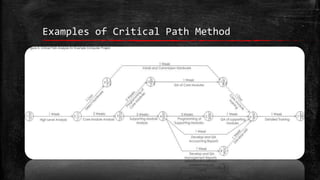
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a scheduling tool used to plan and track projects. It allows tasks to be organized based on their sequence and dependencies. The CPM involves drawing a chart that represents each task as a node with arrows showing the dependencies and sequence. It then determines the earliest and latest start/finish times to identify the critical path - the sequence of tasks that must be completed on time or the project will be delayed. The CPM helps optimize schedules, identify risks, and determine the minimum time needed to complete a project.











![References
▪ Maylor, H., 2010. Project Management. 4th Ed. Chester: Pearson.
▪ MindTools, 2013. Critical Path Analysis and PERT Charts. [Online] Available at:
http://www.mindtools.com/critpath.html [Accessed on 07/11/13]
▪ Margaret Rouse, 2011. Critical Path Method (CPM). [Online] Available at:
http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/critical-path-method-CPM [Accessed
on 07/11/13]
▪ Tutorialspoint, 2013. Critical Path Method. [Online] Available at:
http://www.tutorialspoint.com/management_concepts/critical_path_method.h
tm [Accessed on 07/11/13]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/criticalpathmethod-edit-131125044036-phpapp02/85/Critical-path-method-13-320.jpg)