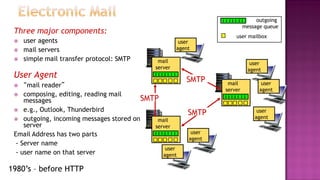
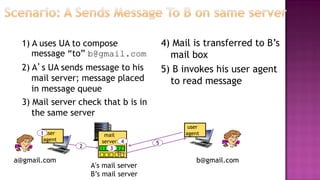
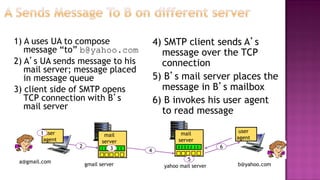
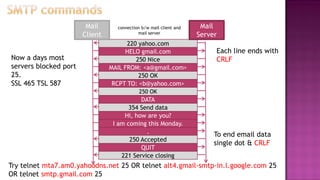
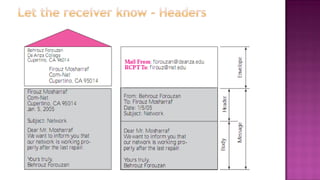
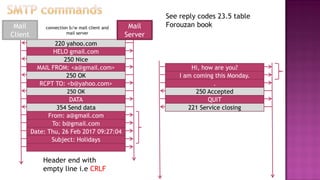
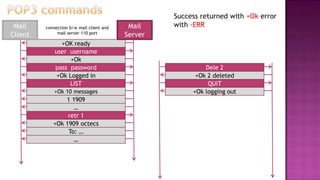
This document discusses email and how it works. There are three main components: user agents like Outlook or Thunderbird, mail servers, and SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol). SMTP is used to transfer emails between mail servers over TCP. It uses commands and responses to reliably transfer messages. Email addresses contain the server name and user name. User agents are used to compose and read emails, which are stored on mail servers in user mailboxes.