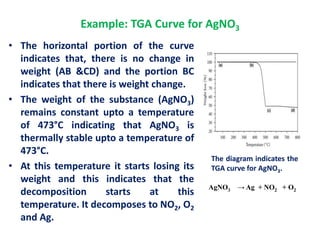
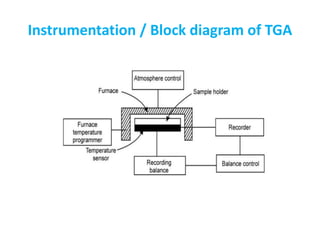
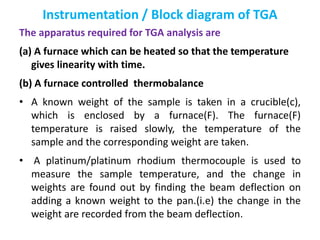
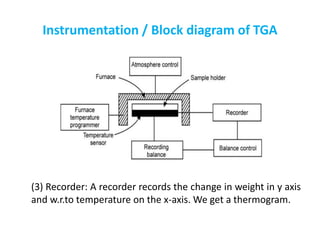
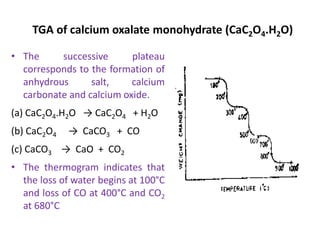
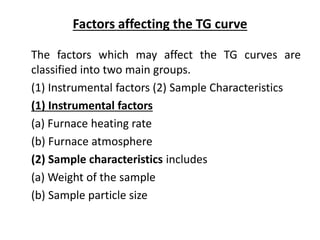
The document discusses thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), a technique where the weight of a substance is recorded as a function of temperature or time as it is heated. In TGA, a sample is heated at a constant rate in a controlled environment while changes in weight are measured and plotted as a thermogram. An example TGA curve is provided for silver nitrate, showing stages of decomposition. The key components of a TGA instrument are described, including a furnace, thermobalance, and recorder. Factors affecting TGA curves like heating rate and sample characteristics are also outlined. Applications of TGA include determining purity and thermal stability.