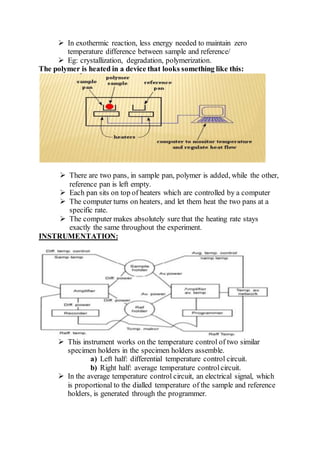
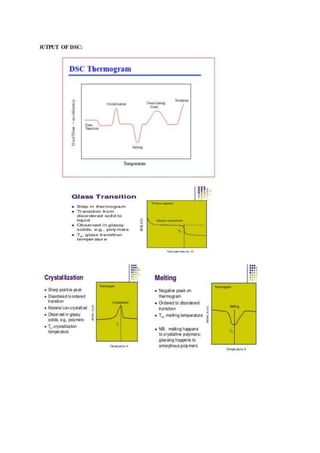
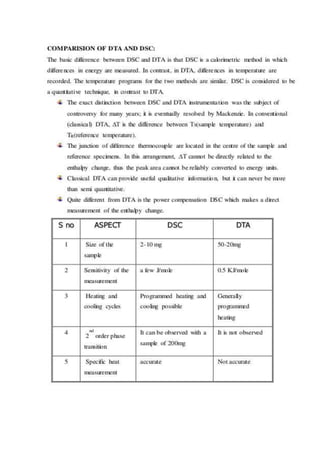
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) is a thermoanalytical technique used to measure heat flow differences between a sample and a reference as both are heated. DSC provides quantitative and qualitative data on material transitions, determining properties such as crystallinity, purity, and thermal stability. The technique involves precise temperature control and is applicable to various sample types while utilizing inert gases to prevent reactions with the environment.