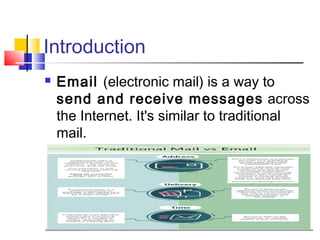
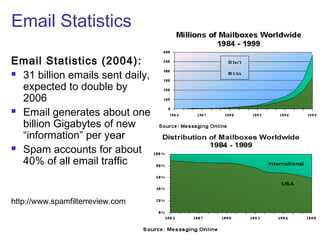
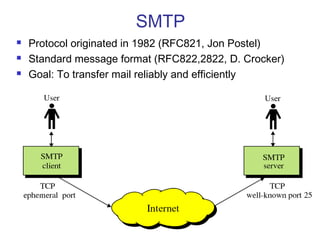
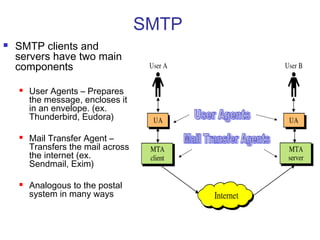
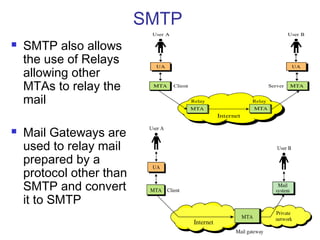
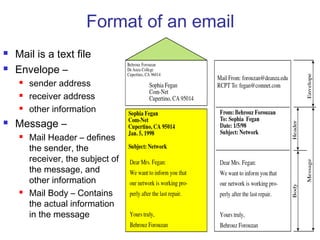
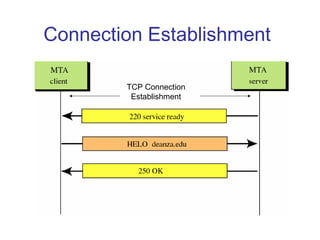
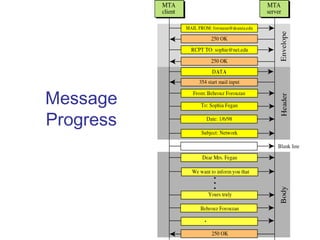
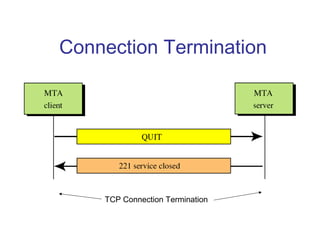
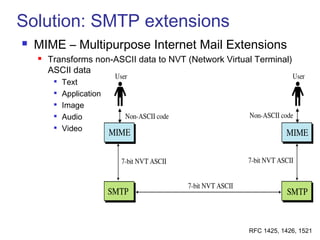
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is the standard protocol for sending email across the internet. SMTP was created in 1982 and uses a client-server model with user agents to prepare messages and mail transfer agents to reliably transfer messages between servers. An email consists of an envelope containing sender and recipient addresses, and a message with a header defining sender, recipient, subject, and a body containing the actual content. SMTP works by establishing a TCP connection between servers, sending commands like MAIL FROM, RCPT TO, and DATA to transfer the message, then terminating the connection. Extensions like MIME allow non-text content like images and files to be included in emails.