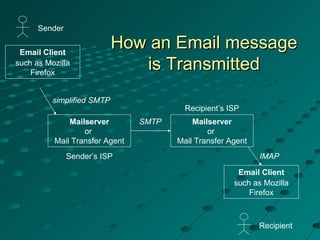
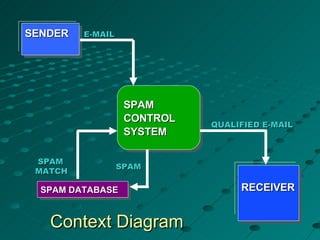
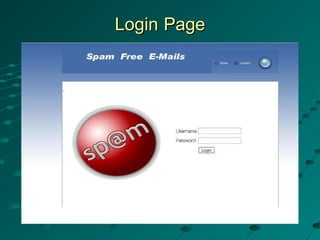
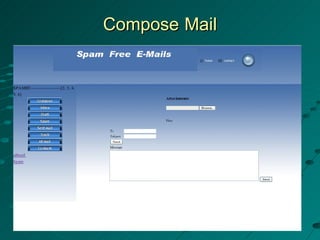
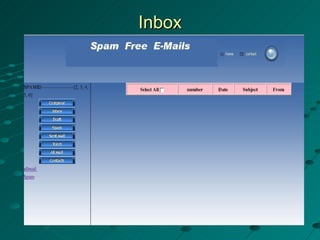
The document describes a spam filtering system that uses JavaMail and SMTP, POP, IMAP protocols. It summarizes the key components and functionality of the system. The system identifies spam messages based on sender, message size, content keywords. It moves identified spam to a specified location. The document outlines the completed and remaining work, including designing login, inbox, compose pages and connecting to an Apache JavaMail server.