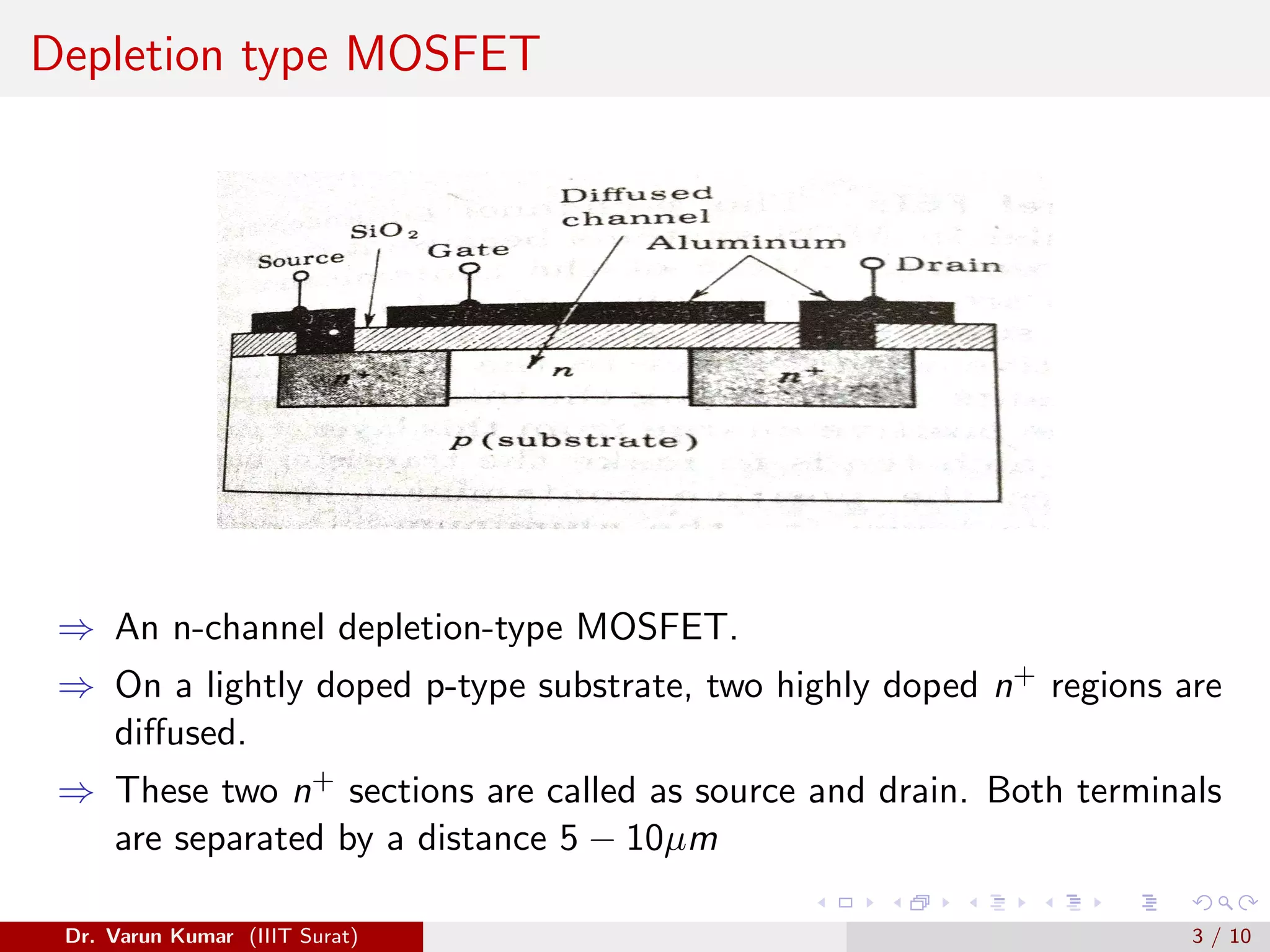
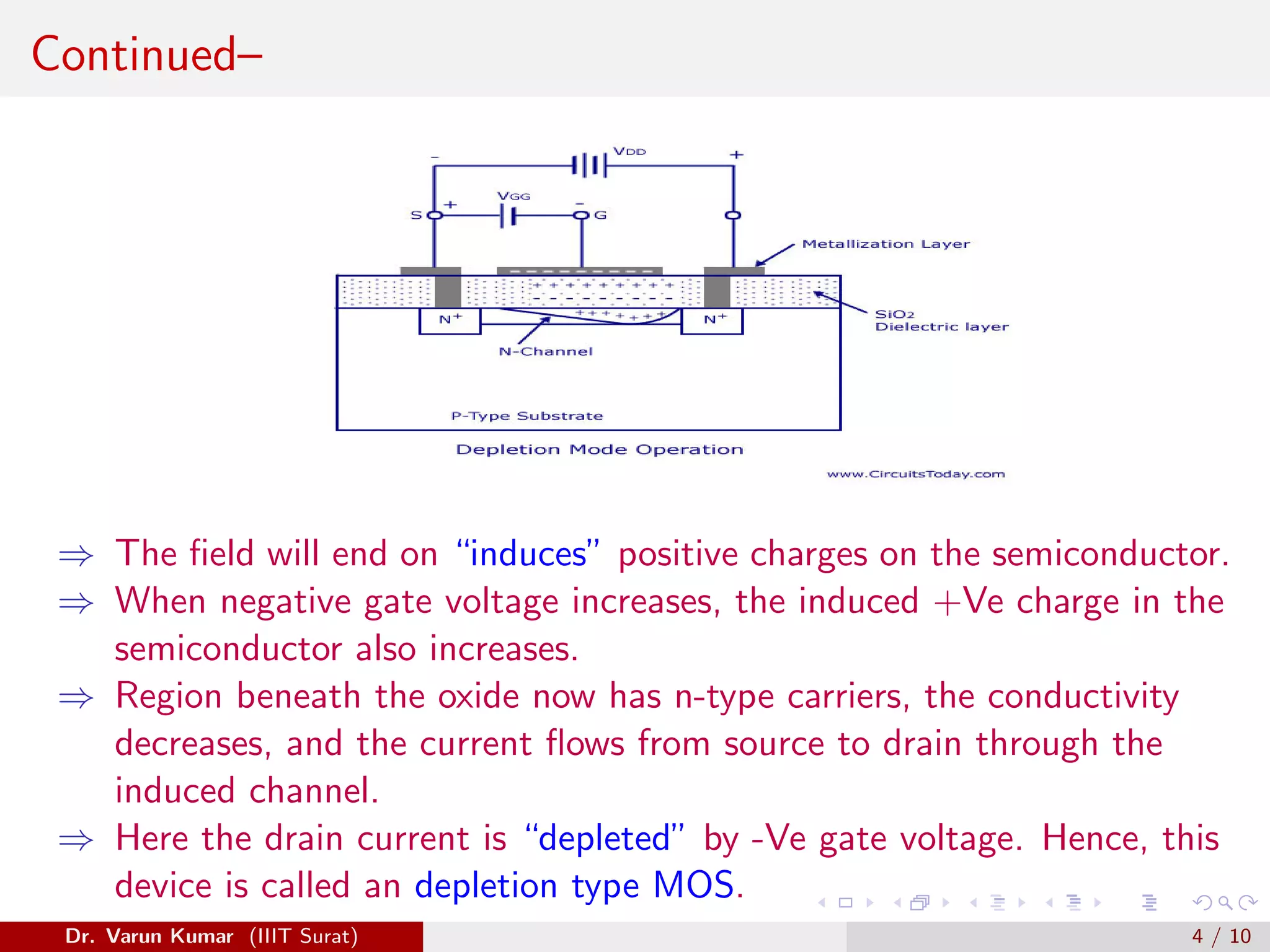
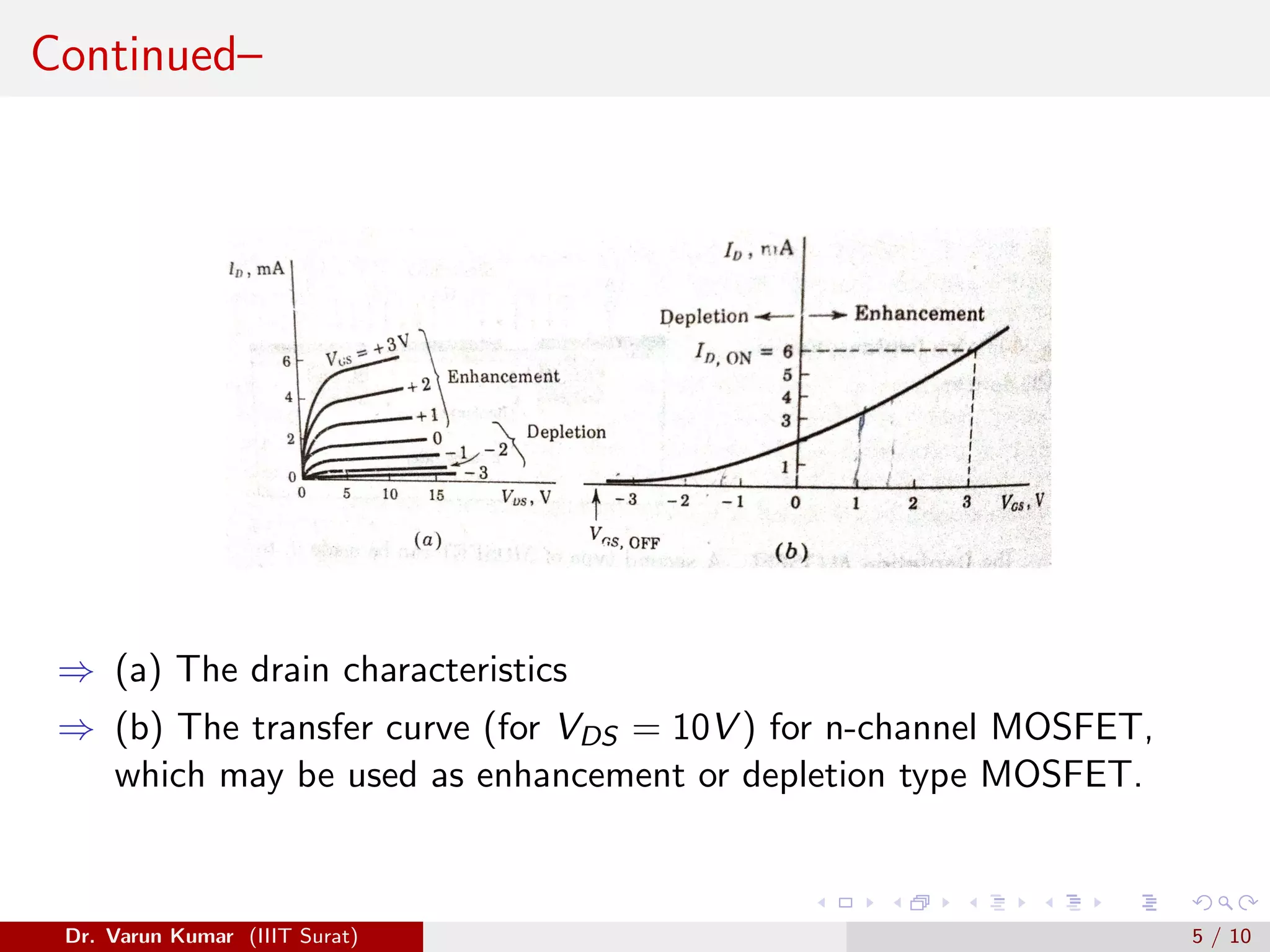
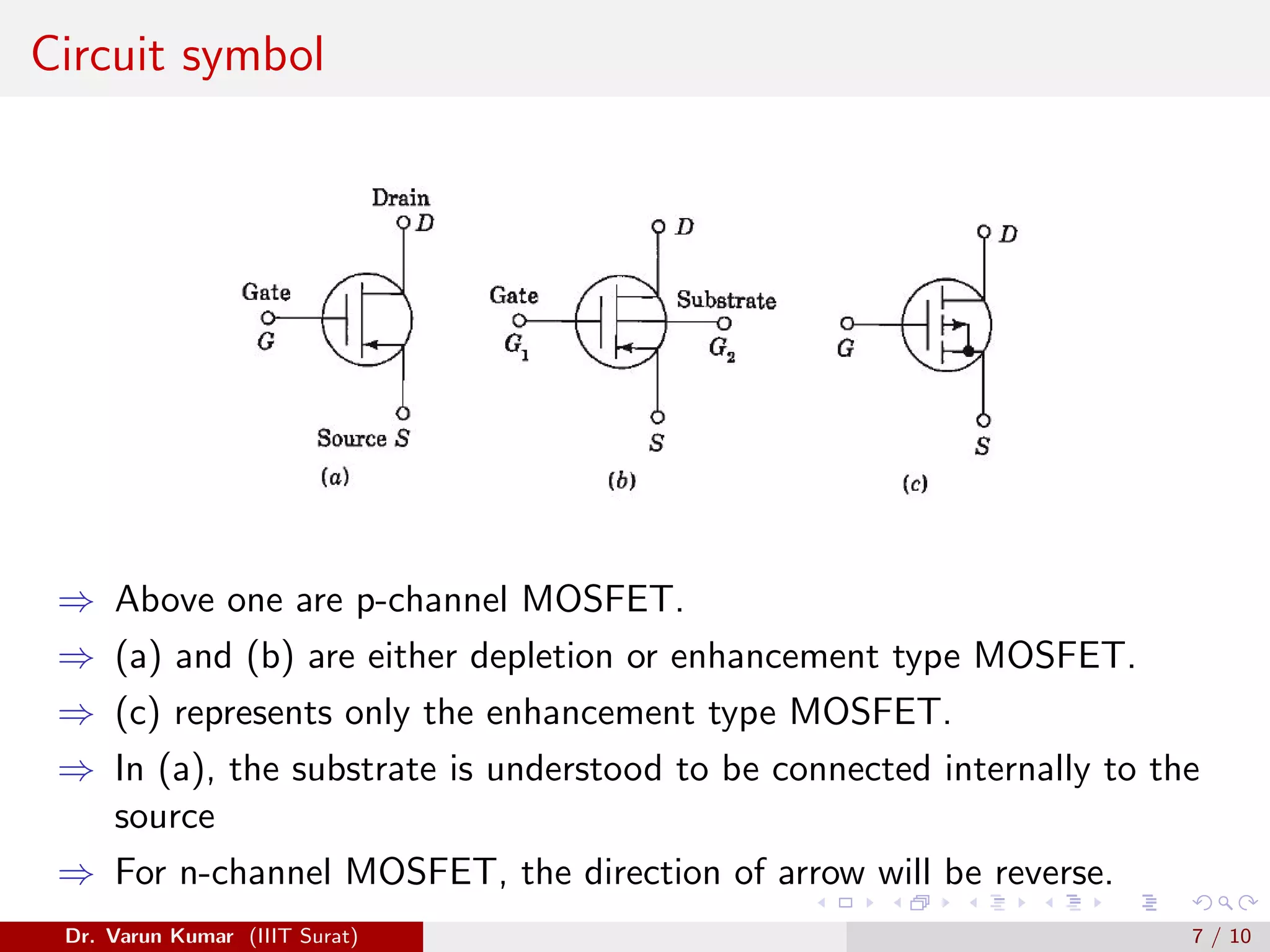
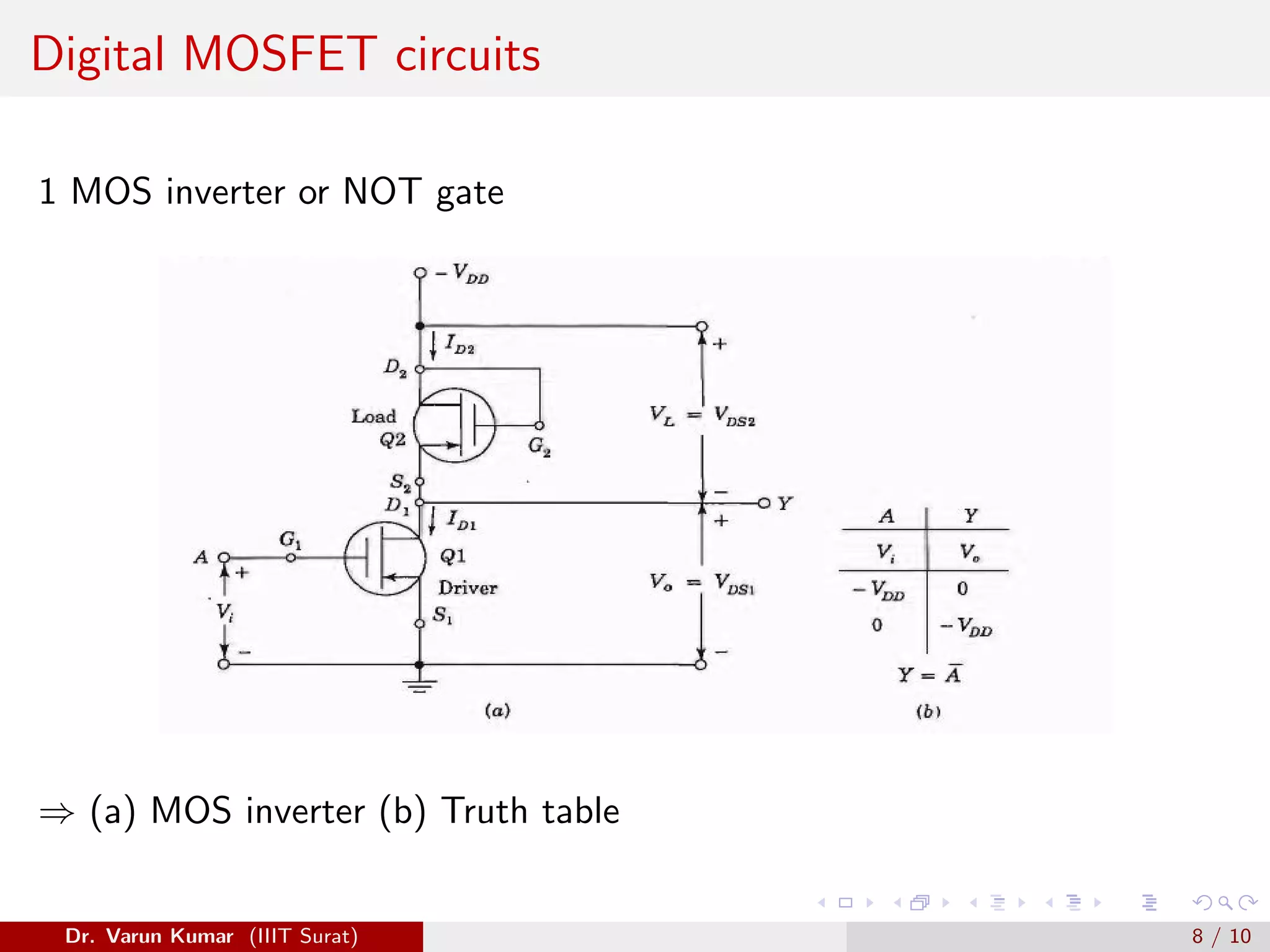
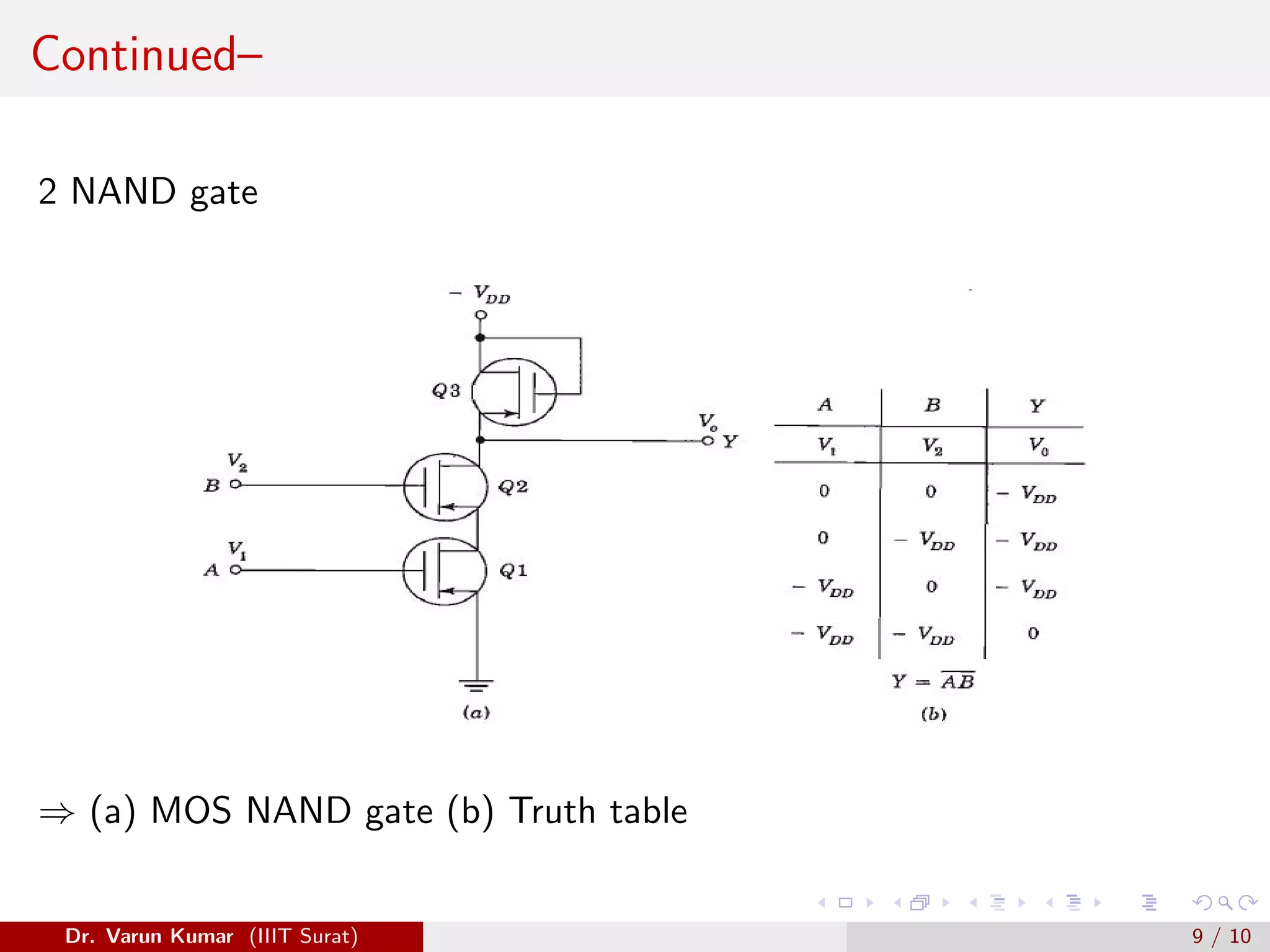
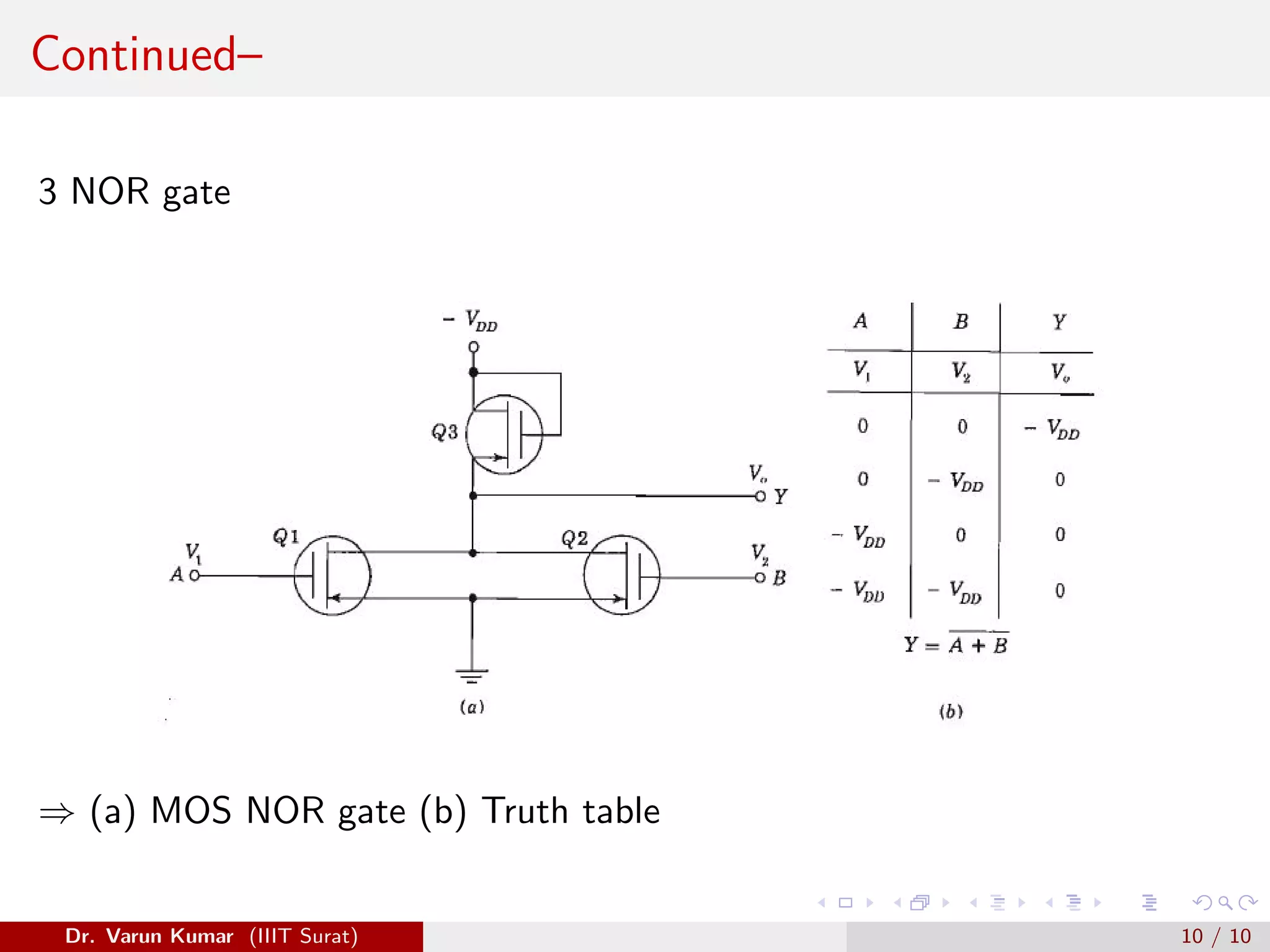
The document discusses depletion MOSFET and digital MOSFET circuits. It describes a depletion-type n-channel MOSFET structure on a p-type substrate with two n+ source and drain regions separated by a distance. When a negative gate voltage is applied, it induces positive charges in the semiconductor beneath the oxide, decreasing conductivity and allowing current to flow through the induced channel. Digital MOSFET circuits include the MOS inverter, which acts as a NOT gate, the NAND gate, and the NOR gate. P-channel devices require more area than n-channel devices for the same resistance due to differences in hole and electron mobility.