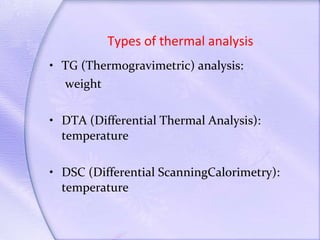
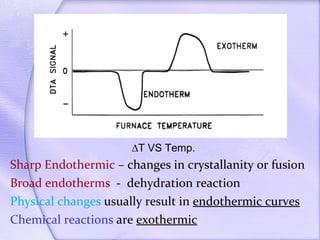
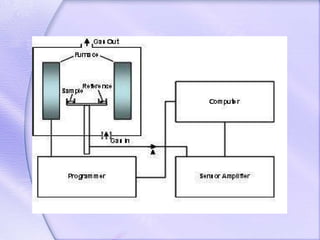
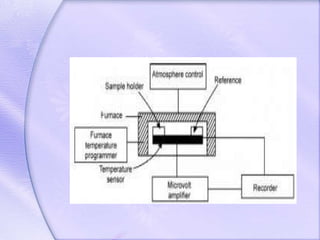
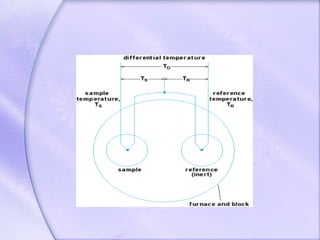
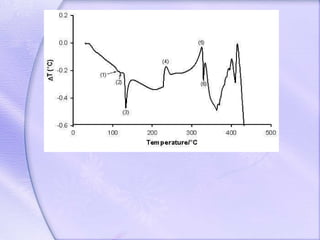
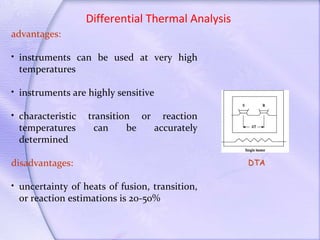
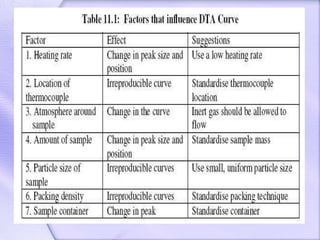
Differential thermal analysis (DTA) is a thermal analysis technique that measures the temperature difference between a sample and an inert reference material as they are heated or cooled. DTA can detect physical or chemical changes in a sample as they occur, such as fusion, crystallization, oxidation, or decomposition. Changes are detected based on the temperature difference that develops between the sample and reference material. DTA provides a characteristic "fingerprint" curve for a sample that can be used to identify materials. Common applications of DTA include quantitative identification and purity assessment of materials.
![DIFFERENTIAL THERMAL ANALYSIS (DTA) Presented By Mr. Shaise Jacob Faculty Dept. of Pharmaceutical Analysis Nirmala College of Pharmacy Muvattupuzha, Kerala India E mail - [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dtafinal-111115231835-phpapp01/75/DIFFERENTIAL-THERMAL-ANALYSIS-DTA-ppt-1-2048.jpg)