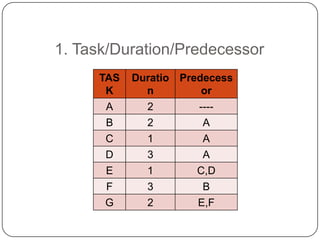
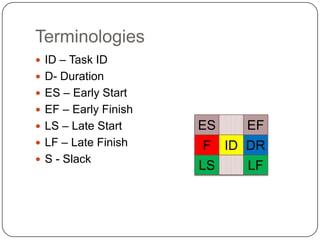
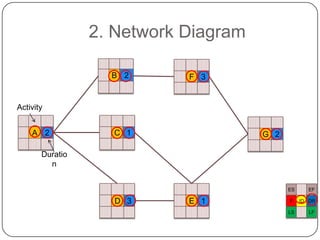
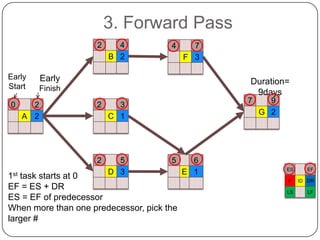
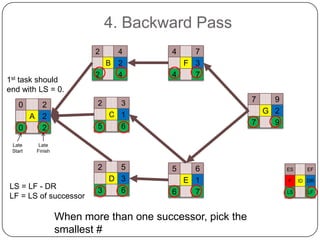
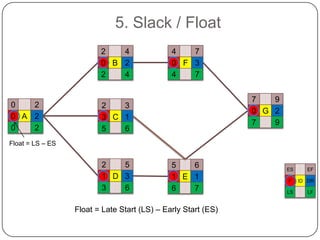
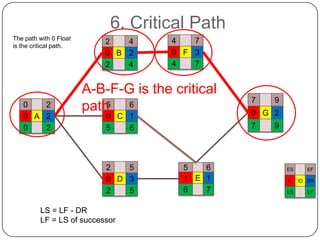
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a project modeling technique developed in the late 1950s that identifies the longest sequence of tasks that determine the minimum project duration. It involves specifying activities, drawing a network diagram, performing forward and backward passes to determine early and late start/finish times, and calculating slack time to identify critical tasks that have zero float. The critical path is crucial for project management, as any delay in its tasks will result in a project delay.