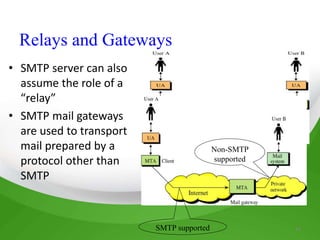
This document provides an overview of SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) including its history, general features, how it works, and limitations. SMTP is an Internet standard used to transfer email between Mail Transfer Agents (MTAs). It originated in 1980 and was standardized in 1981. Key points are that SMTP operates over TCP port 25 in a request-response format, uses status codes to indicate success or failure, and relies on MTAs like Sendmail to route and deliver messages between servers. However, it only supports basic 7-bit ASCII encoding and is susceptible to misuse like spamming.







![8
Sendmail
Mail Transfer Agent [MTA] : is a computer program or software agent
that transfers electronic mail messages from one computer to another.
• Sendmail is a MTA
• Supports several mail transfers including SMTP
• Pro’s
• Can perform header rewriting, mail routing
• Extensive support available
• Con’s
• Not secure
• Code is bulky [compared to other MTA’s such as qmail]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/simplemailtransferprotocol-150904171532-lva1-app6892/85/Simple-mail-transfer-protocol-8-320.jpg)

![11
Link Layer PCI IP-PCI
Keyword: argument(s)
Command format:
Response format:
3-digit status code [textual information]
How SMTP works?
Link Layer PCI IP-PCI TCP-PCI SMTP command/responseTCP-PCI SMTP command/responseTCP-PCI SMTP command/response](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/simplemailtransferprotocol-150904171532-lva1-app6892/85/Simple-mail-transfer-protocol-11-320.jpg)



