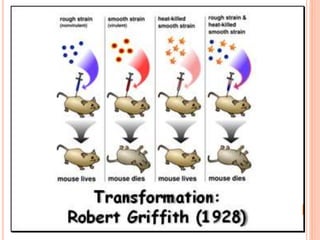
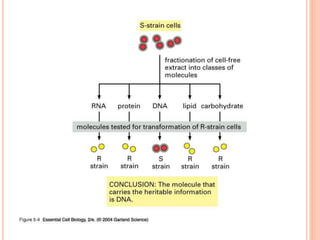
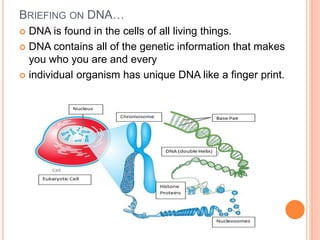
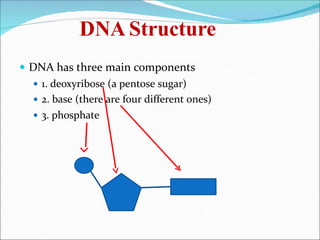
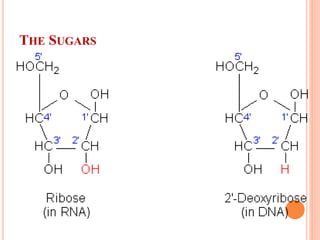
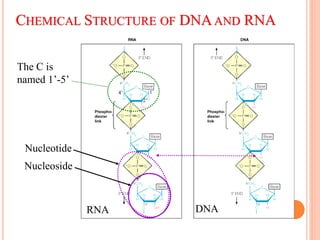
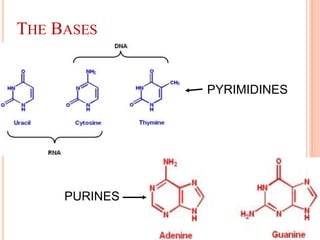
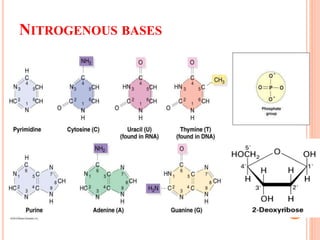
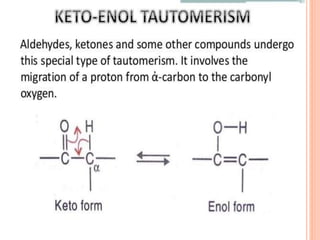
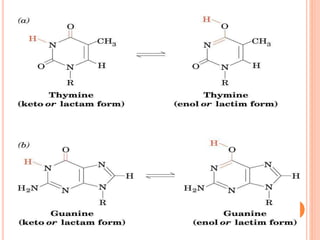
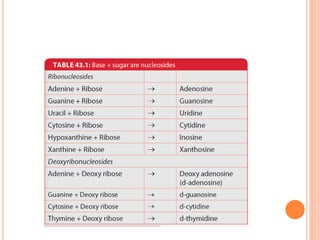
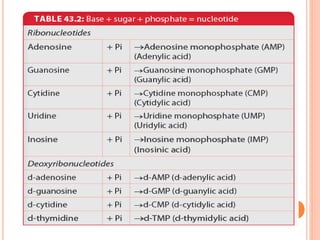
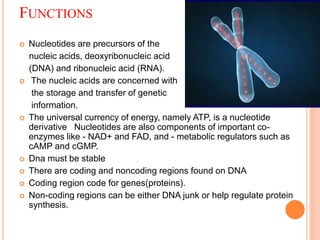
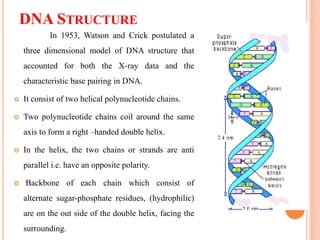
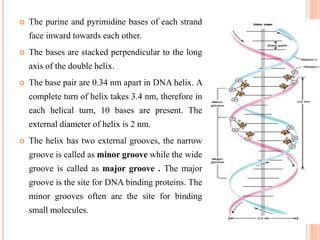
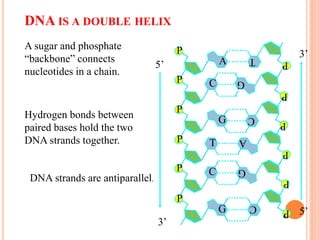
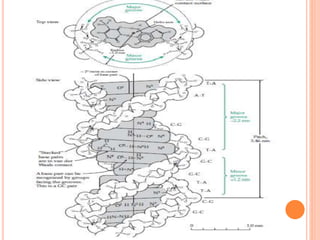
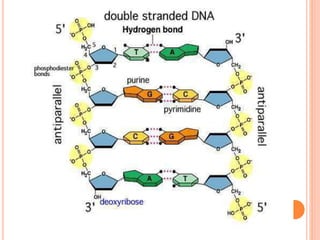
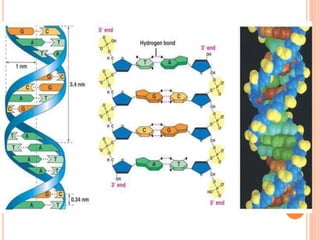
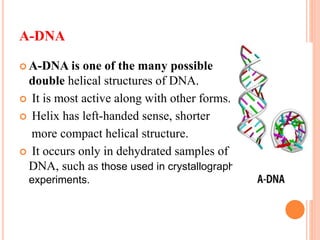
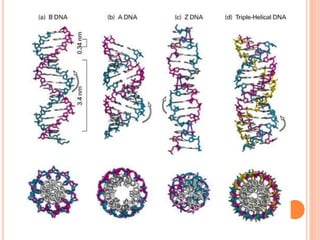
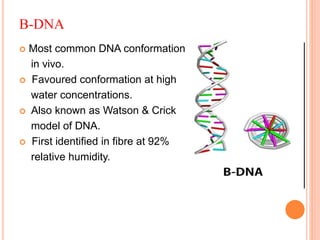
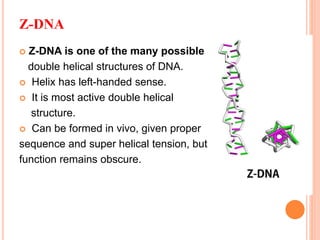
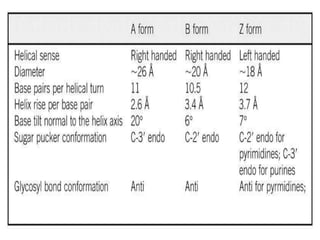
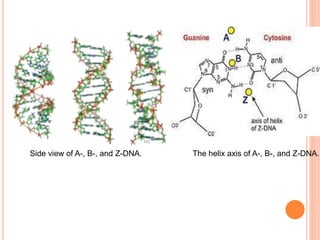
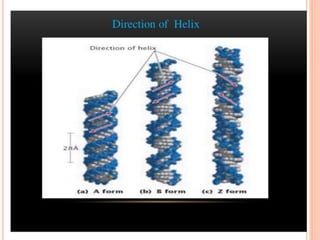
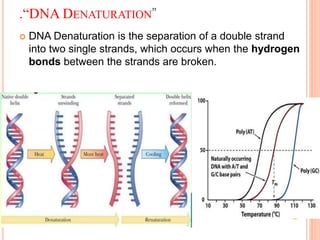
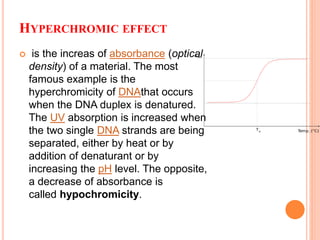
DNA contains the genetic instructions for living organisms. It exists as a double helix structure with two strands bonded together via hydrogen bonds between complementary nucleotide base pairs. Watson and Crick discovered the double helix structure in 1953, which has a sugar-phosphate backbone and pairs of nucleotides containing one of four nitrogenous bases. The structure allows DNA to stably store and replicate genetic information through its various forms including A-DNA, B-DNA, and Z-DNA.