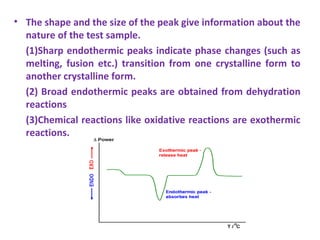
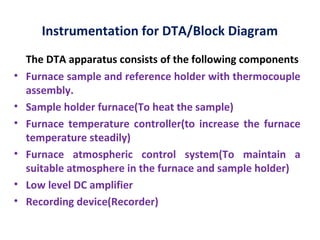
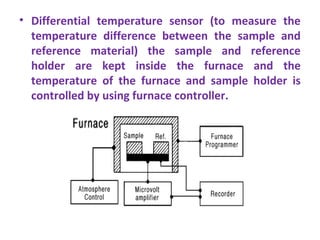
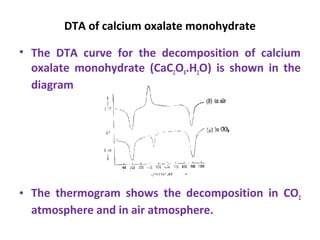
Differential thermal analysis (DTA) measures the temperature difference between a sample and an inert reference material as both are subjected to identical temperature programs in a controlled atmosphere. During endothermic or exothermic transitions in the sample, such as melting or chemical reactions, a temperature difference is recorded. The shape and size of peaks in the DTA curve provide information about the nature of the sample and the type of transition, such as phase changes or dehydration. DTA is used to study materials like polymers and drugs, determine heat of reactions, and test purity and quality of substances including cements, soils, and glasses.