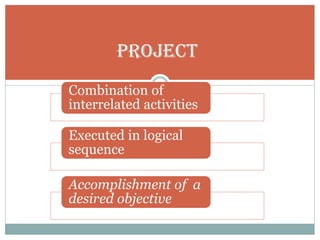
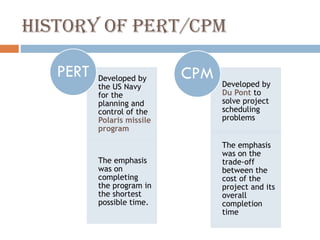
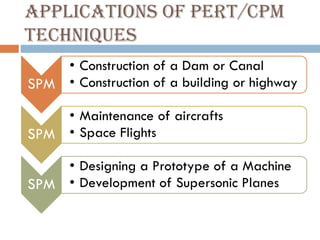
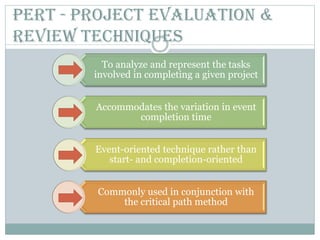
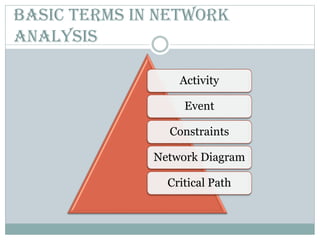
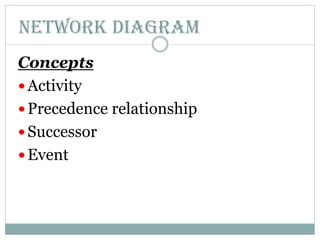
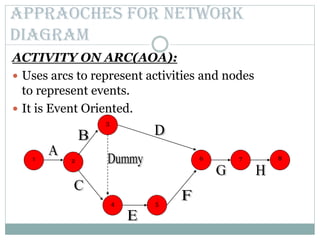
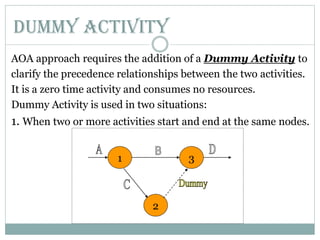
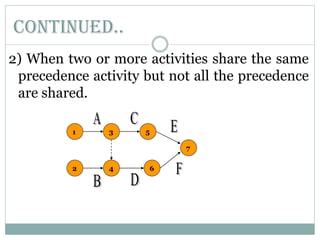
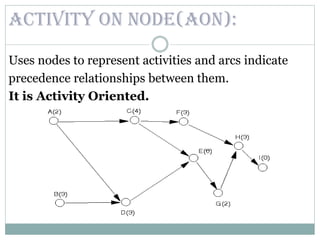
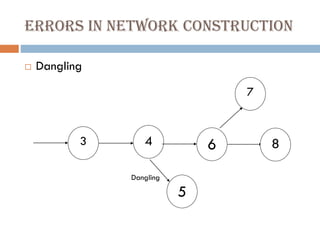
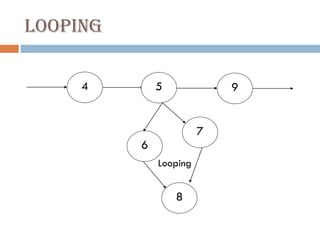
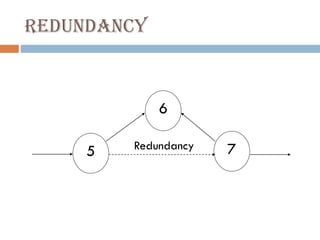
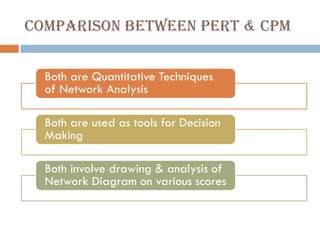
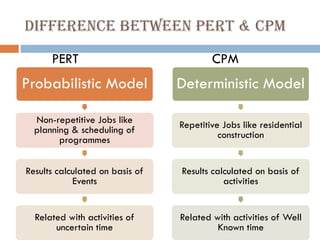
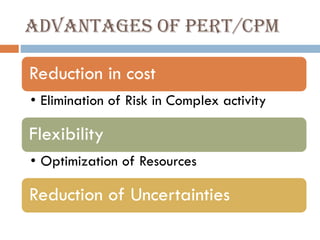
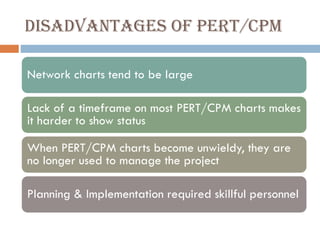
This document discusses network diagrams, PERT (Project Evaluation and Review Technique), and CPM (Critical Path Method) for project scheduling. It provides the history and applications of PERT/CPM, the steps involved, and compares PERT and CPM. Key points covered include defining a project, developing activity relationships, drawing the network diagram, estimating activity times, determining the critical path, and using the network to plan and control the project. Advantages and disadvantages of PERT/CPM techniques are also presented.