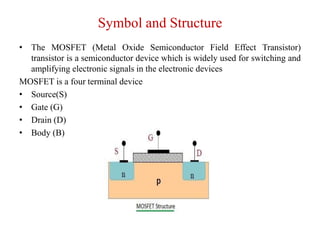
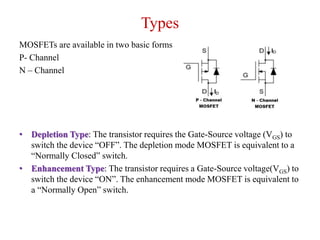
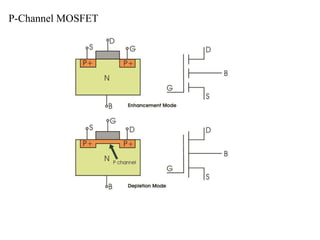
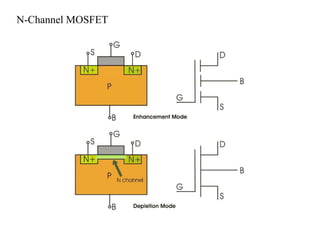
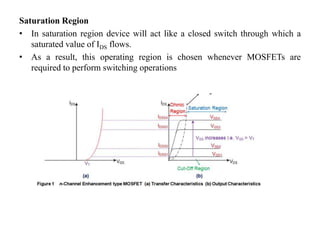
The MOSFET is a four-terminal semiconductor device used for switching and amplifying electronic signals. It comes in two basic forms, P-channel and N-channel, and two modes, depletion and enhancement. MOSFETs exhibit three operating regions - cut-off, where no current flows; ohmic or linear, where current increases with drain-source voltage; and saturation, where current reaches a maximum. MOSFETs are voltage-controlled, unipolar devices that can switch or amplify depending on their operating region.