Embed presentation
Downloaded 640 times


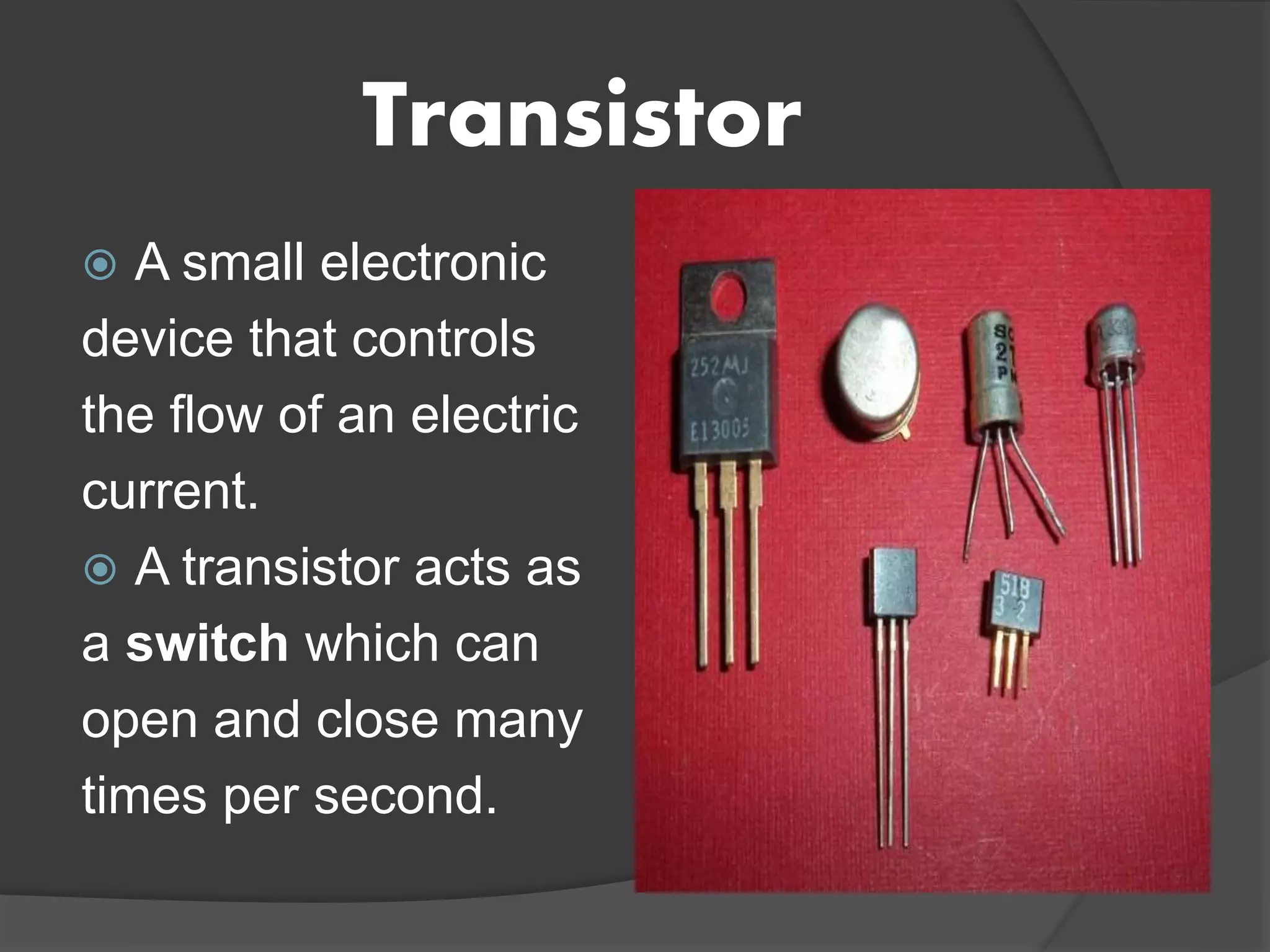
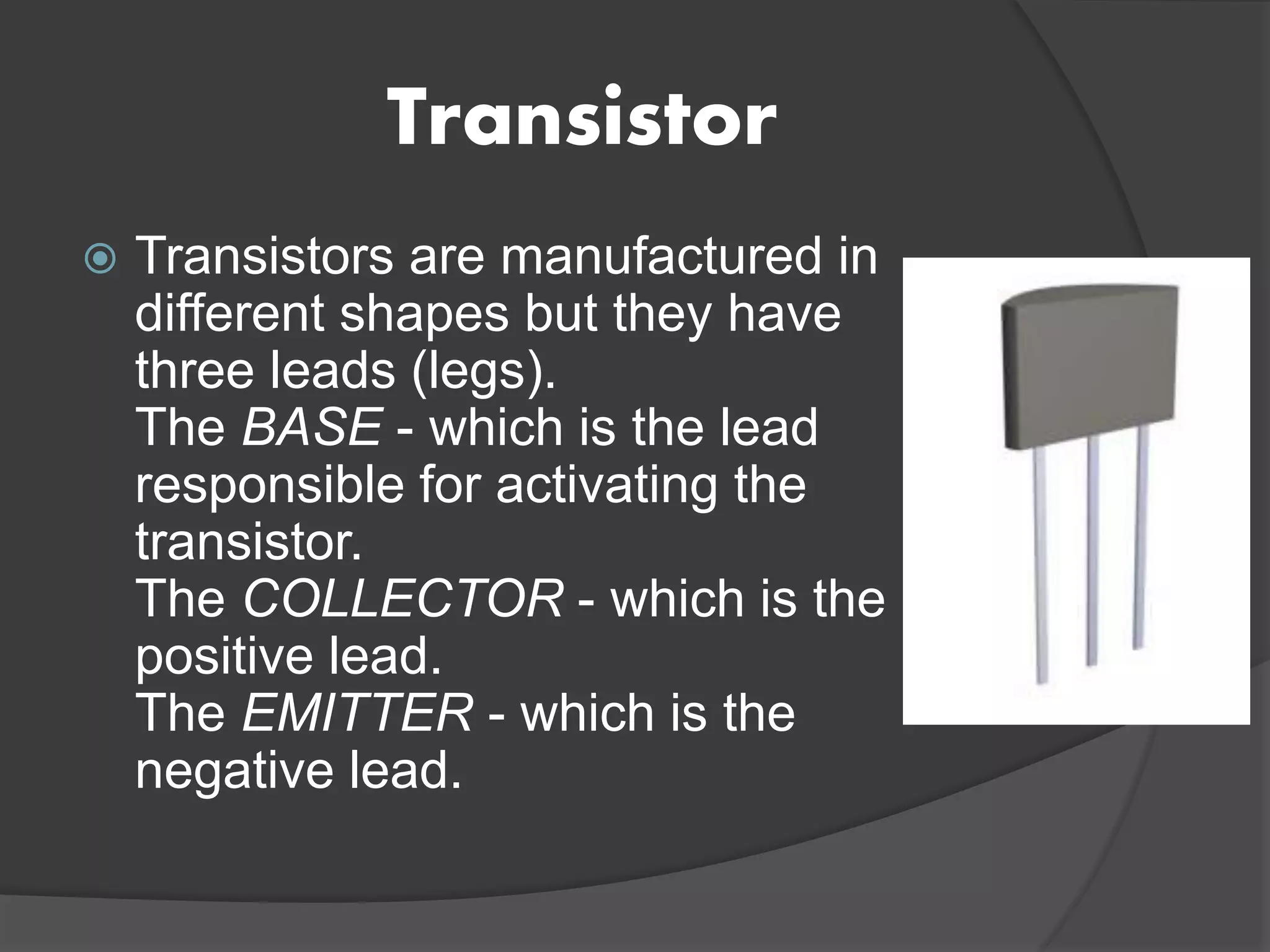
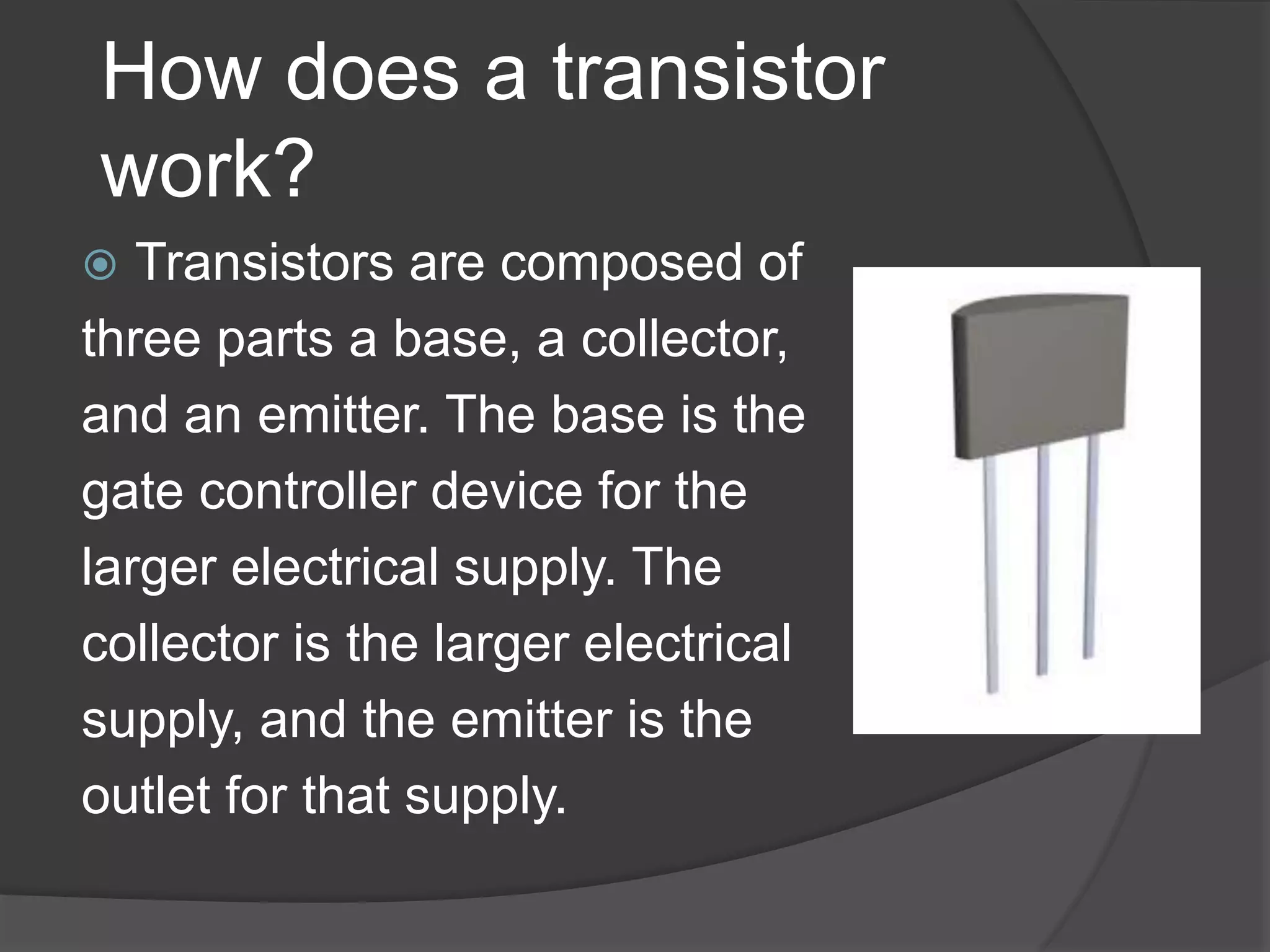



A transistor is a small electronic device that controls the flow of electric current. It acts like a switch that can open and close many times per second. There are two main types of transistors - NPN and PNP - which differ in how they allow or block the flow of electric current between three terminals: the base, collector, and emitter. The base terminal controls the flow of current between the collector and emitter terminals.









