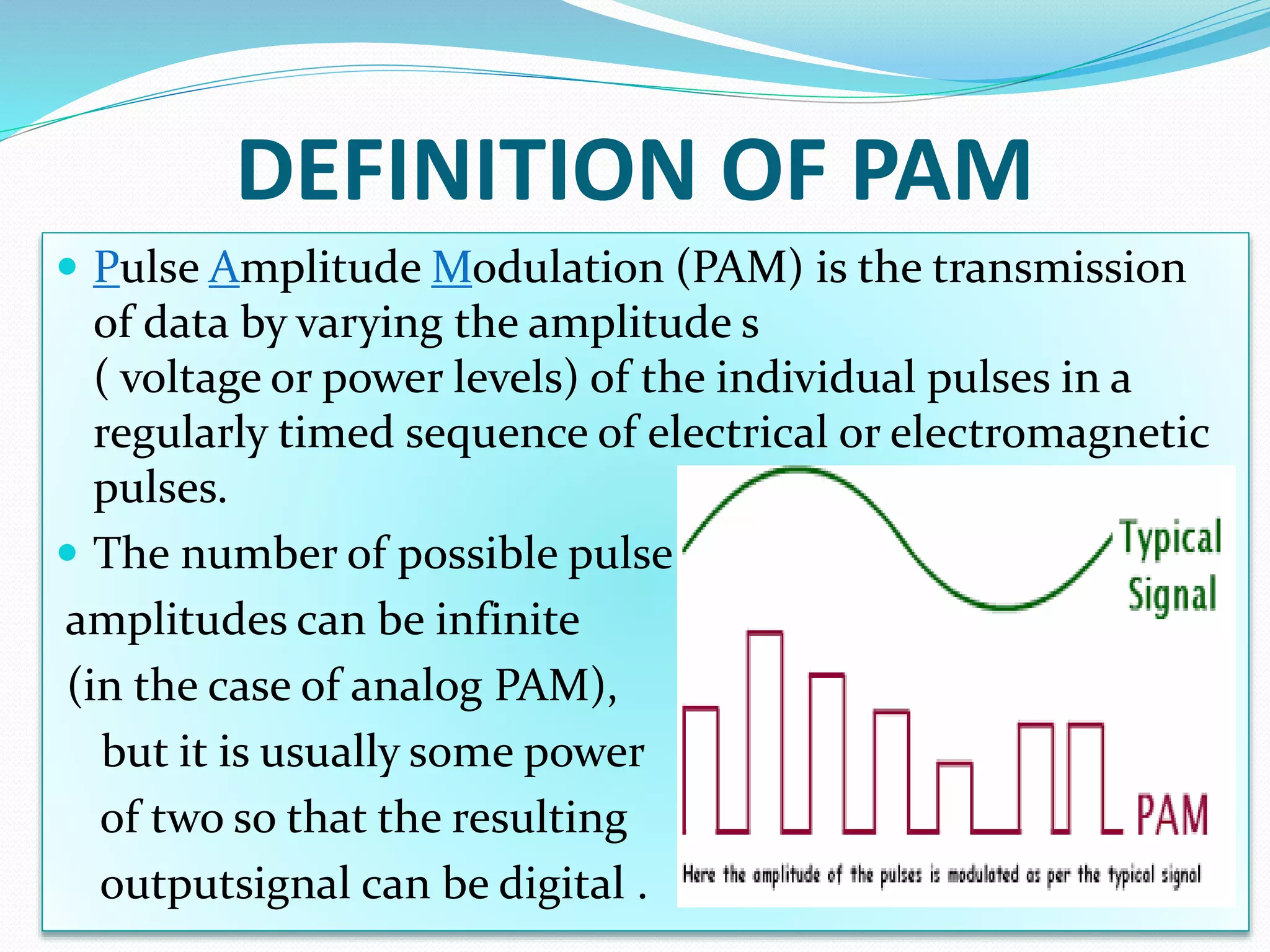
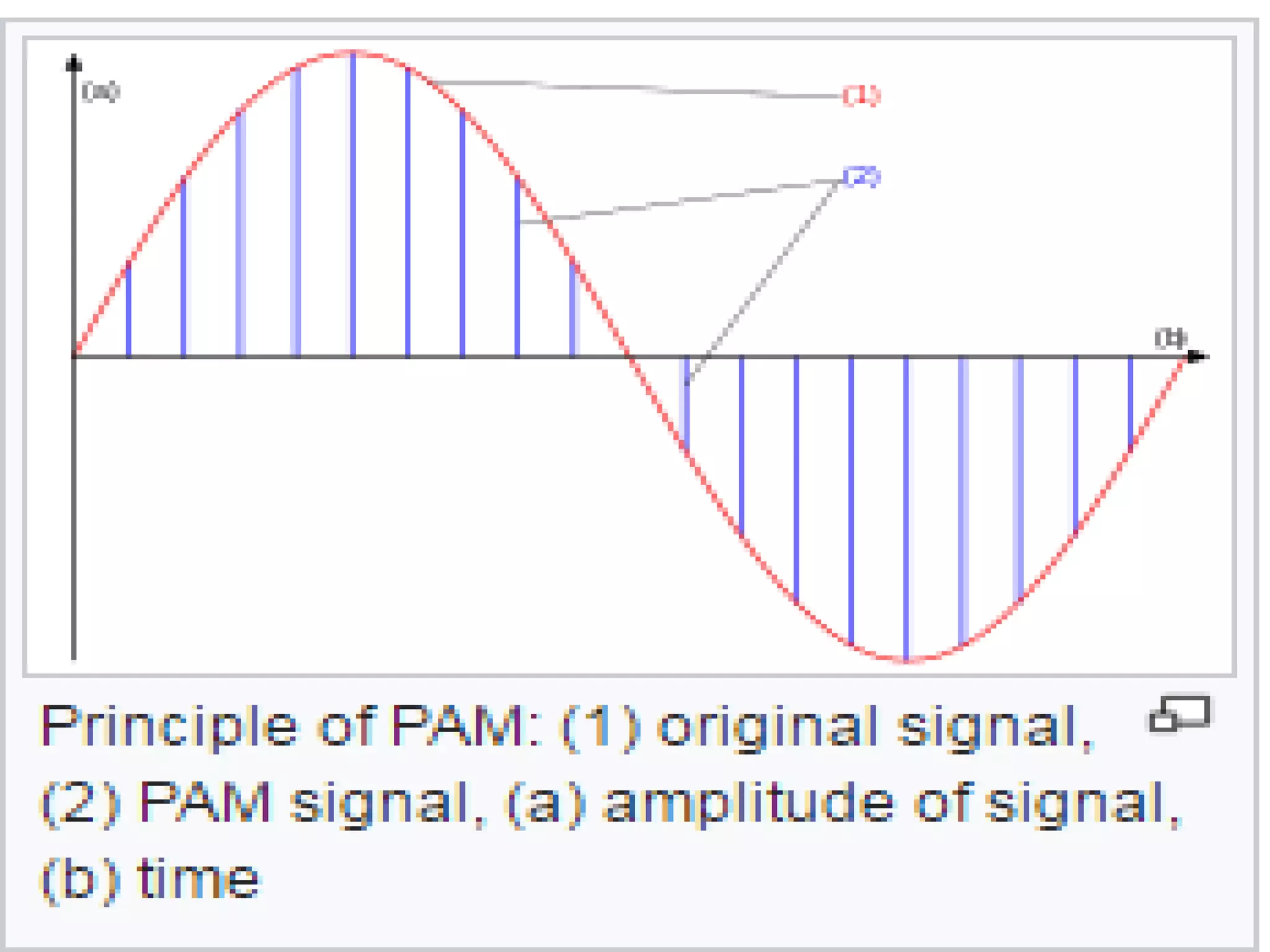
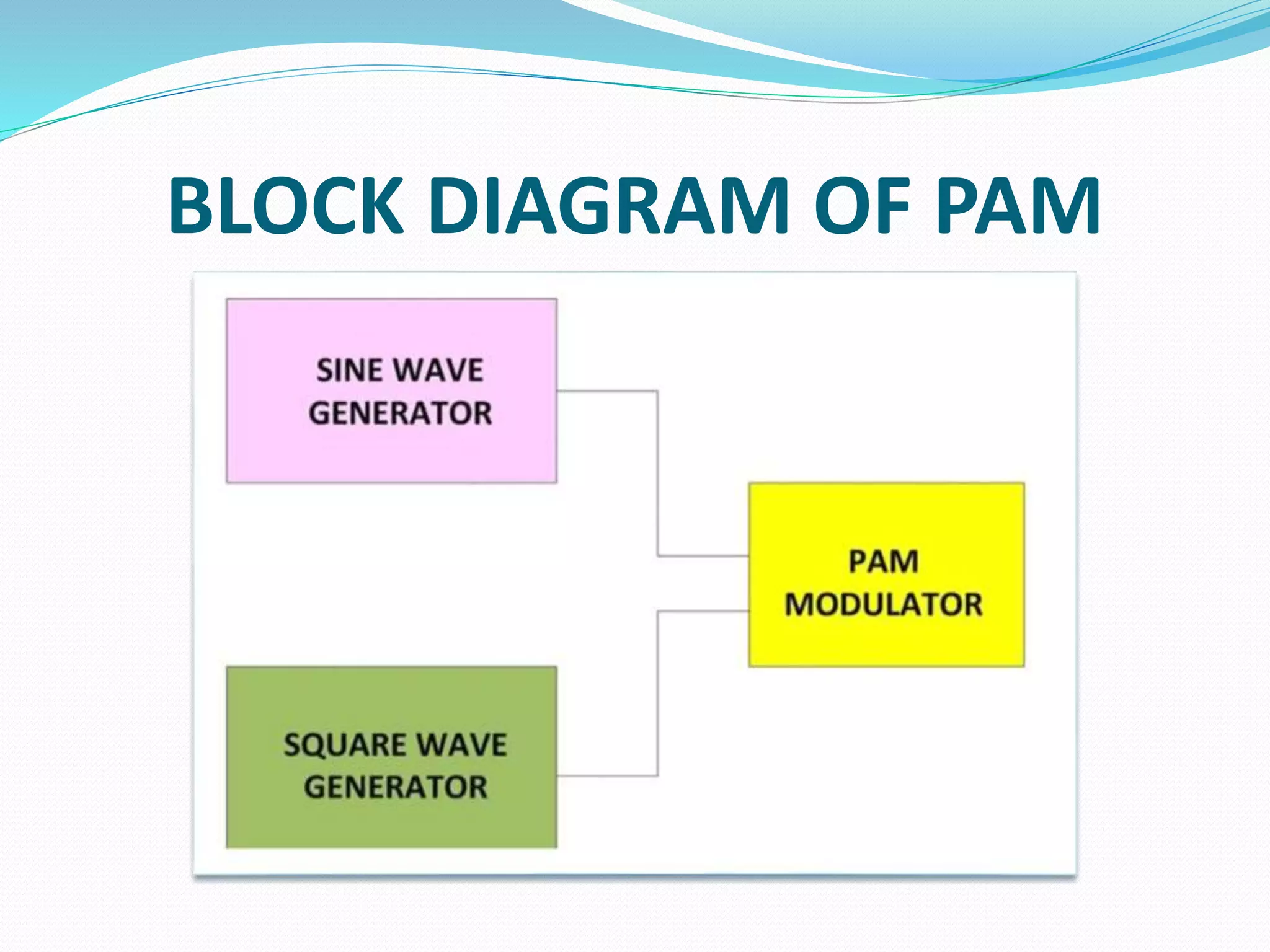
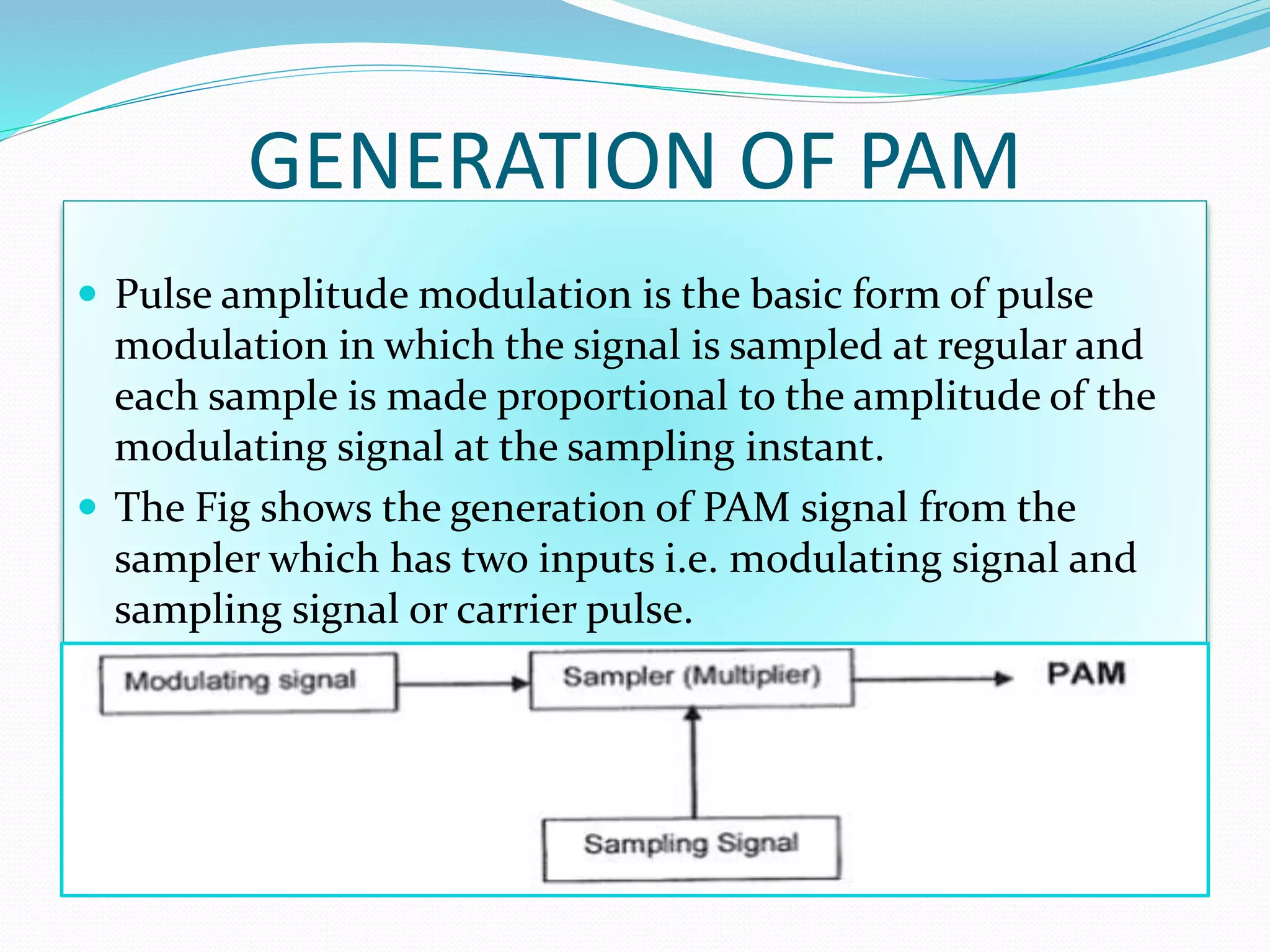
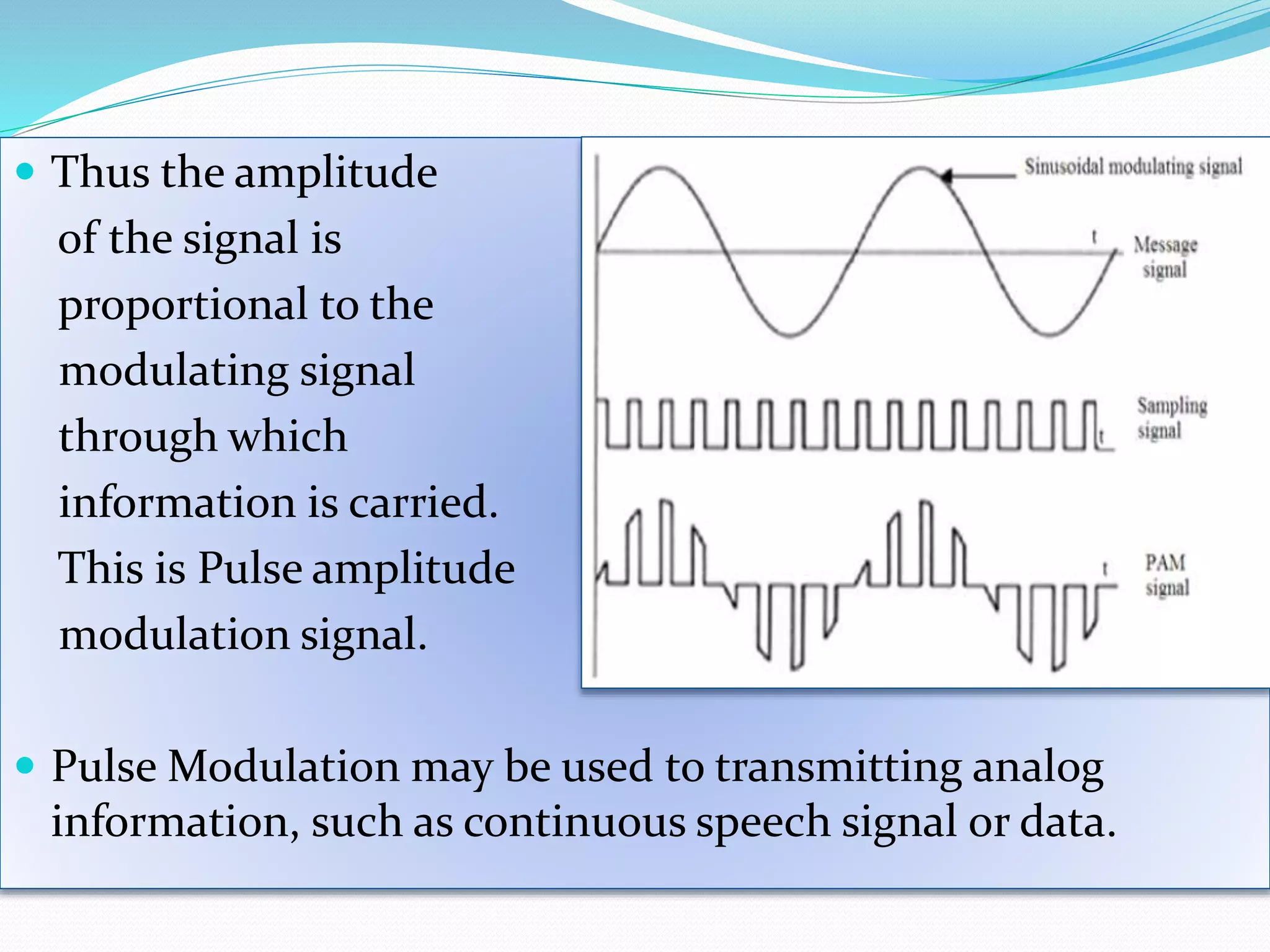
Pulse amplitude modulation (PAM) is a modulation technique where the amplitude of pulses in a regularly timed sequence is varied according to the amplitude of the modulating signal. There are two types of PAM: single polarity PAM which adds a DC bias to ensure all pulses are positive, and double polarity PAM where pulses can be both positive and negative. PAM is generated by sampling the modulating signal at regular intervals and making each sample proportional to the amplitude of the modulating signal at the time of sampling. The amplitude of the PAM signal then carries the information contained in the modulating signal.