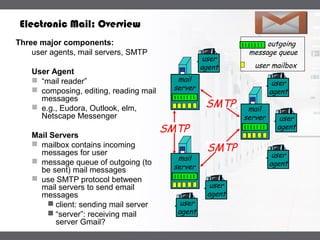
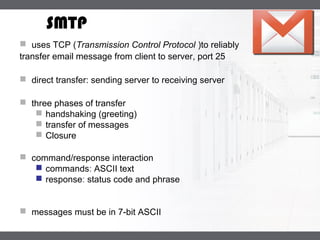
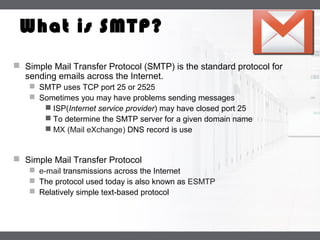
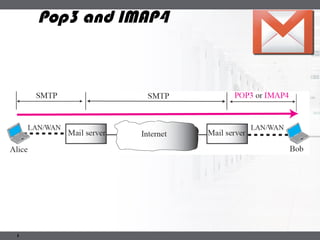
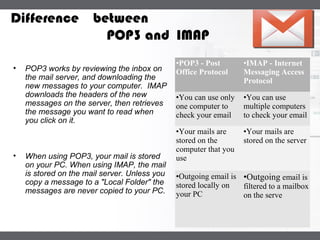
A mail server is a computer that handles email delivery. It implements the client and server portions of SMTP to reliably transfer messages between servers using TCP on port 25. A mail server stores users' incoming emails in their mailboxes and queues outgoing messages to be sent. IMAP and POP3 are additional protocols that allow users to access their mailboxes to read and manage messages.