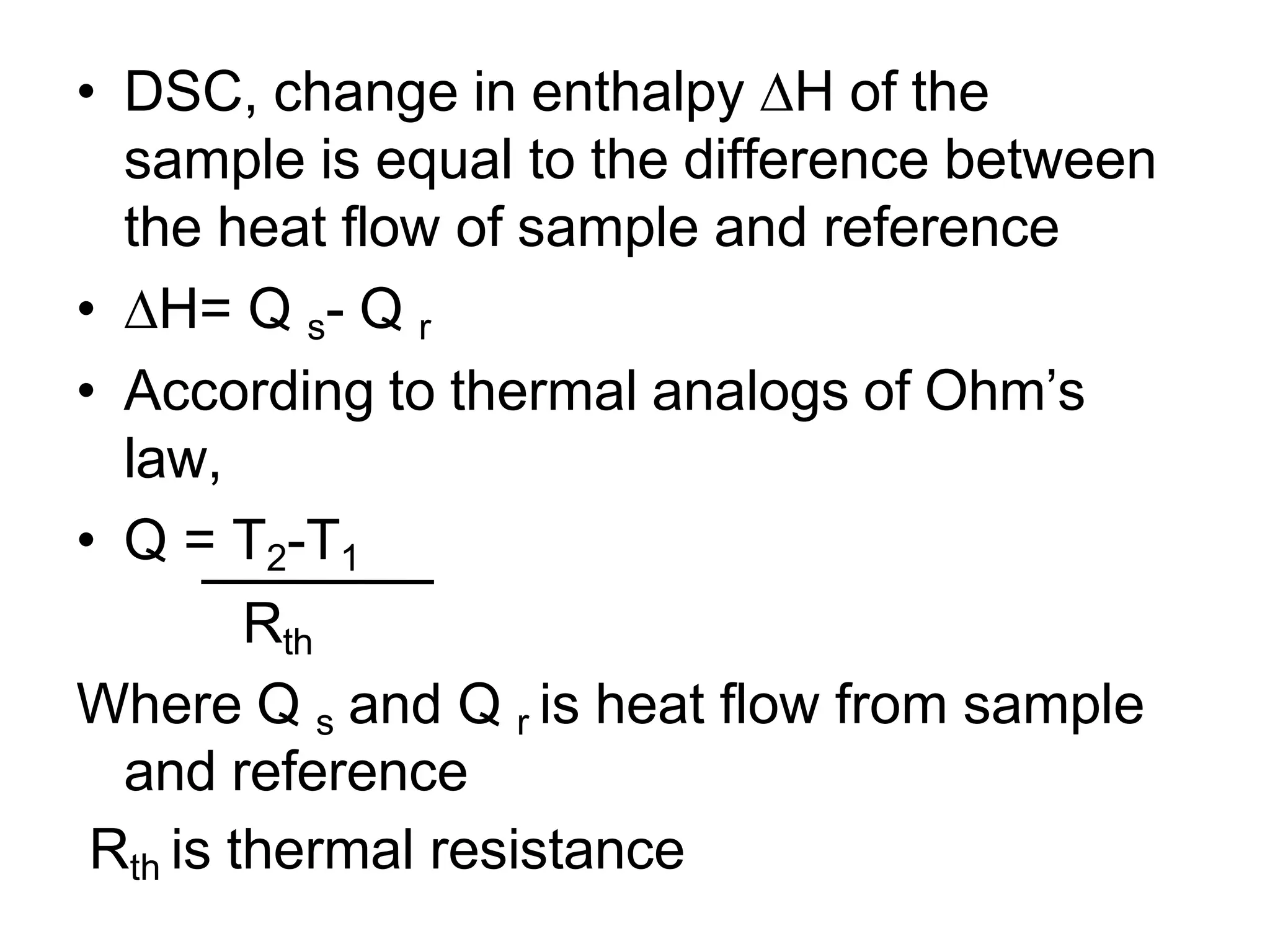
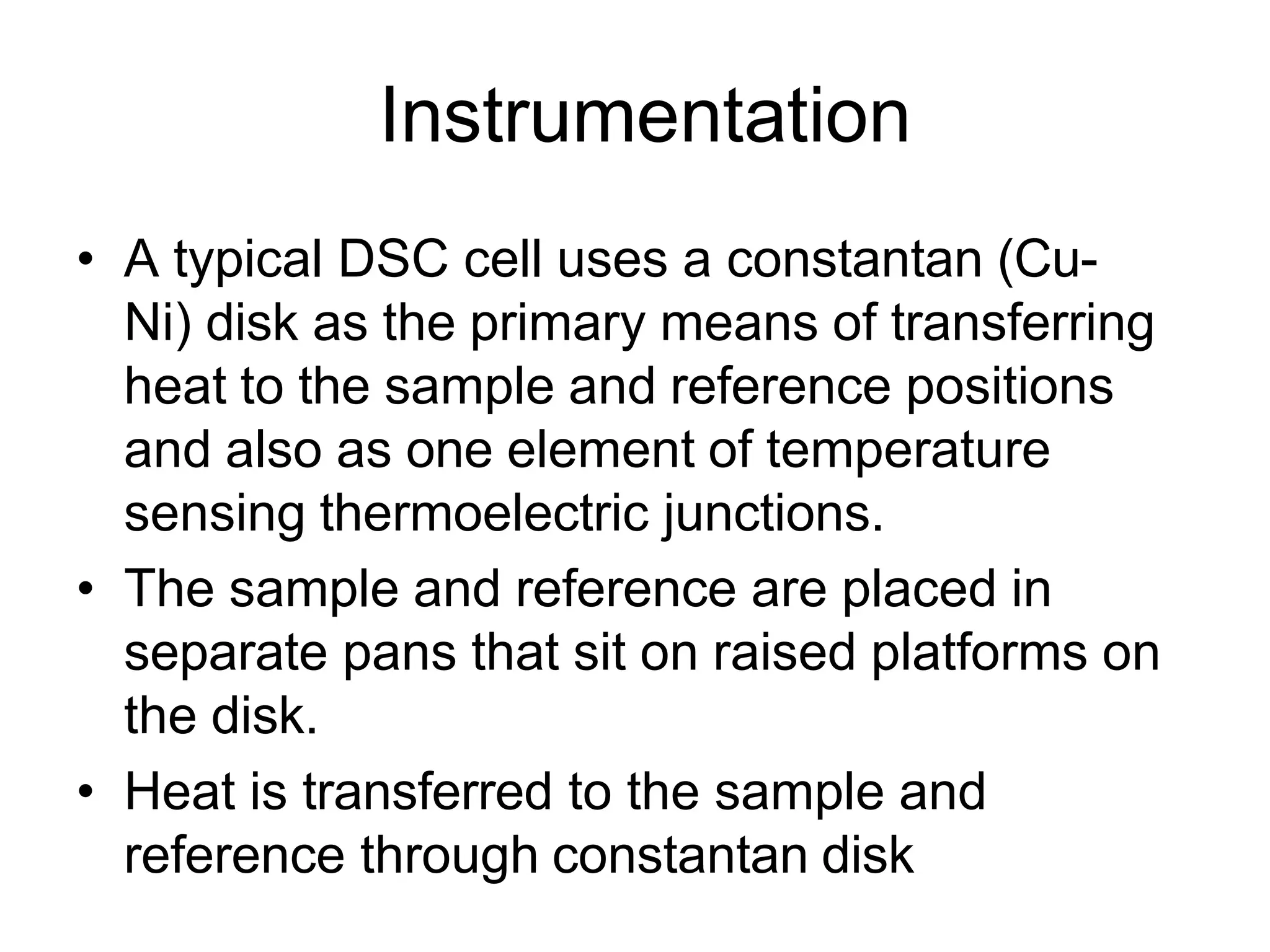
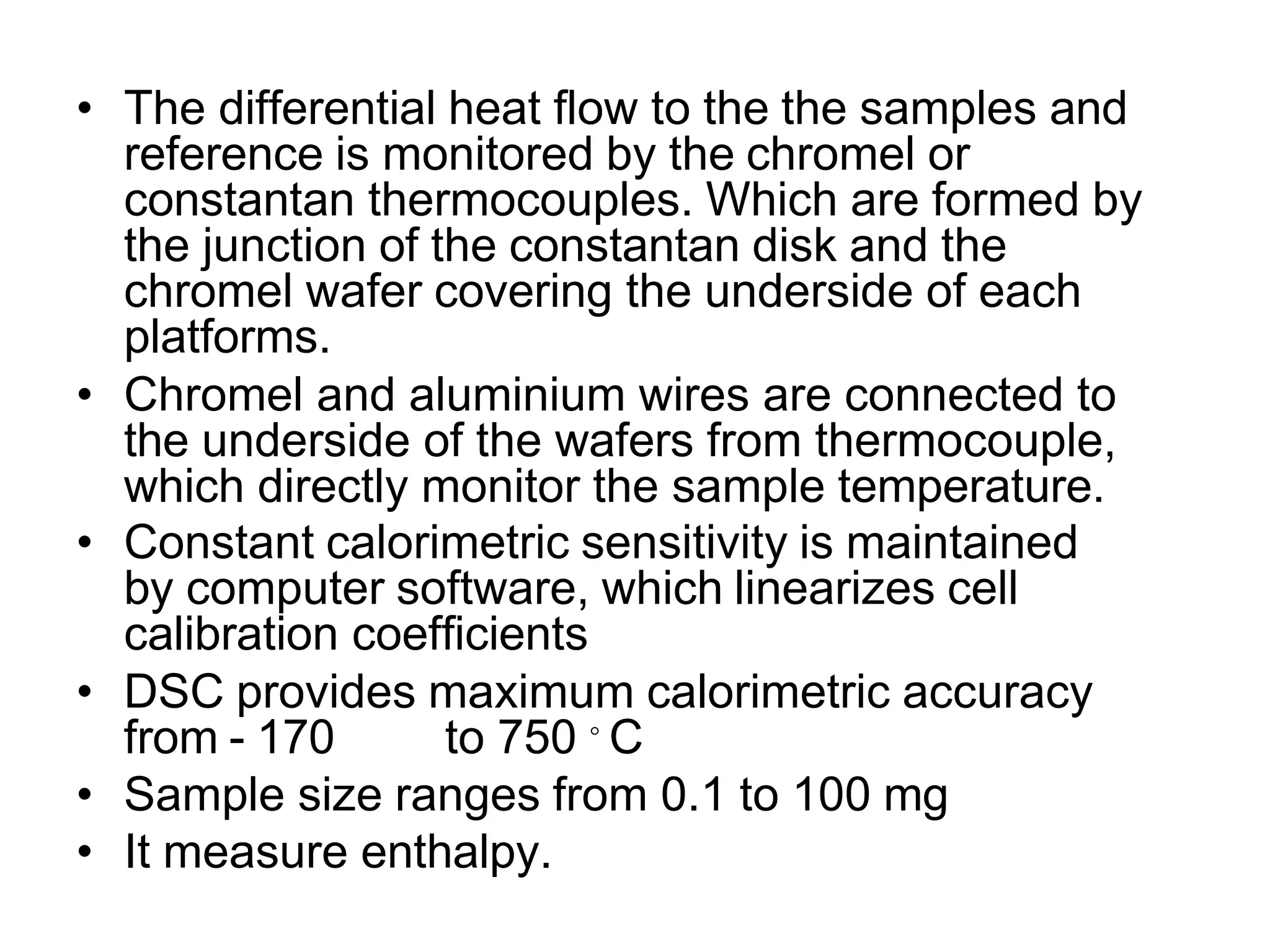
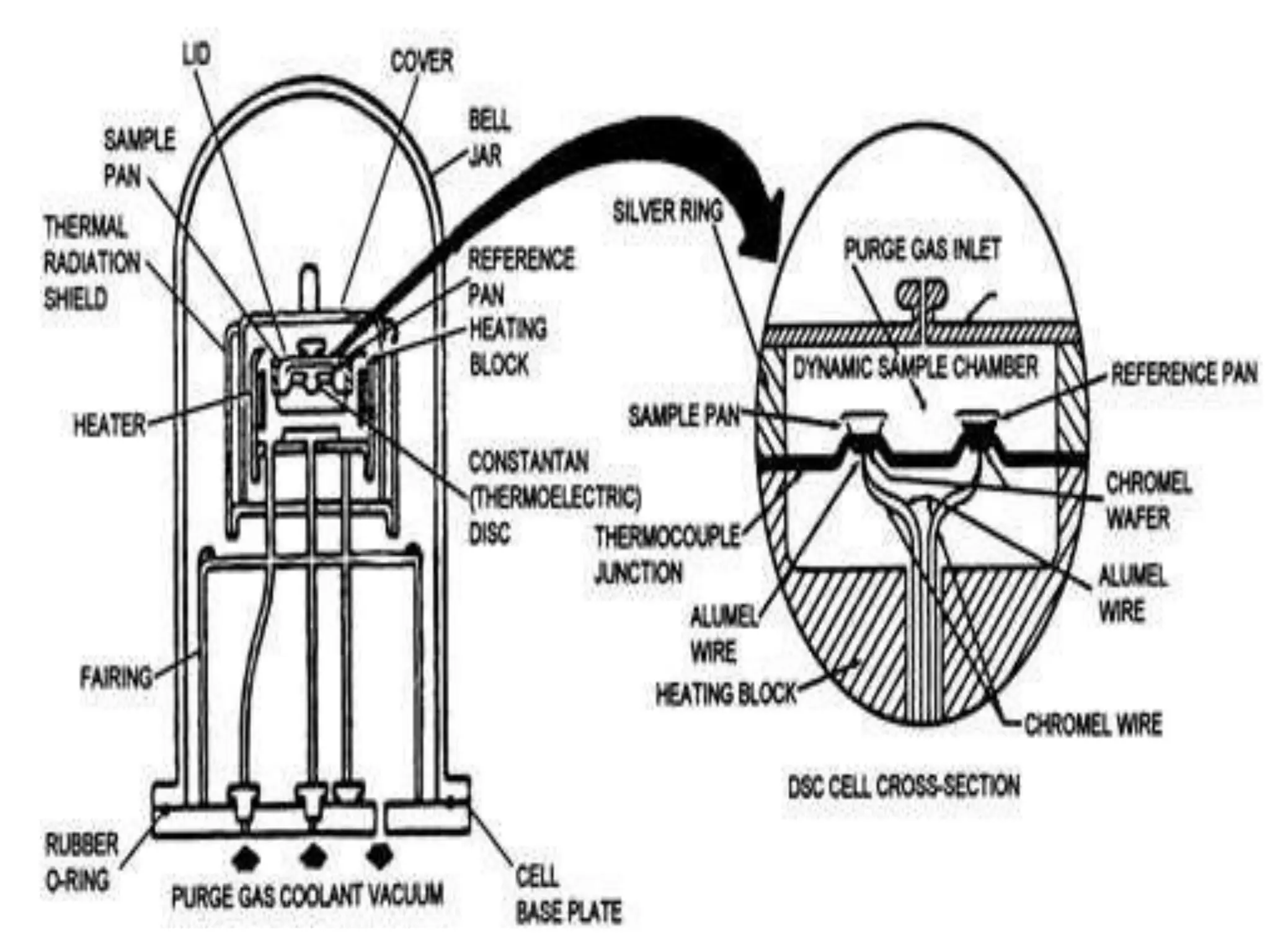
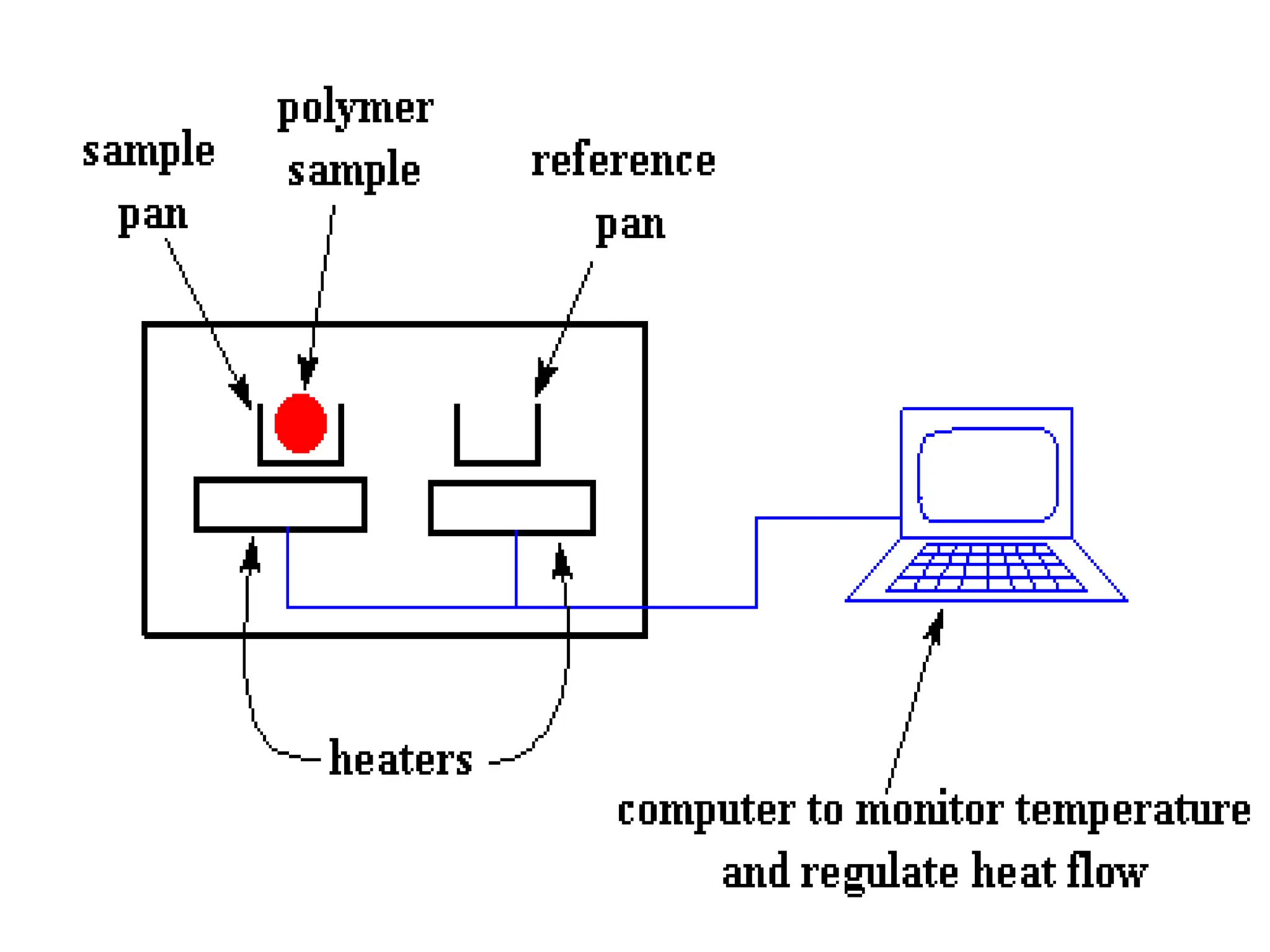
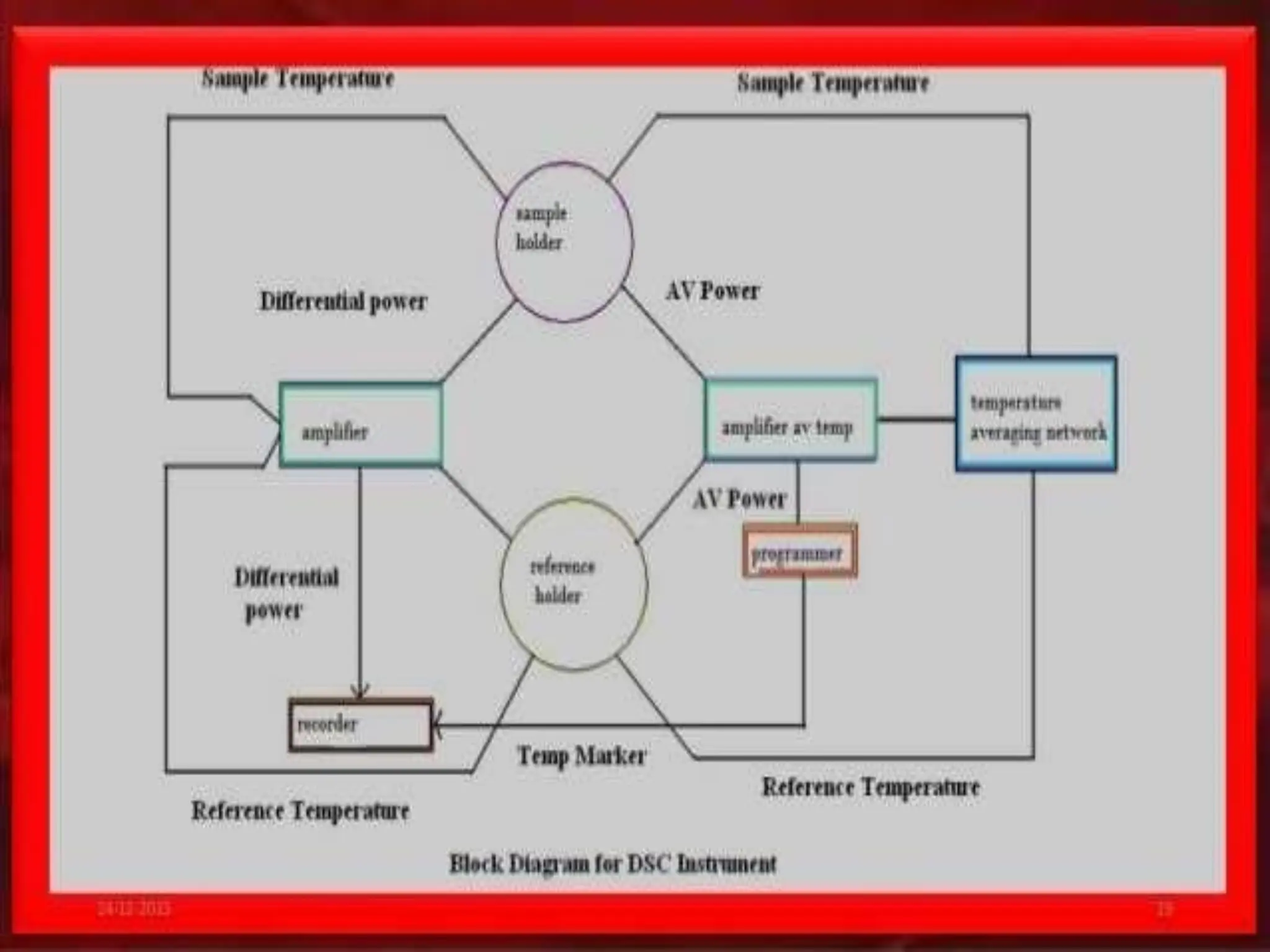
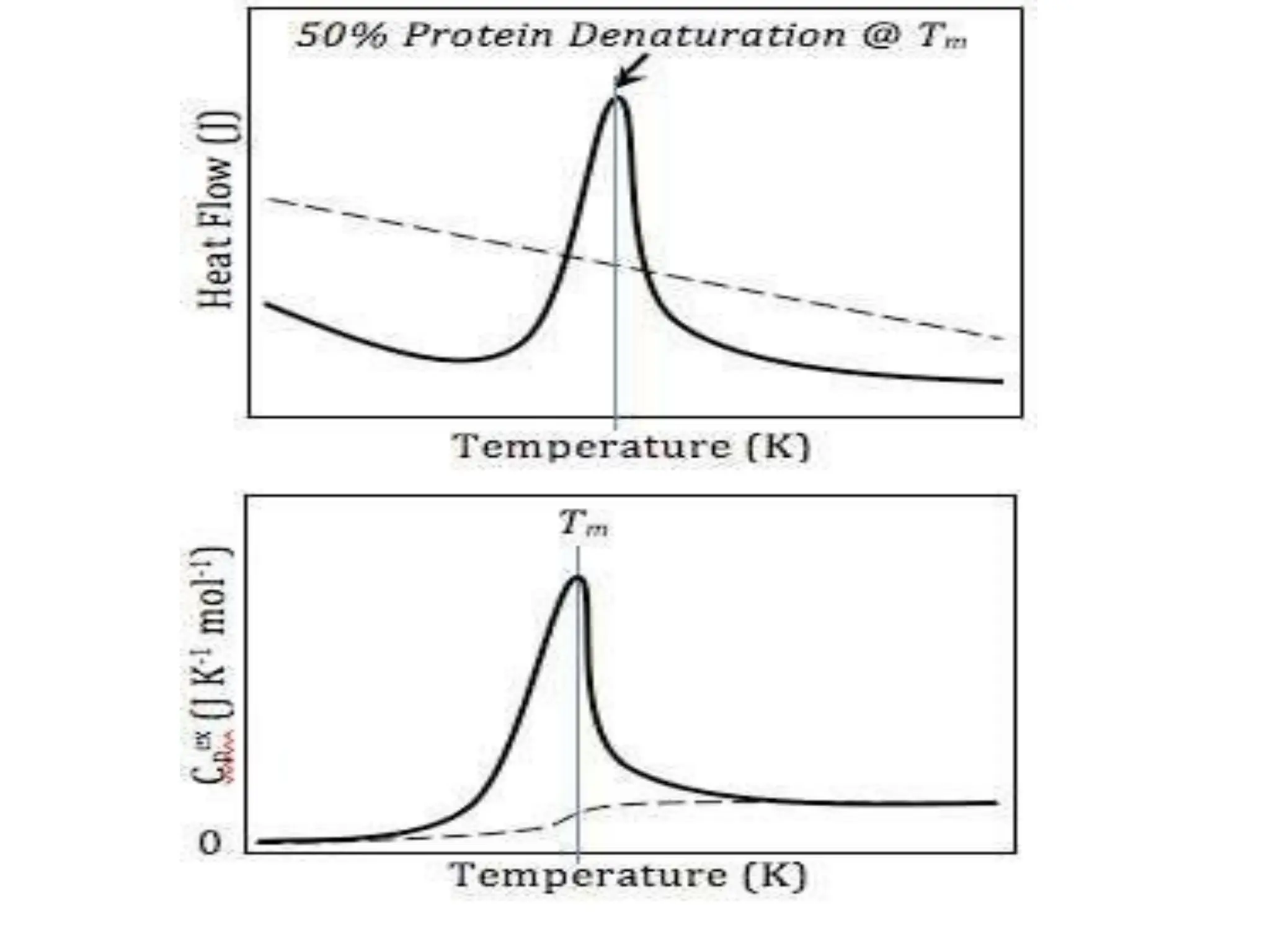
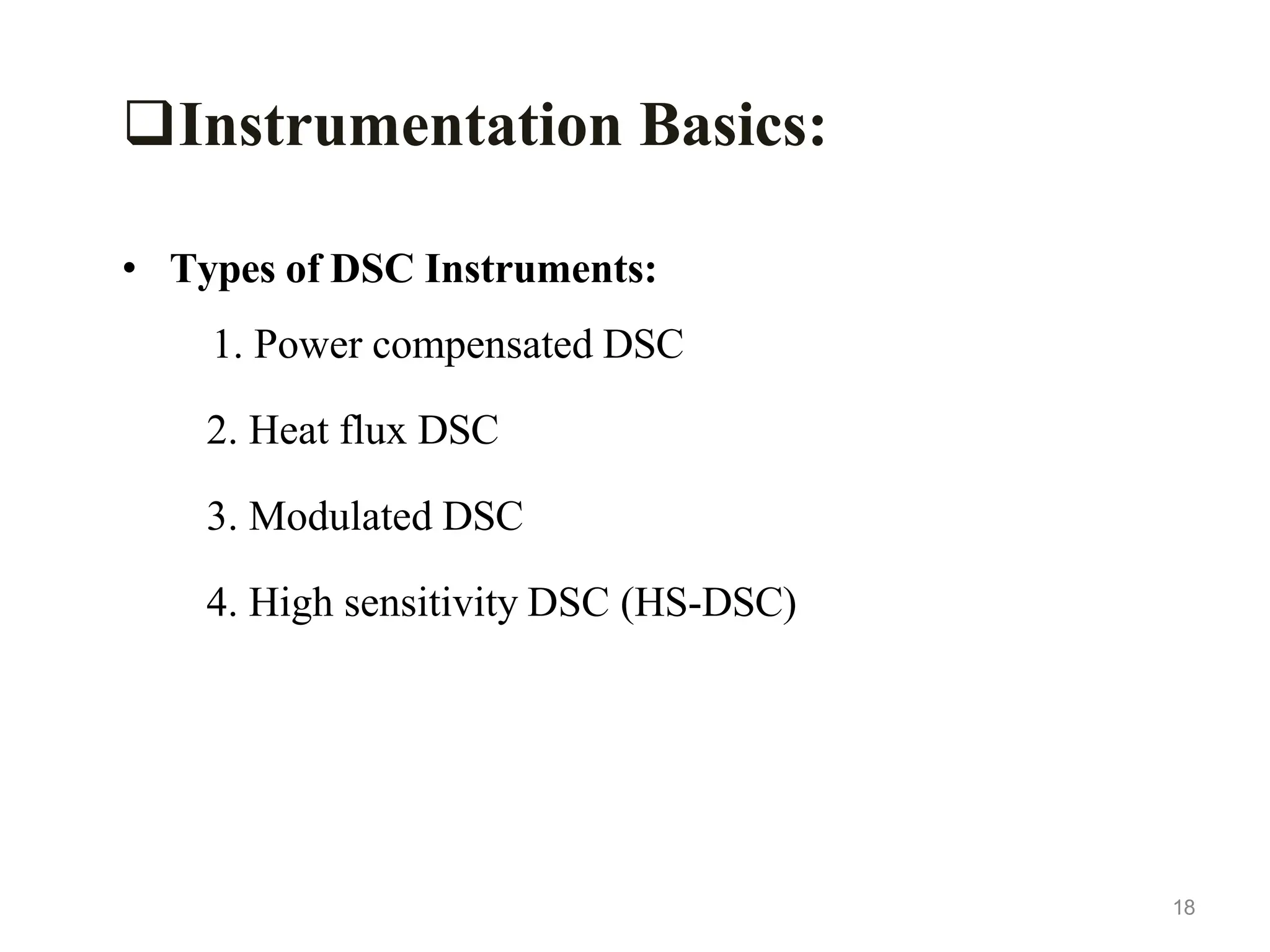
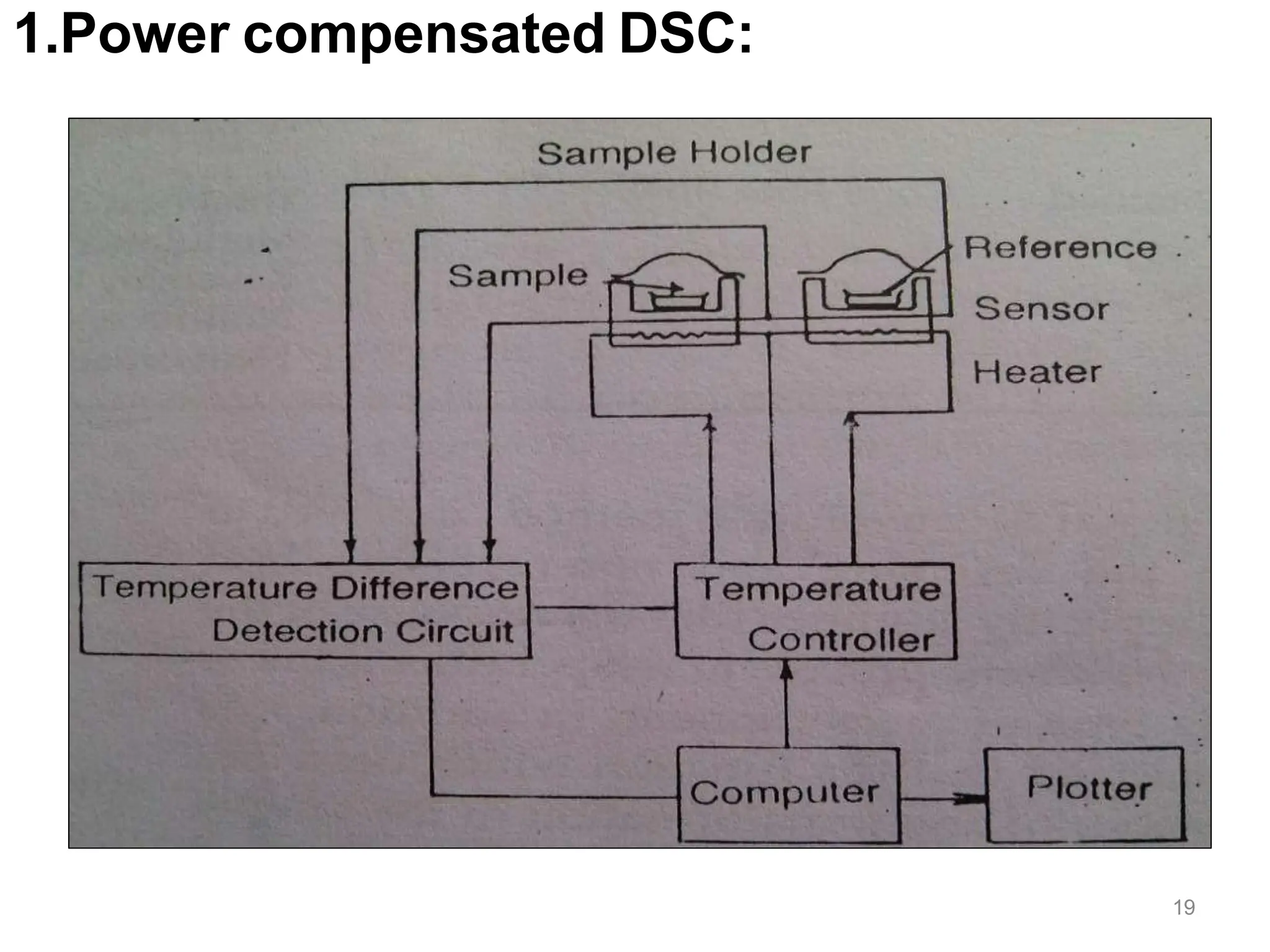
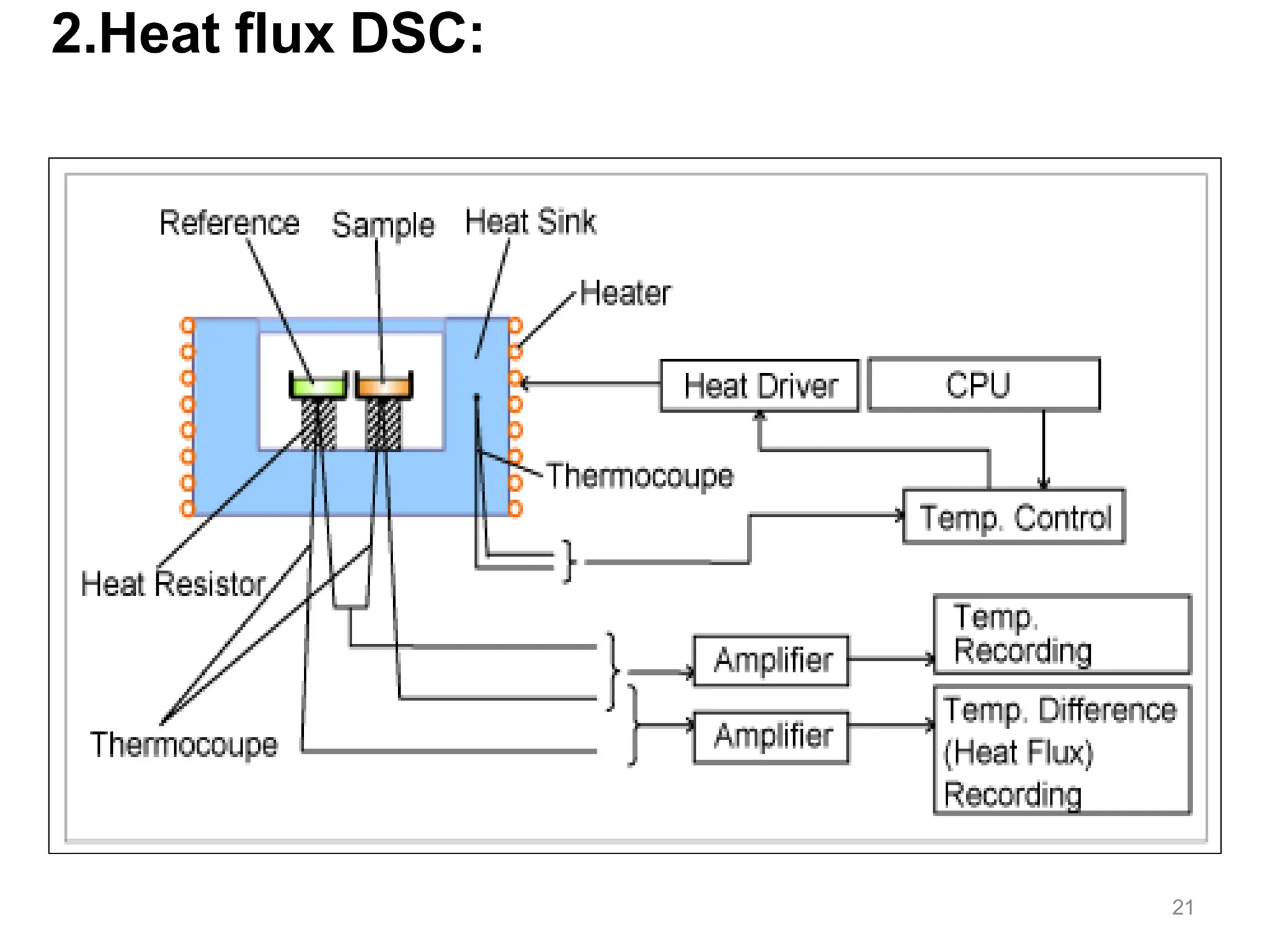
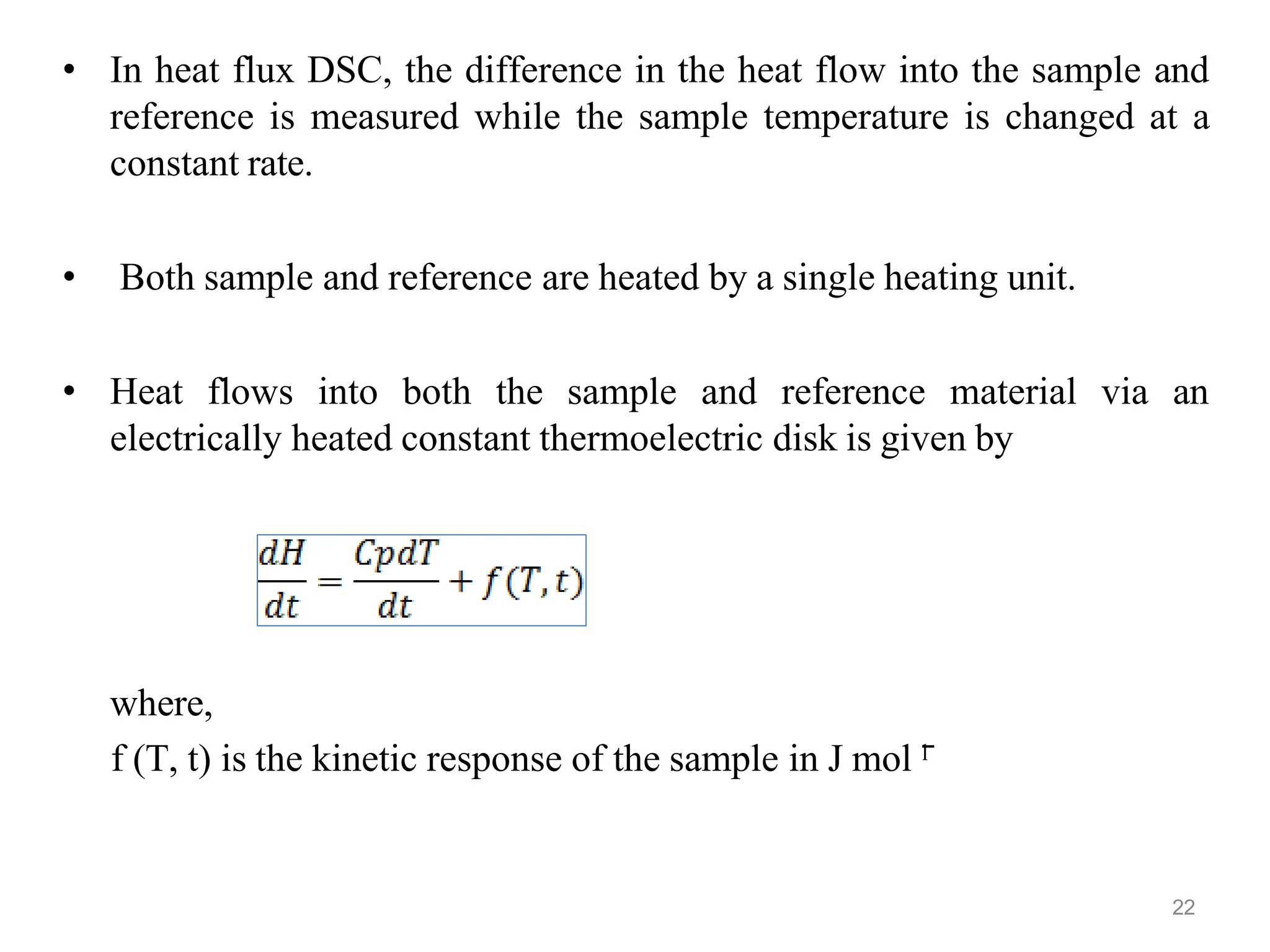
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) is a thermal analysis technique that measures the heat flow into or out of a sample as it is heated, cooled, or held at constant temperature. DSC can be used to analyze physical and chemical changes that involve endothermic or exothermic processes, such as phase transitions, crystallization, melting, and curing. DSC provides quantitative and qualitative material characterization by measuring the heat flow and temperature differences between a sample and an inert reference sample as they undergo temperature changes. The heat flow is directly related to transitions in materials and can be used to determine transition temperatures and associated enthalpies.