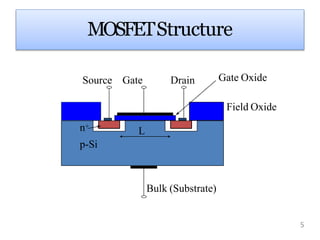
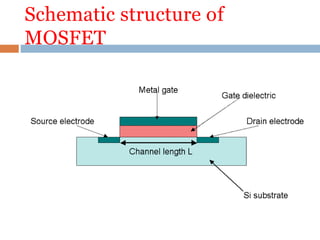
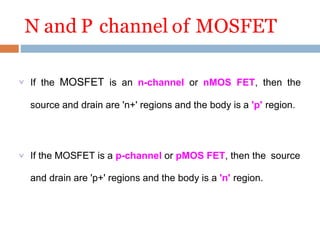
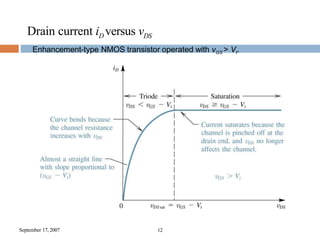
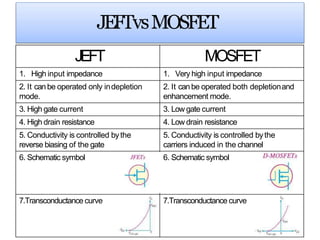
The presentation summarized the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET). It described the basic structure of a MOSFET, including the gate, source, drain, field oxide and gate oxide layers. It explained the working principle of a MOSFET, noting that applying a positive or negative gate voltage can invert the p-type semiconductor surface to n-type, controlling the flow of electrons between the source and drain. Finally, it discussed common applications of MOSFETs in electronics like calculators, memory devices, power amplifiers and automobile sound systems.