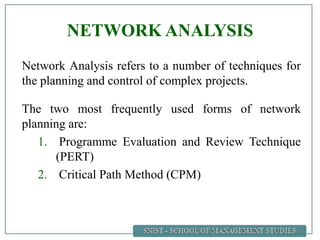
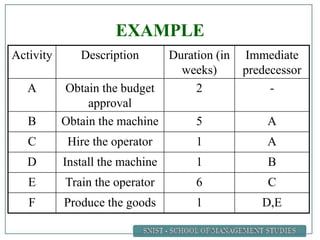
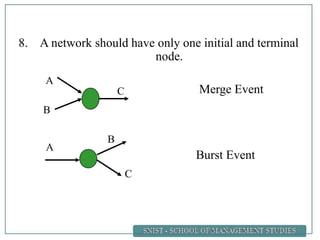
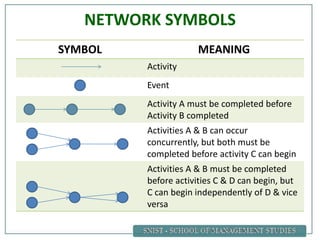
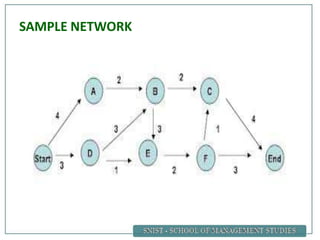
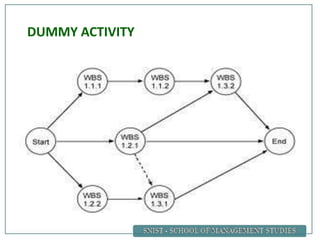
A project is defined as a temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product or service. Network analysis techniques like the Critical Path Method (CPM) and Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) are used to plan and schedule complex projects. These methods involve identifying all activities, their durations, and logical relationships to construct a network diagram. The critical path is then determined by calculating the longest path of linked activities from start to finish, which must be carefully managed to ensure on-time project completion.