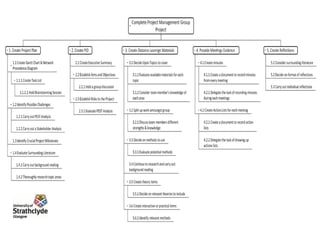
The Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a hierarchy that breaks down a project into smaller tasks and packages. It splits the task list into logical packages that can be used for cost control and reporting. The lowest level of each activity in the WBS should be an individual task that can be completed by one person within a defined time period. However, the WBS does not show task dependencies, durations, or resource requirements. Alternative structures include the Product Breakdown Structure, which breaks down complex products into components, and the Cost Breakdown Structure, which identifies cost categories and should be completed after the WBS.