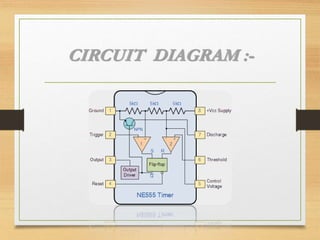
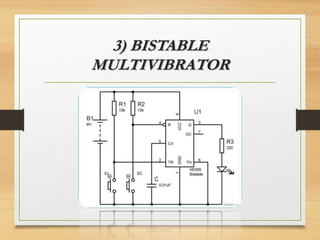
The document presents an overview of the 555 timer, an integrated circuit designed for various timing and pulse generation applications. It includes details on its pin configuration, types (monostable, astable, bistable multivibrators), functioning, and related formulas. Applications of these configurations include frequency dividers, pulse stretchers, square-wave oscillators, and more.