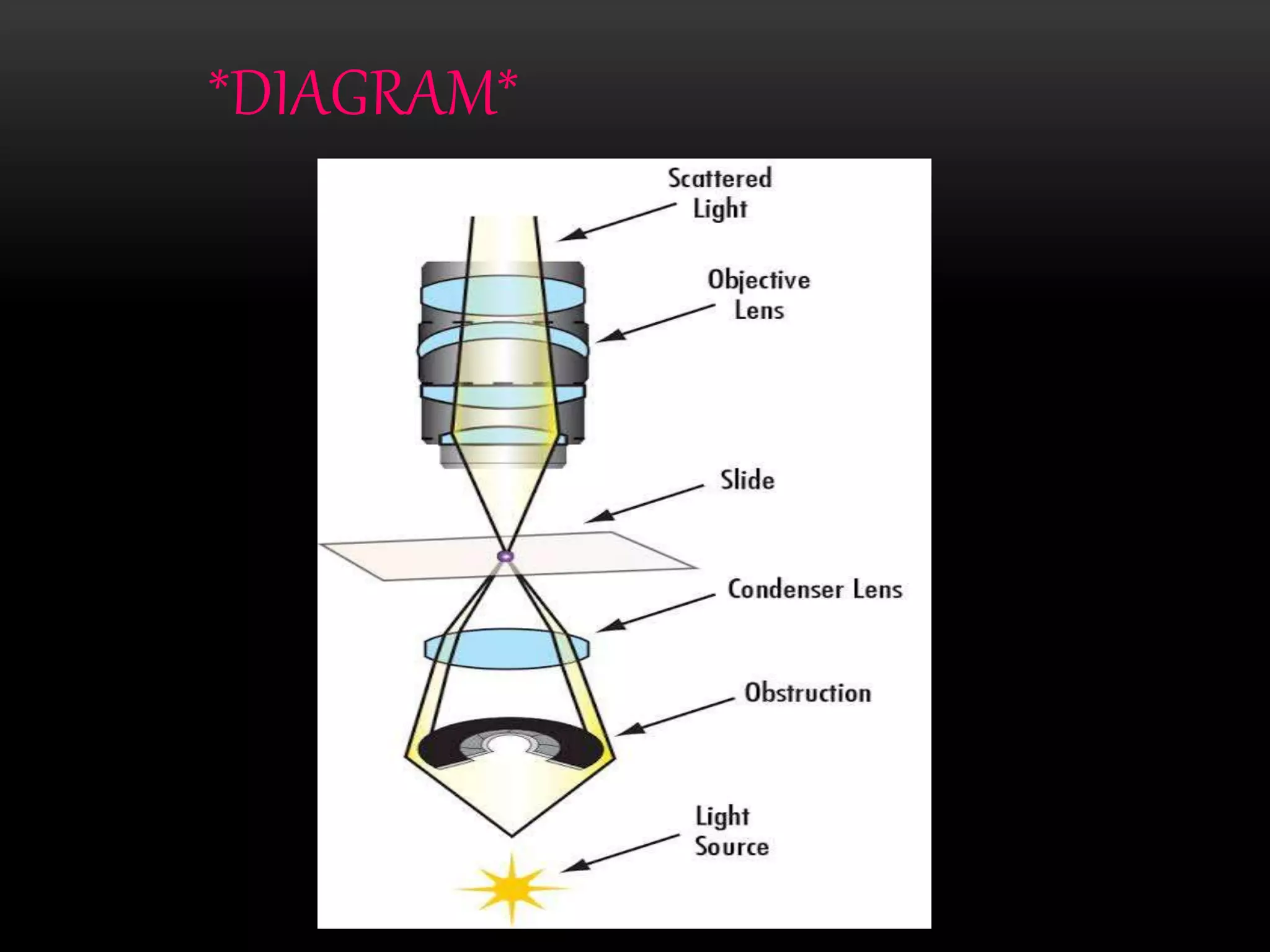
The document describes the components, working principle, and applications of a dark field microscope. A dark field microscope illuminates specimens from the side so that scattered light from the specimen is visible against a dark background. Key components are the light source, condenser lens, and objective lens. The microscope can be used to observe unstained living cells, bacteria, algae, and other microorganisms by revealing their internal structure in contrast to the dark background field. Applications include identifying bacteria, observing unstained cells and internal structures of microorganisms.