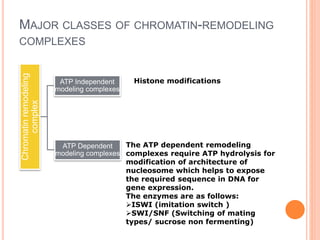
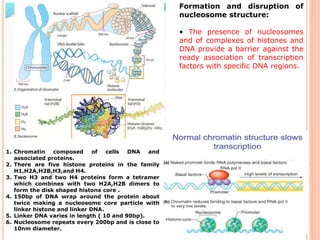
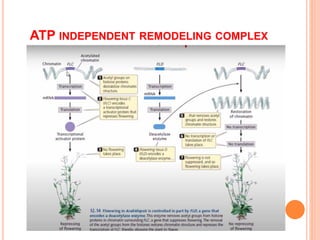
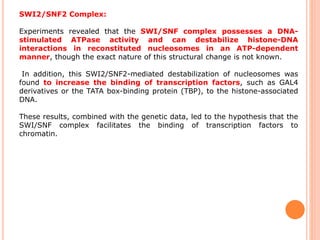
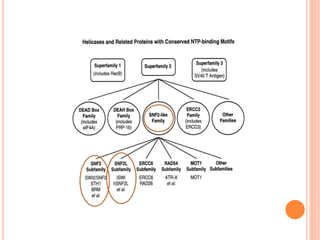
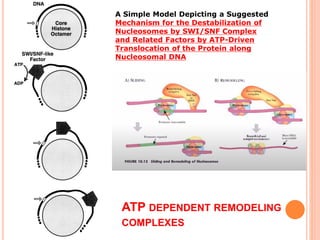
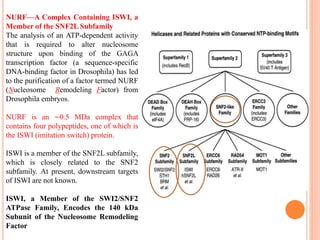
1. Chromatin remodeling complexes use ATP hydrolysis to modify nucleosome structure and expose DNA for gene expression. The main classes are ATP-independent complexes and ATP-dependent complexes like ISWI and SWI/SNF.
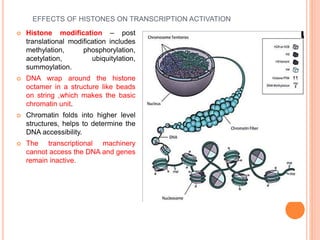
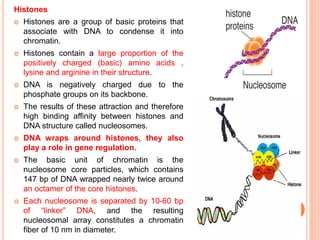
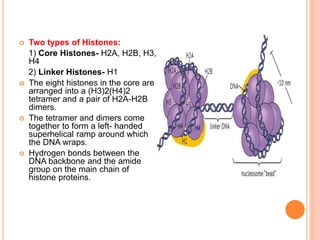
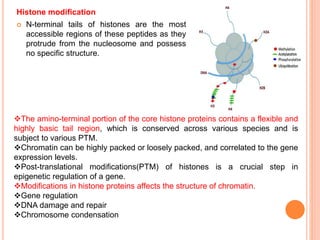
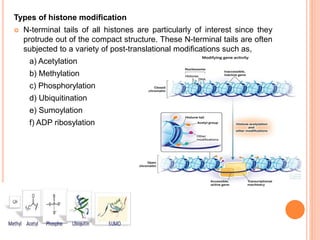
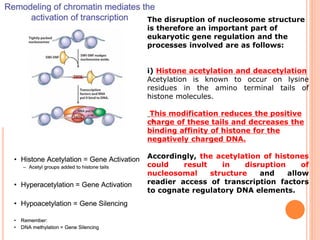
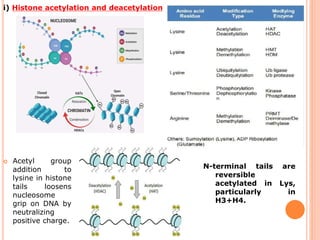
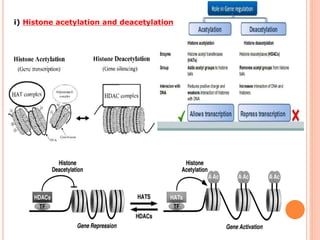
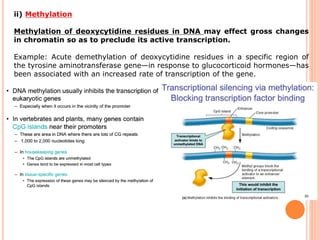
2. Post-translational modifications of histone tails like acetylation, methylation, and phosphorylation can affect chromatin structure and transcription by altering DNA-histone interactions.
3. Chromatin remodeling is important for differential gene expression in specialized cell types and controlling DNA accessibility for transcription.