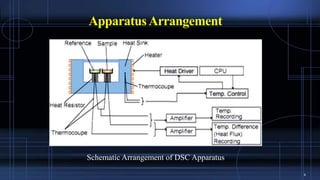
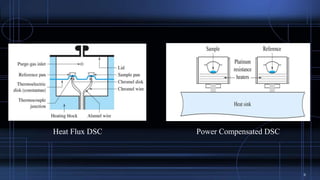
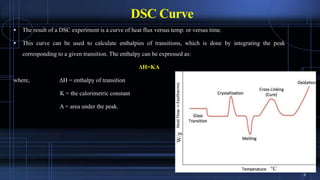
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) measures the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference. During a DSC analysis, a sample and an empty reference pan are heated at a controlled rate while measuring the heat flow into each. Changes in heat flow indicate thermal transitions like melting or crystallization. DSC provides quantitative and qualitative data on endothermic and exothermic processes, including transition temperatures and enthalpies. The technique is widely used to characterize polymers, pharmaceuticals, and other materials.