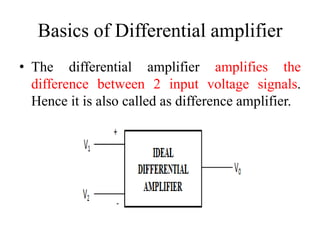
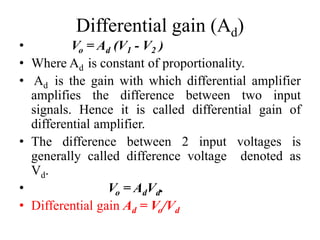
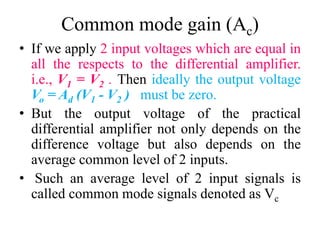
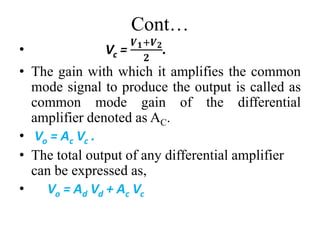
Differential amplifiers amplify the difference between two input signals while rejecting input signals that are common to both inputs. They have advantages like excellent stability, versatility, and immunity to noise and interference. The differential gain (Ad) is the gain with which the difference between the two input signals (V1-V2) is amplified to produce the output (Vo). The common mode gain (Ac) is the gain resulting from any common signals applied to both inputs. Differential amplifiers have high differential gain, low common mode gain, and high common mode rejection ratio (CMRR), which is the ratio of Ad/Ac expressed in decibels and indicates the ability to reject common mode signals.