer messages in three phases - handshaking, transfer, and closure. POP retrieves emails from the POP server to the user's machine using a TCP connection on port 110 in two stages - authentication and message transfer.