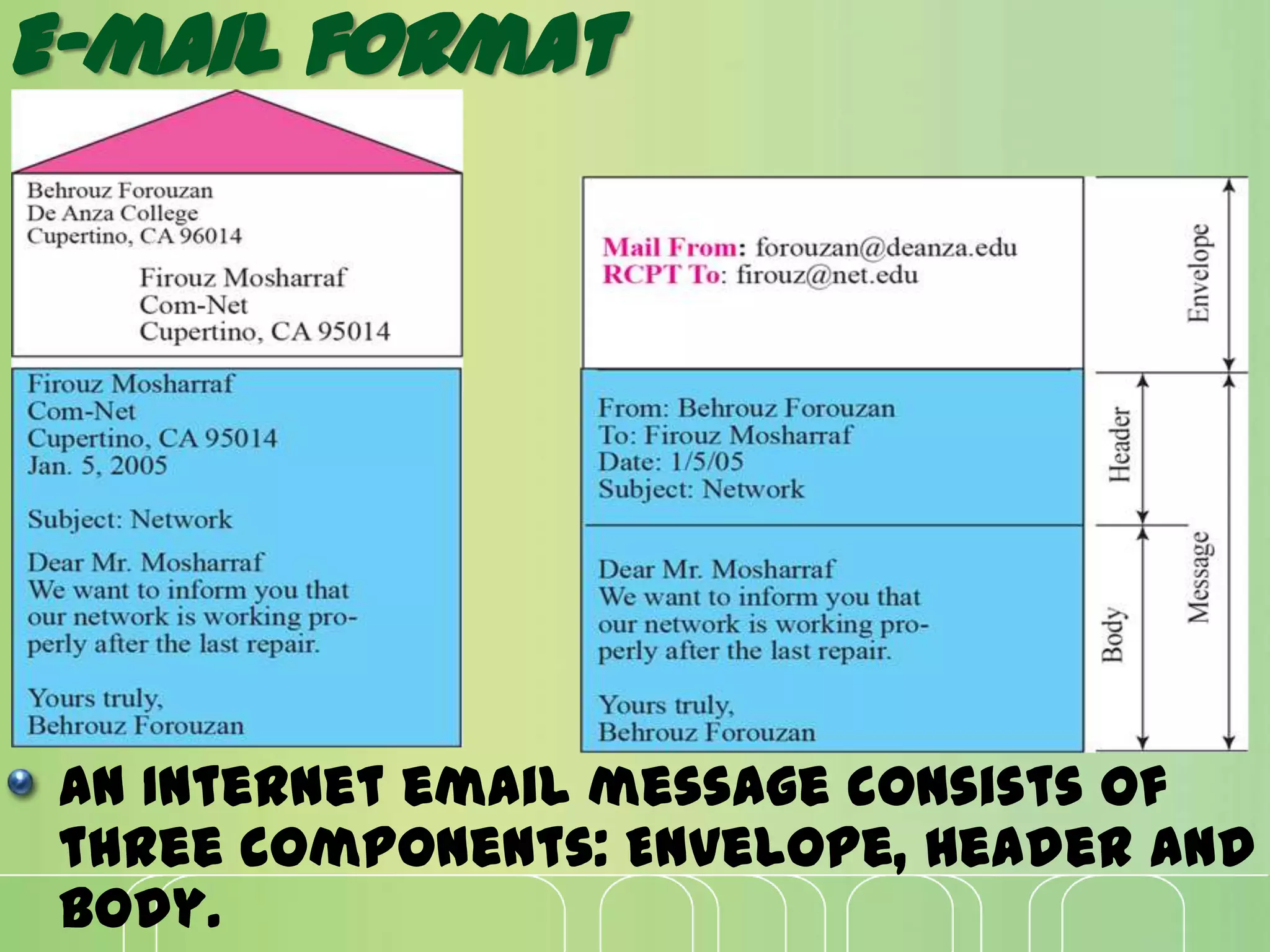
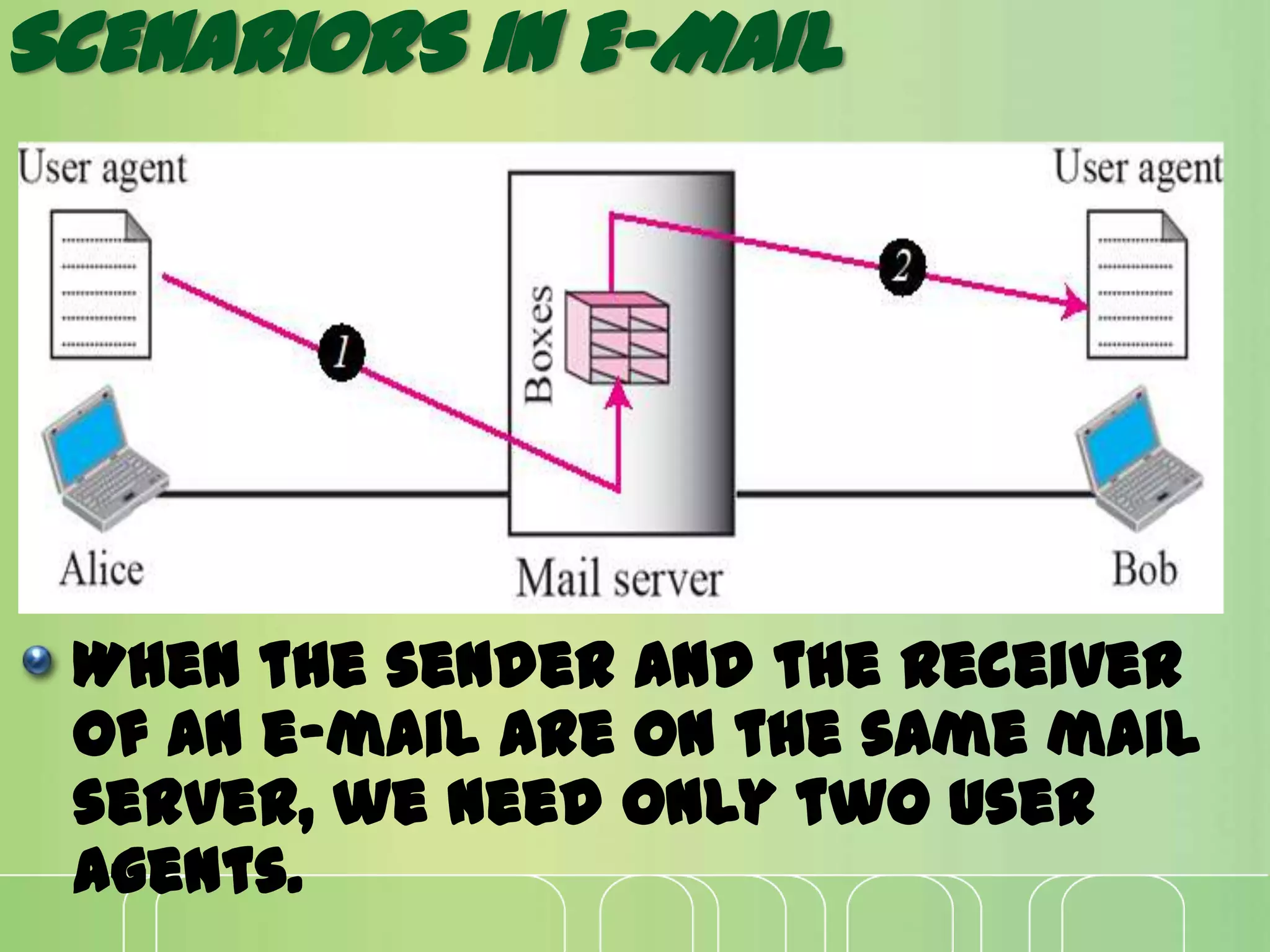
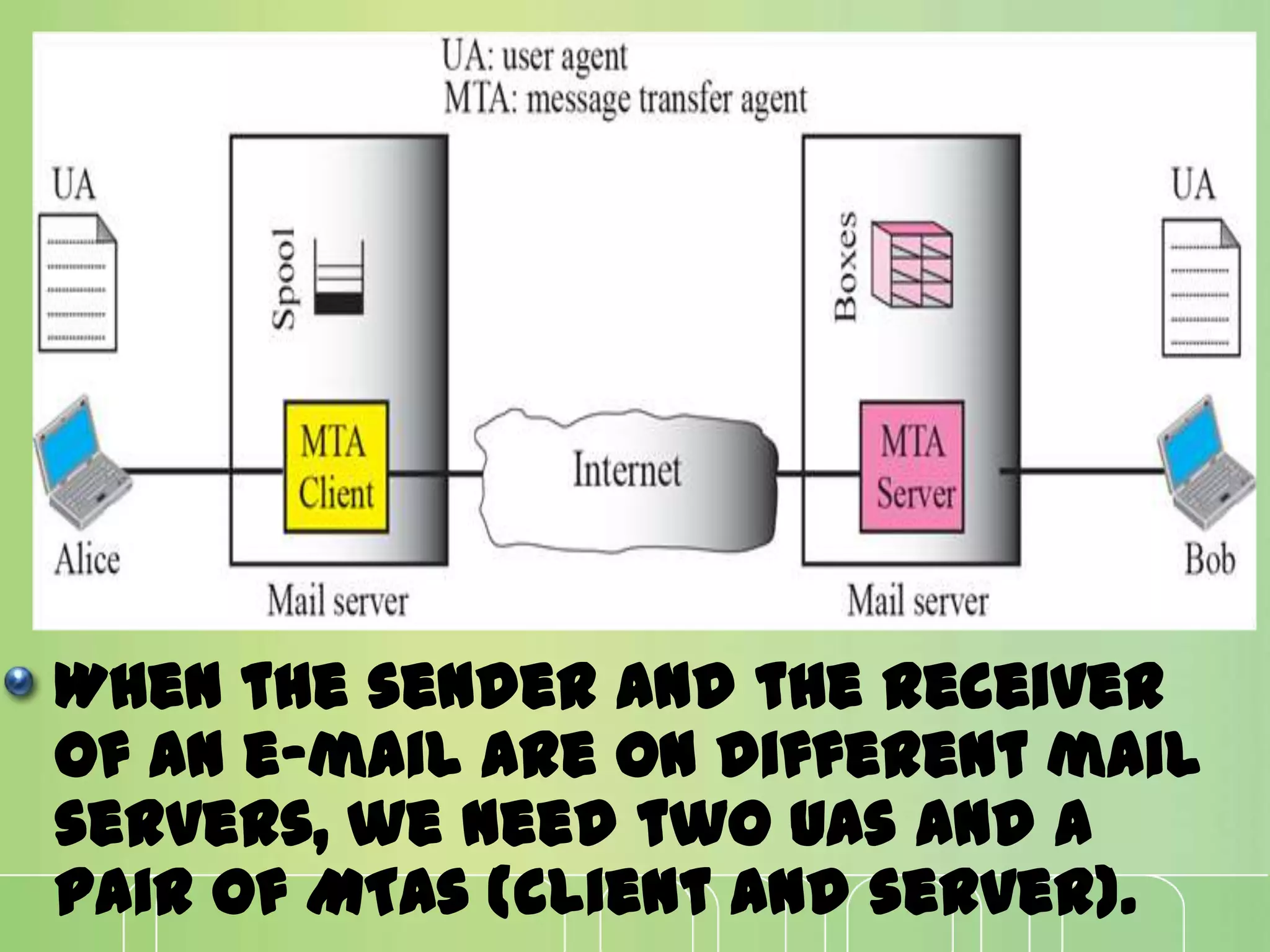
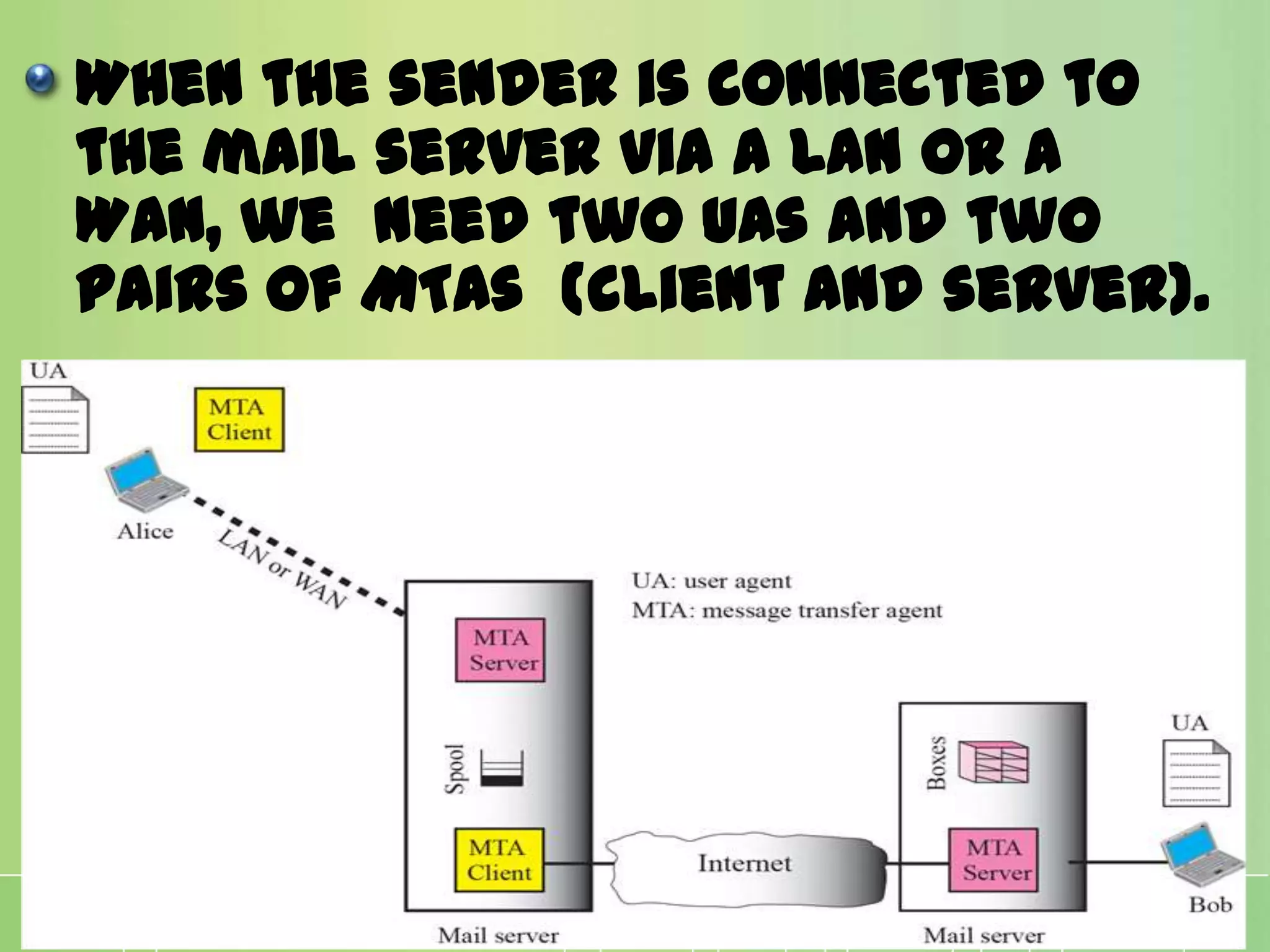
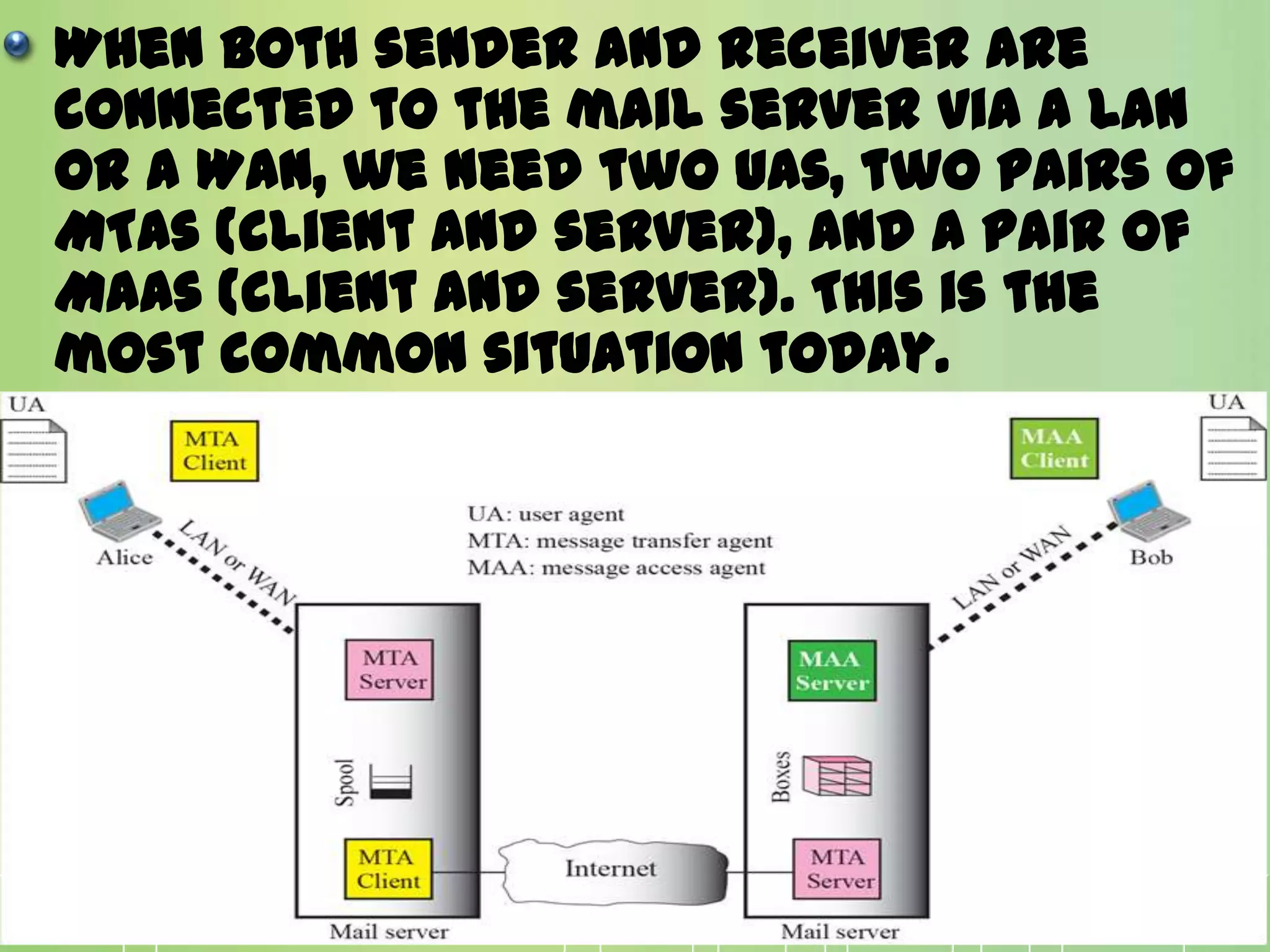
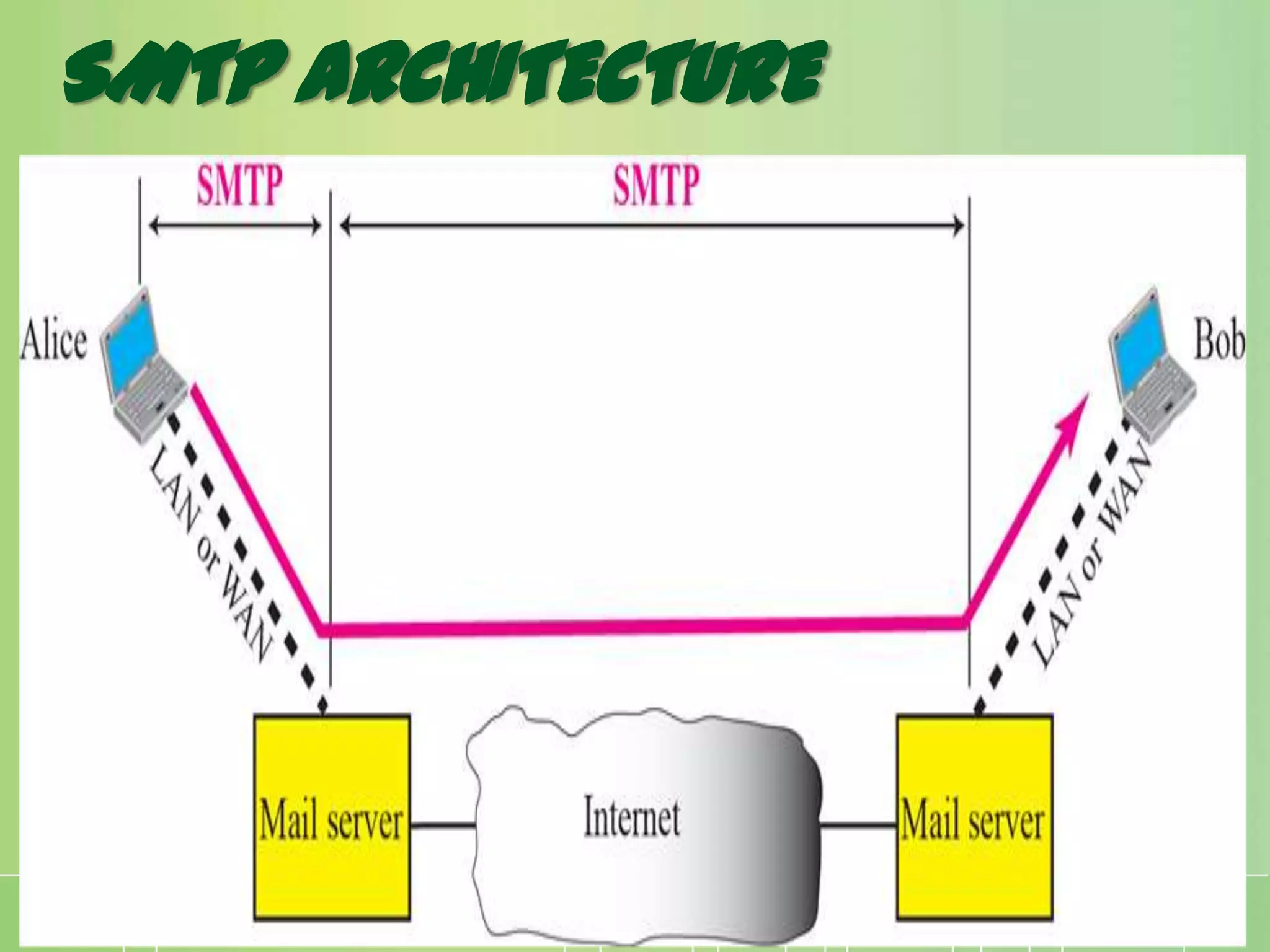
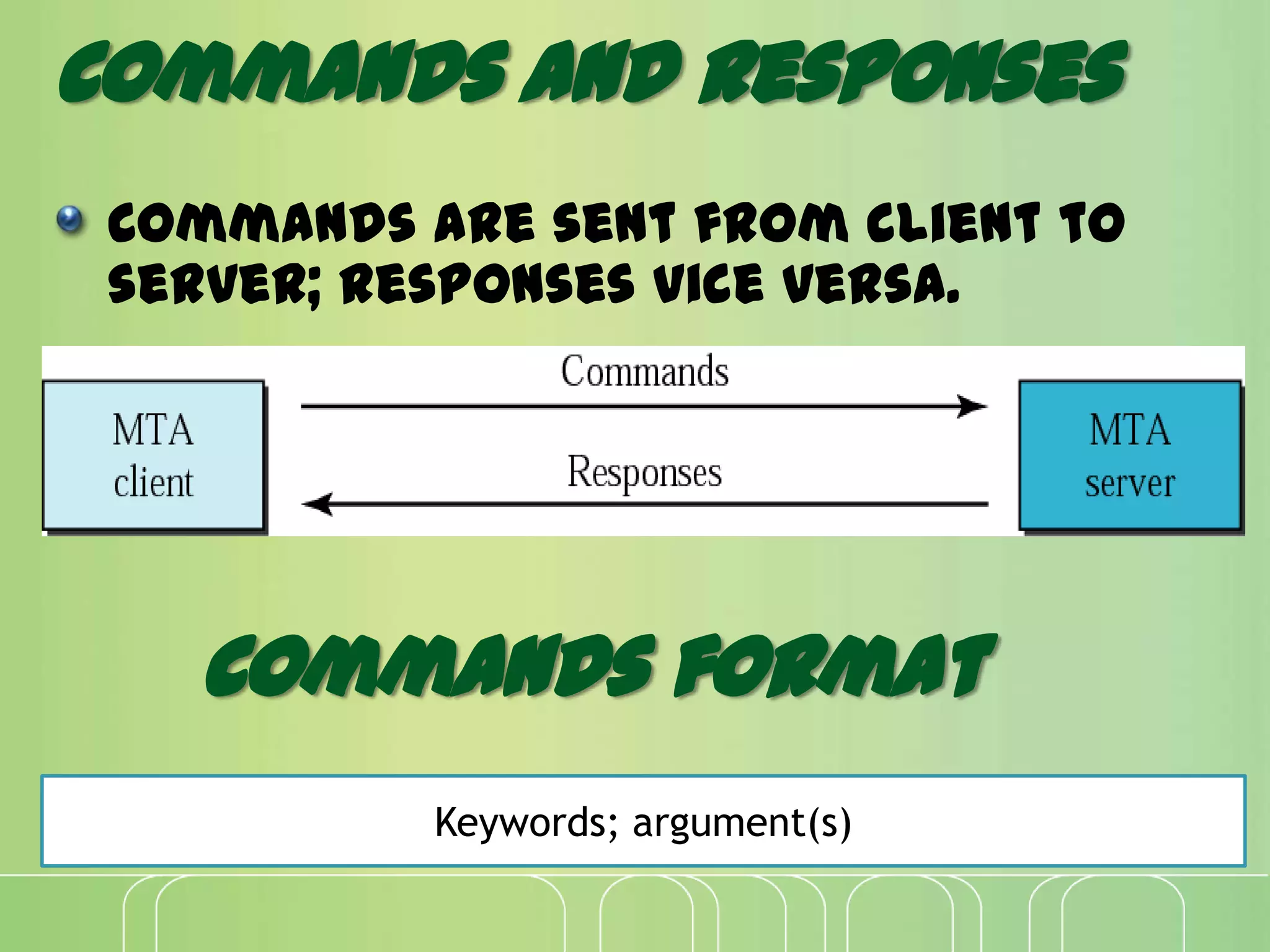
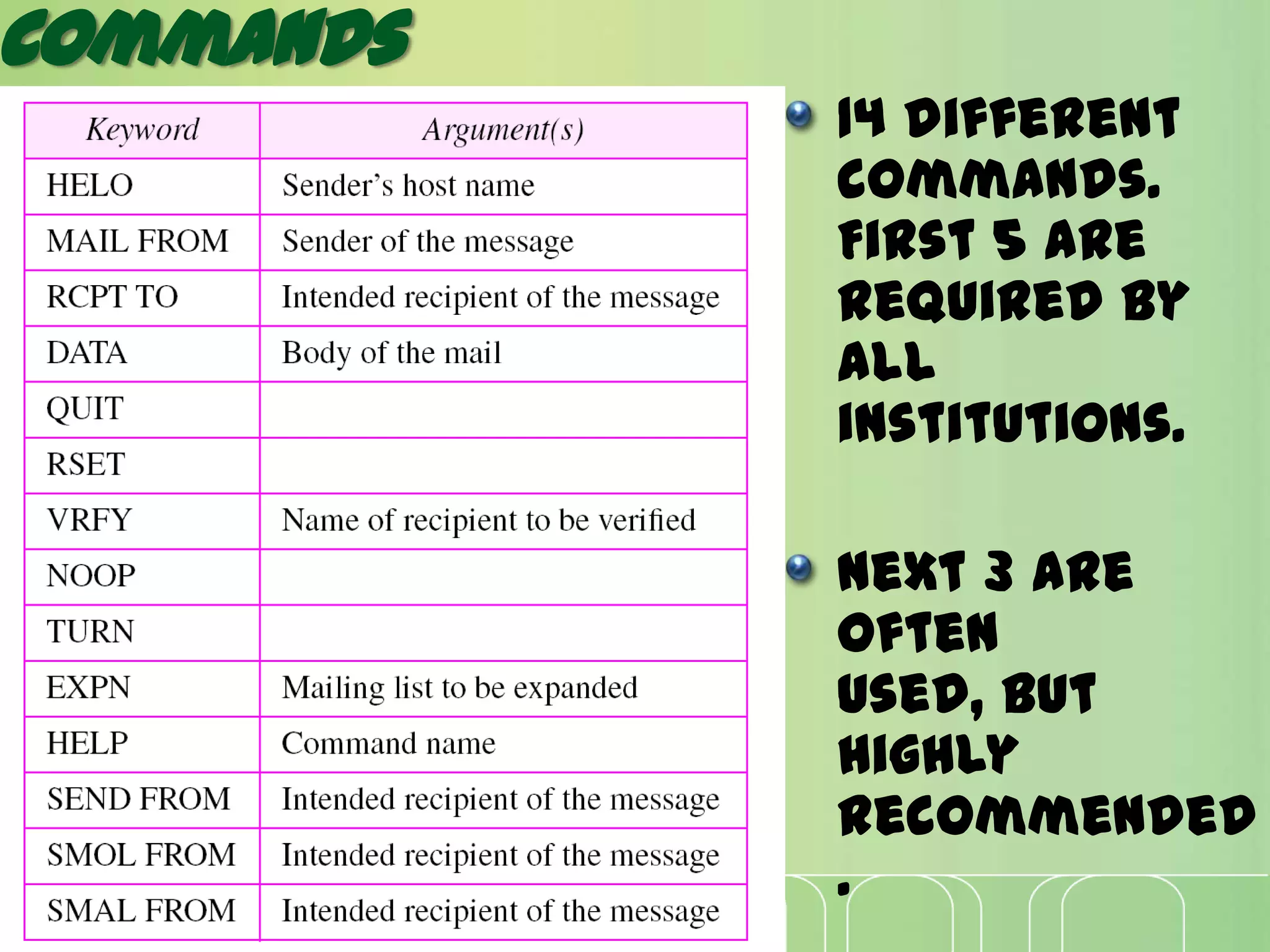
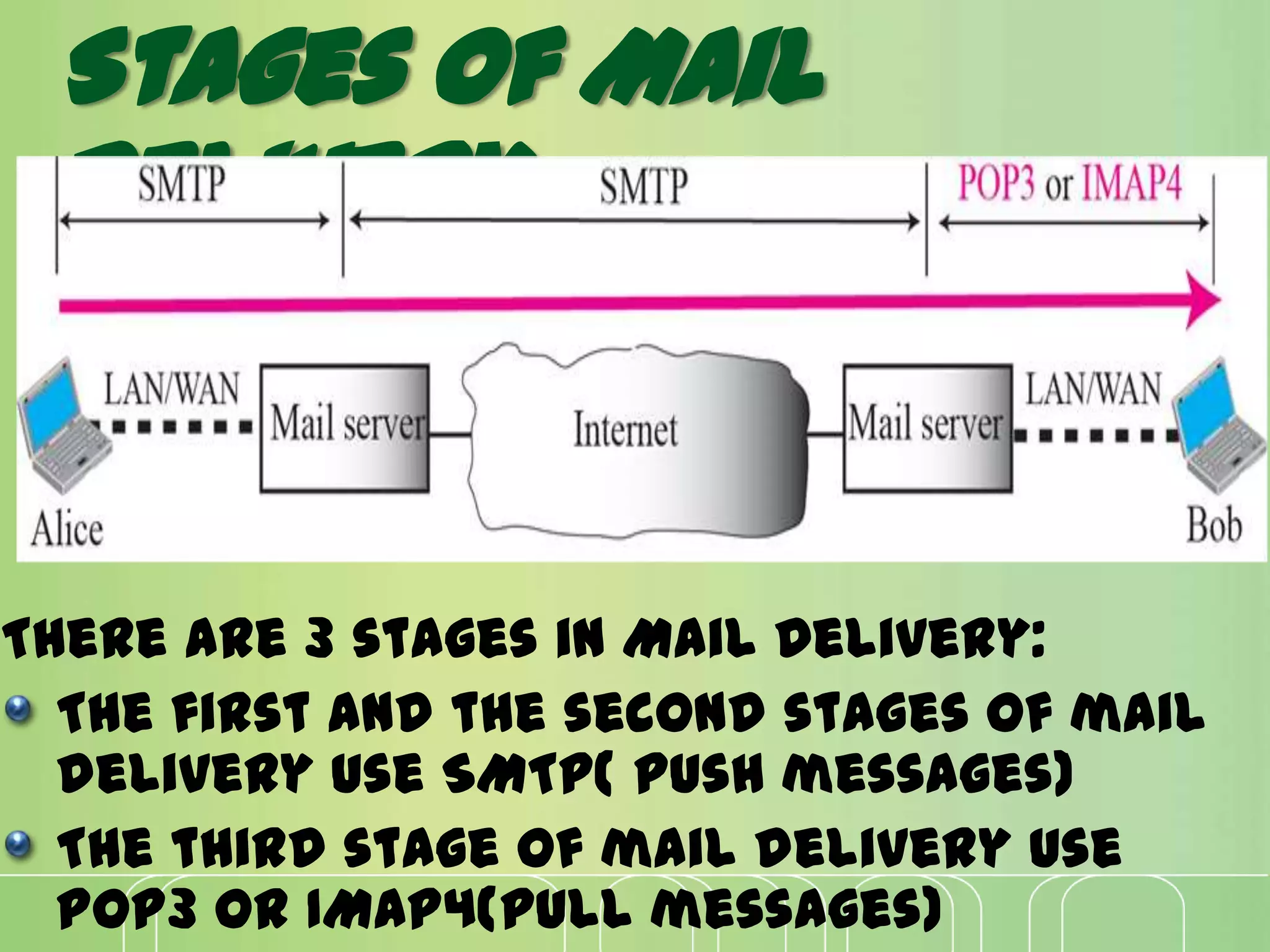
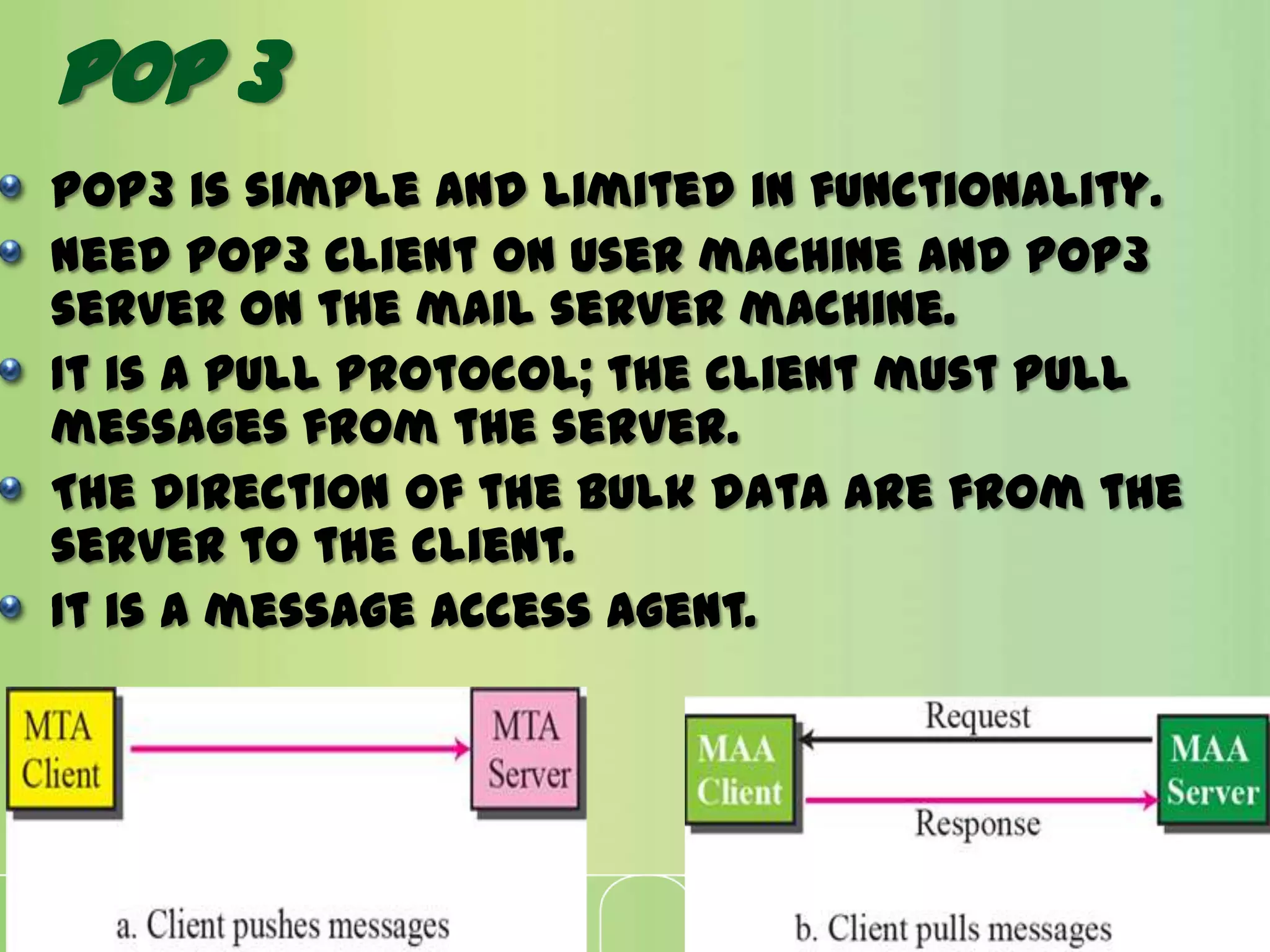
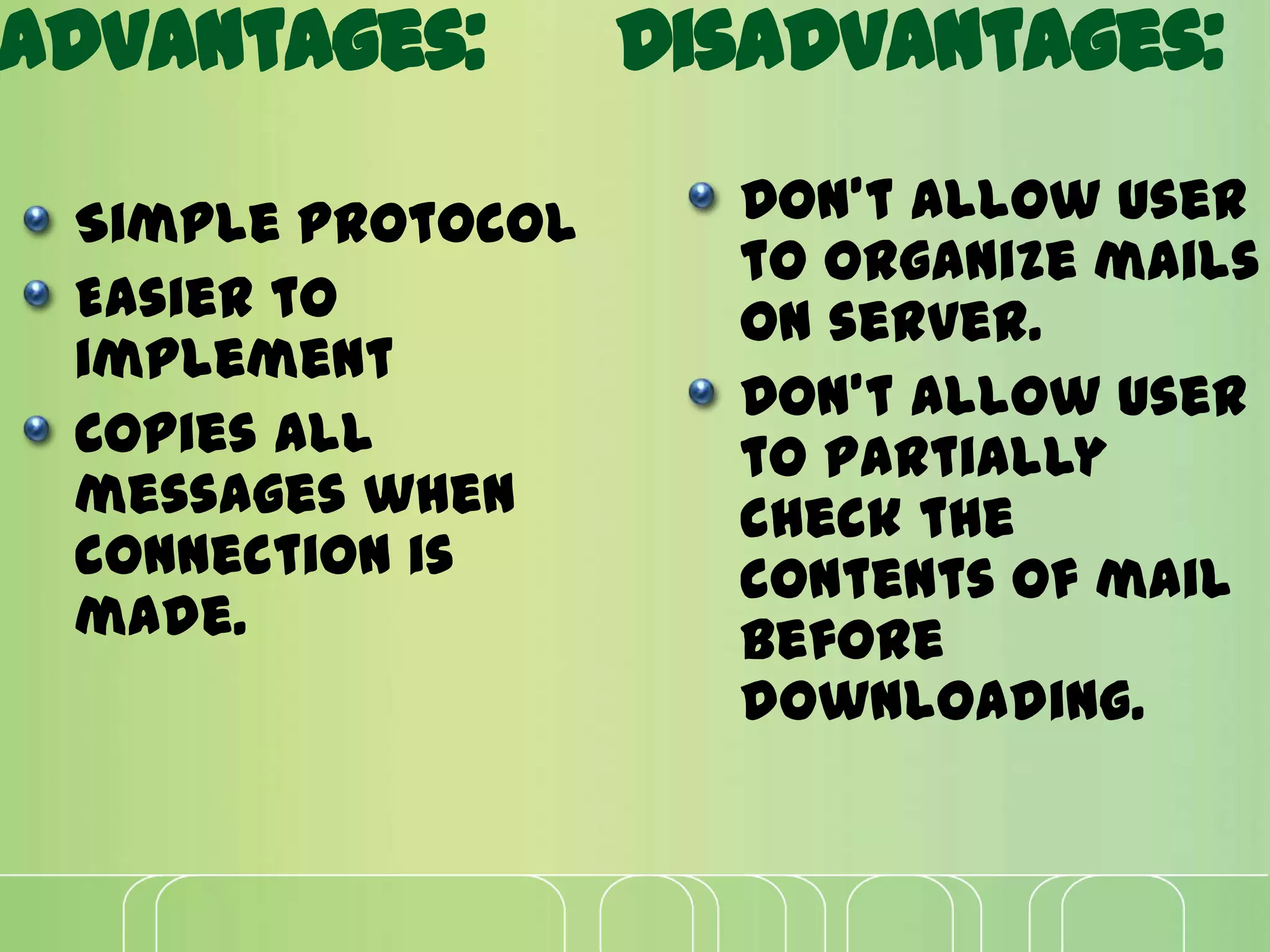
This document discusses electronic mail (e-mail) and how it works. It describes the key components of an e-mail system including user agents, message transfer agents, and message access agents. It explains the store-and-forward model that modern e-mail uses to send and receive messages between users. It also outlines the main protocols used for e-mail - SMTP for sending messages between servers, and POP3 or IMAP for users to access their messages. IMAP is generally preferred as it allows accessing and organizing messages from multiple devices.