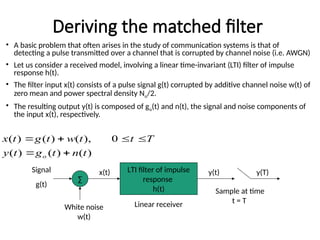
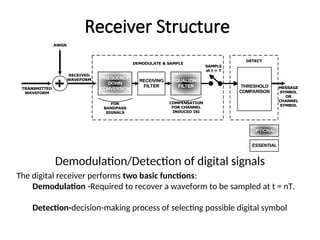
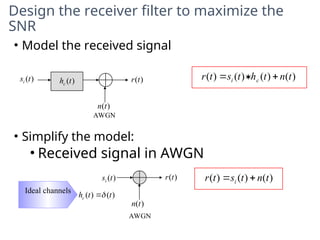
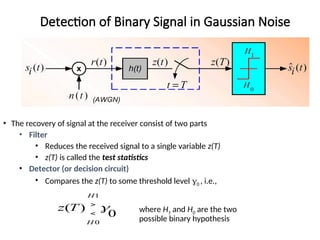
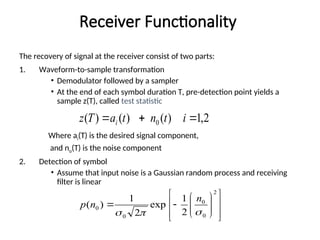
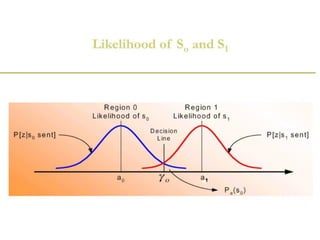
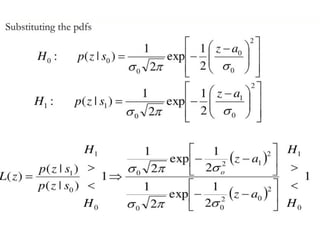
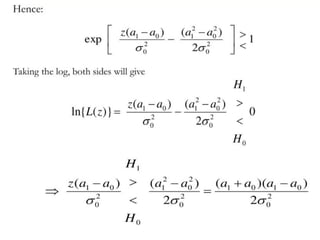
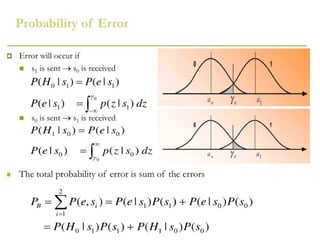
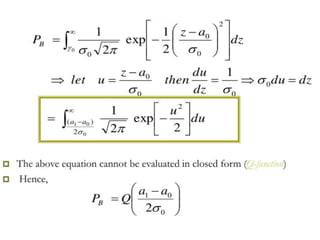
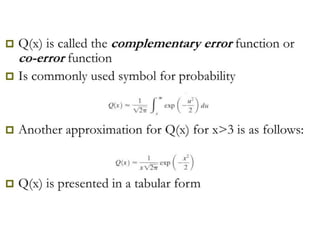
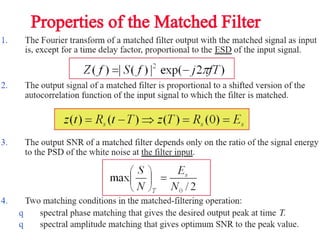
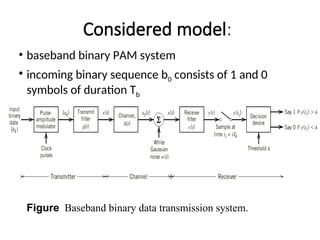
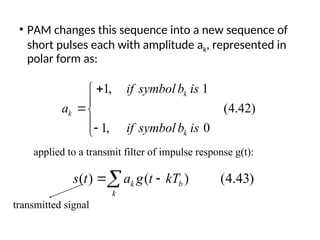
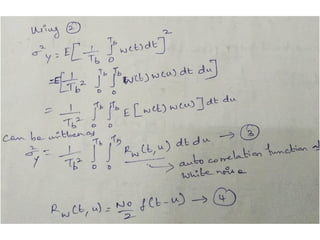
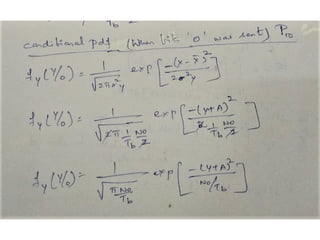
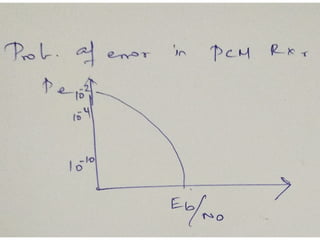
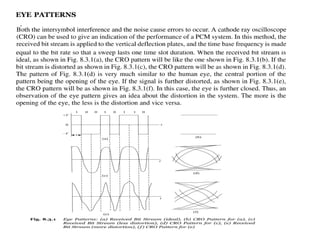
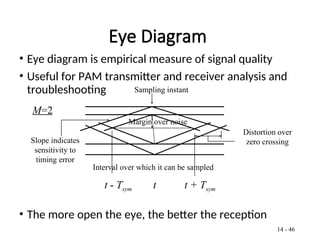
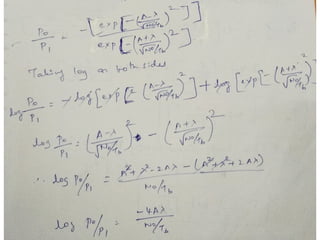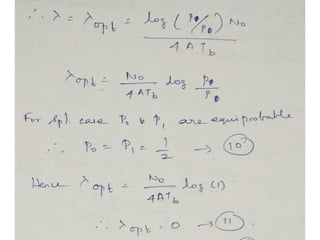A matched filter is utilized in communication systems to maximize the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) while minimizing undetected errors by allowing signal frequencies to pass and suppressing noise. The document details the derivation and structure of matched filters, including their application in detecting pulses over a noisy channel, as well as concepts like PAM and its effects on inter-symbol interference. Key components of a digital receiver's functionality including demodulation and detection of binary signals in Gaussian noise are also discussed.