This document provides an overview of internet protocols for email (SMTP) including:
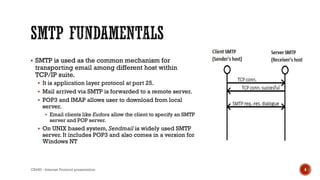
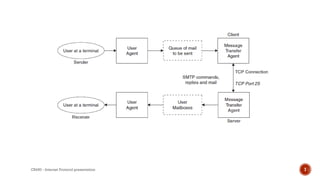
- SMTP is used to transfer email between servers and works in a client-server model. Email clients use POP3 or IMAP to retrieve messages from servers.
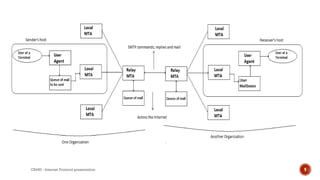
- Key components include user agents (email clients), message transfer agents (MTA servers), and protocols like SMTP, POP3, and IMAP.
- SMTP uses a stored-and-forward method to route emails through intermediate servers within a network on its way to the destination address.