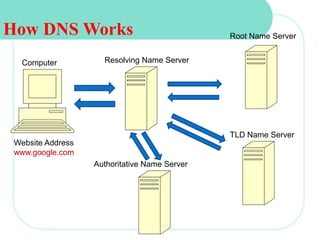
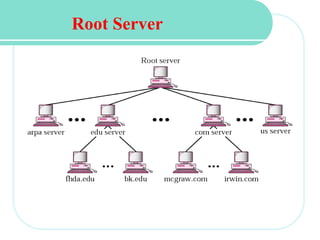
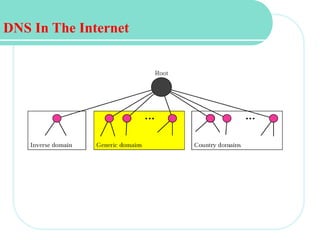
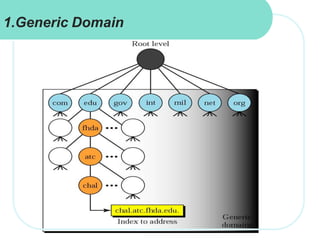
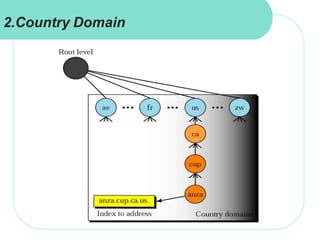
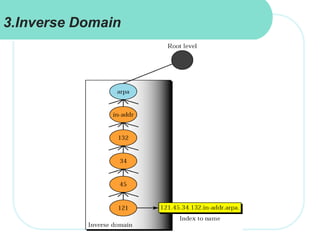
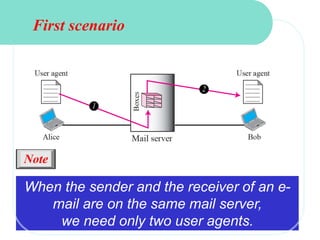
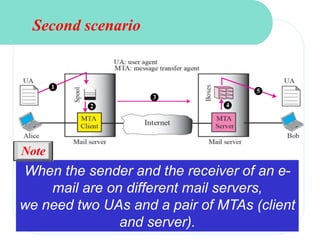
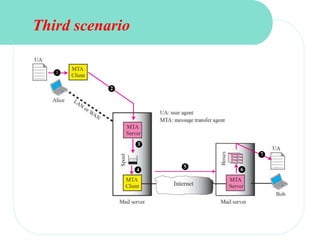
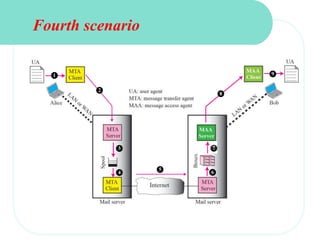
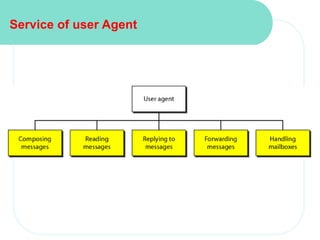
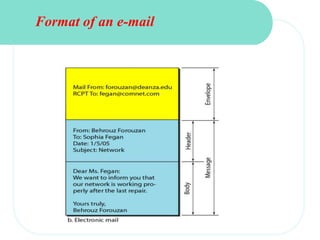
The document discusses computer networks and email. It describes how DNS works by converting domain names to IP addresses so humans can access websites using names instead of numbers. It then explains the basic architecture of email, including common email providers and protocols like SMTP, POP, and IMAP. SMTP is used to transfer messages between servers, while POP and IMAP deal with receiving and accessing emails from the server. The document also provides details on email message format, with the header containing sender/recipient info and the body containing the actual content.