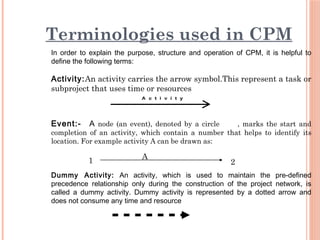
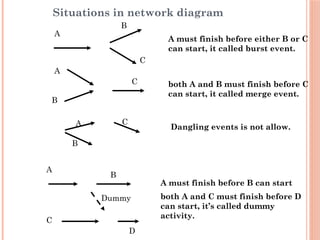
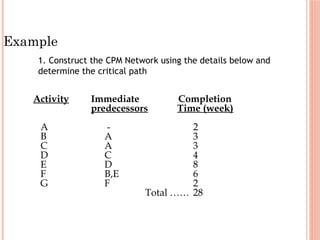
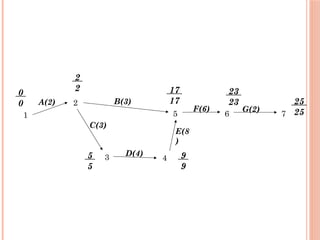
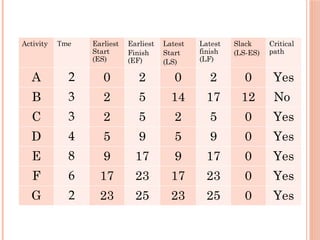
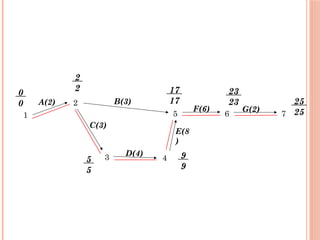
The document introduces Critical Path Method (CPM) for project scheduling. It defines CPM as a technique that uses mathematical calculations to schedule project activities based on their duration and dependencies. CPM was developed in 1950 to assist in building and maintaining chemical plants. The document outlines the key steps in CPM including constructing a network diagram of activities with durations and dependencies, performing forward and backward passes to calculate early/late start/finish times, and identifying the critical path with zero float. An example applies these steps to determine the critical path of a project with seven activities is the A-C-D-E-F-G path of 25 weeks.