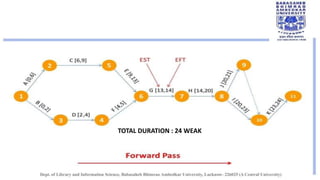
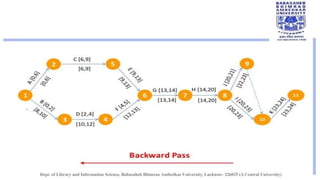
The document discusses the Critical Path Method (CPM), a project management technique developed in the late 1950s for scheduling activities and predicting project duration. It outlines CPM's purposes, including calculating finish dates and identifying critical and non-critical activities within a project. The document further explains the concepts of floats and critical paths, providing a detailed example with tools for constructing network diagrams.