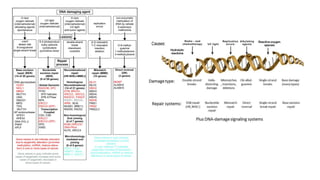
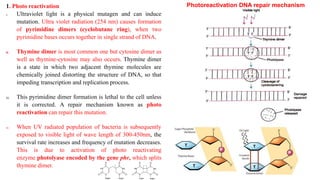
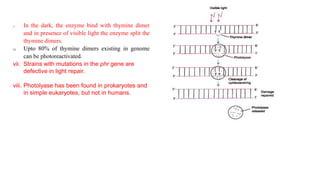
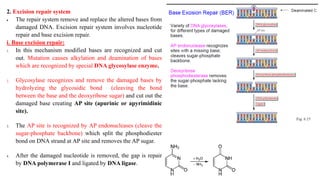
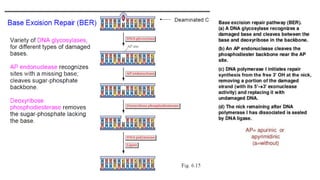
This document discusses DNA repair mechanisms, specifically nucleotide excision repair. It provides details on:
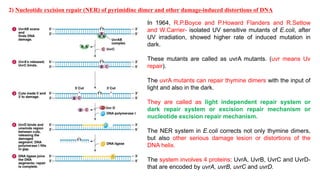
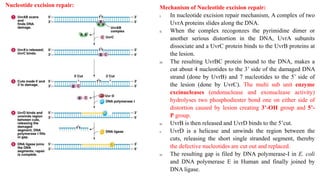
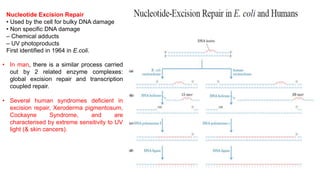
1) Nucleotide excision repair is a mechanism to repair DNA damage such as thymine dimers caused by UV light. It involves the uvrA, uvrB, uvrC, and uvrD genes which encode proteins that recognize distortions in DNA structure and cut out the damaged region for replacement.
2) If nucleotide excision repair fails, it can result in genetic disorders like xeroderma pigmentosum which increases skin cancer risk, or Cockayne syndrome which involves neurological issues.