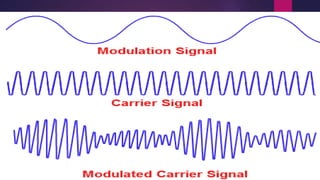
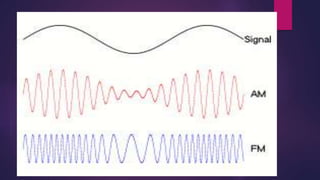
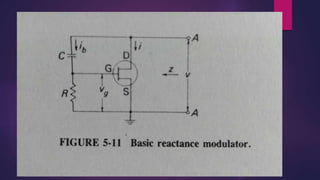
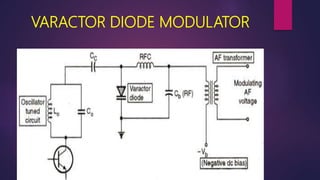
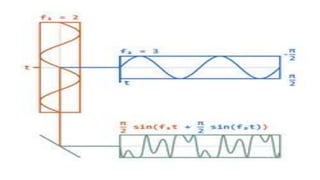
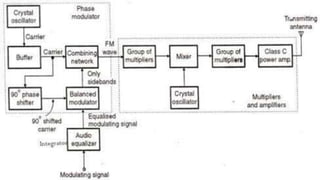
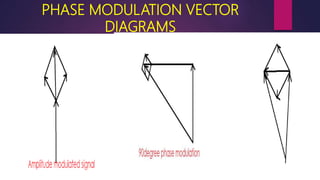
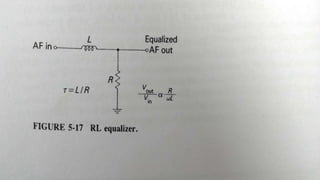
This document discusses the generation of frequency modulation (FM) using direct and indirect methods. The direct method uses a reactance modulator like a varactor diode or FET placed across an LC oscillator tank circuit to vary the capacitance or inductance in proportion to the modulating voltage. The indirect method generates FM through phase modulation using a crystal oscillator and phase modulator, then detecting the phase changes to create FM. Vector diagrams are also presented to illustrate phase modulation. Effects of frequency changing like multiplication and mixing on FM signals are explained.