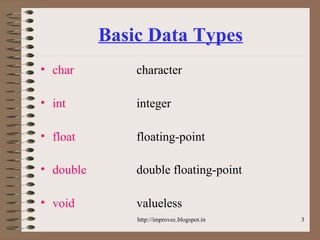
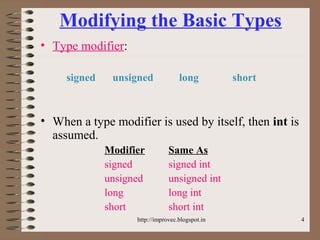
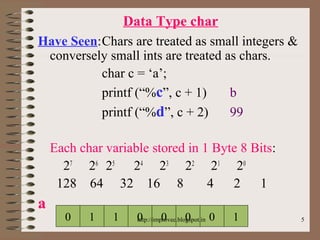
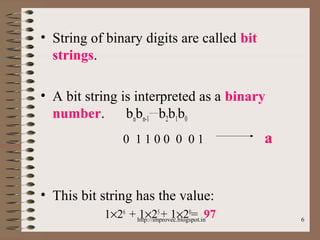
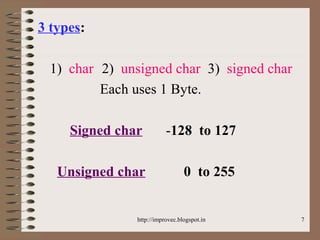
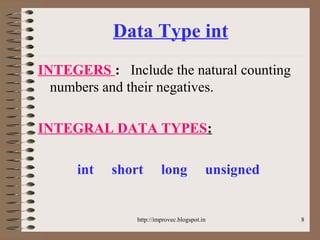
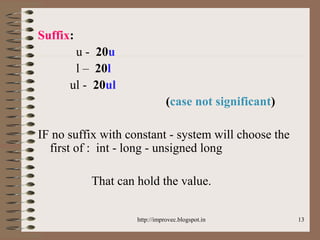
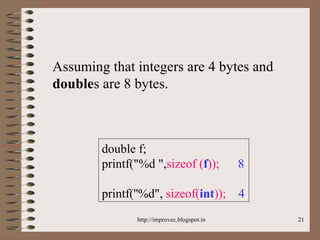
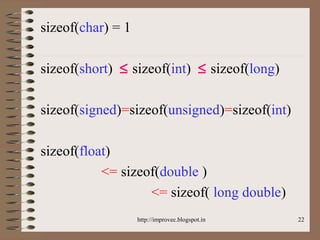
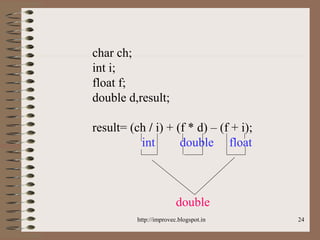
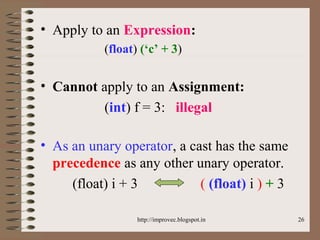
The document discusses fundamental data types in C including integer, floating point, character, and void types. It describes how variables must be declared before use and explains basic type modifiers like short, long, and unsigned. The summary also covers integer storage sizes and ranges, floating point precision and representation, and type conversions in C using casts and arithmetic promotion.