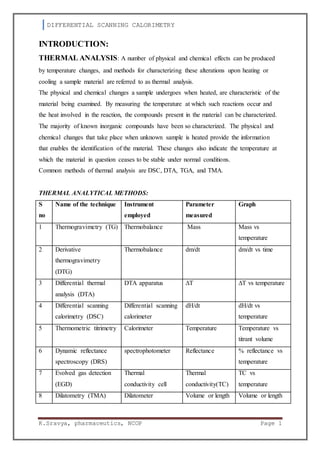
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) is a thermal analysis technique that measures the heat flow into or out of a sample as it is heated, cooled, or held at constant temperature. DSC directly measures the energy required to establish a zero temperature difference between a sample and an inert reference material as both are subjected to an identical temperature program. This allows the determination of transition temperatures such as melting points and glass transition temperatures. DSC is commonly used in pharmaceutical analysis to characterize materials such as purity determination, polymorphism detection, and stability studies. The basic components of a DSC instrument include sample and reference pans, a furnace to heat the pans at a controlled rate, and sensors to measure the heat flow difference between