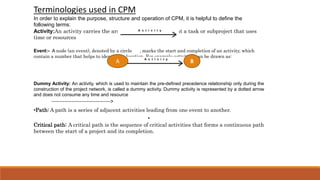
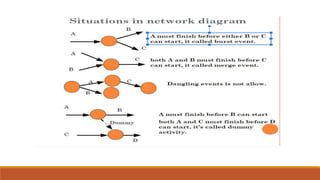
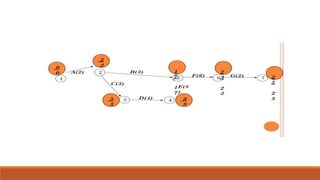
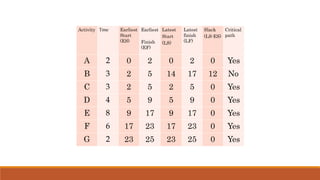
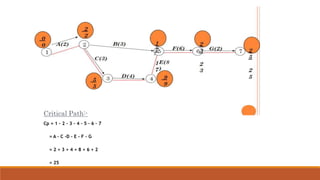
The document introduces the Critical Path Method (CPM) as a scheduling technique for managing project activities by identifying the longest sequence of dependent tasks, known as the critical path. It outlines the essential steps for calculating early and late start and finish times, determining float, and highlights the benefits and limitations of CPM and its relationship with the Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT). Additionally, it distinguishes the methodologies' applications, emphasizing their use in various industries such as construction, maintenance, and project management.